Table of Contents
What is Financial Planning?
Financial planning means preparing a financial plan. A financial plan is also called a plan. A financial plan is an estimate of the total capital requirements of the company. It selects the most economical sources of finance. It also tells us how to use this finance profitably. A financial plan gives a total picture of the future financial activities of the company.
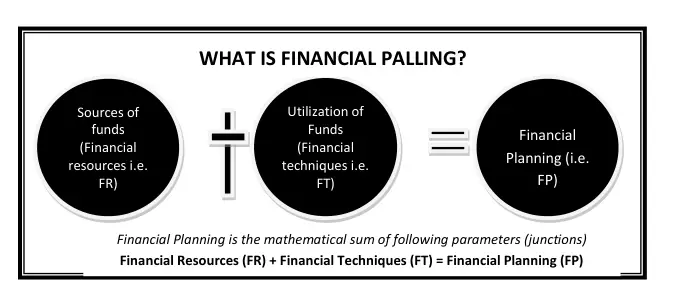
Financial Planning is the mathematical sum of the following parameters: Financial Resources (FR) + Financial Techniques (FT) = Financial Planning.
A financial plan contains answers to the following Questions:
- How much finance (short-term, medium-term, and long-term) will be required by the y?
- Form where this finance will be acquired (gathered)?
- In other words, what are the sources of finance?
- That is owned capital (promoter contribution, share capital) and borrowed capital (debentures, loans, overdrafts, etc.)
- How will the company use this acquired finance?
That is the application or utilization of funds. A financial plan is generally prepared during the promotion stage. It is prepared by the Promoters (entrepreneurs) with the help of experienced (practicing) professionals.
The promoters must be very careful while preparing the financial plan. This is because an evil financial plan will lead to over-capitalization or under-capitalization. It is very difficult to correct an evil financial plan. Hence immense care must be taken while preparing a financial plan.
Types of Financial Plans
After the company starts, the finance manager does the financial planning. The types of financial plans are depicted and briefly explained below:
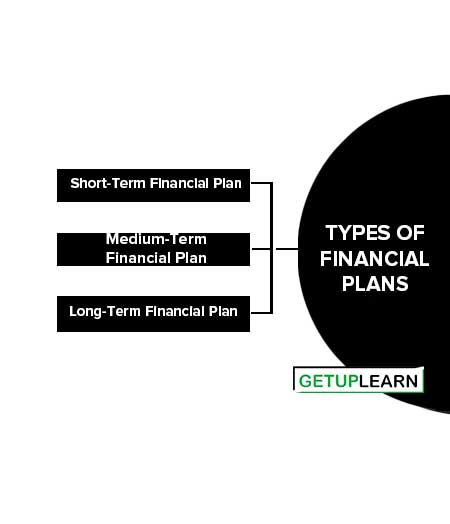
Short-Term Financial Plan
A short-term financial plan is prepared for a maximum of one year. This plan looks after the working capital needs of the company.
Medium-Term Financial Plan
A medium-term financial plan is prepared for a period of one to five years. This plan looks after the replacement and maintenance of assets, research, development, etc.
Long-Term Financial Plan
A long-term financial plan is prepared for a period of more than five years. It looks after the long-term financial objectives of the company, its capital structure, expansion activities, etc.
Objectives of Financial Planning
These are the objectives of financial planning:
-
Determining capital requirement: This will depend upon factors like the cost of current and fixed assets, promotional expenses, and long-range planning. Capital requirements have to be looked at with both aspects: short-term and long-term requirements.
-
Determining capital structure: The capital structure is the composition of capital, i.e., the relative kind and proportion of capital required in the business. This includes decisions on the debt-equity ratio- both short-term and long-term.
- Framing financial policies with regard to cash control, lending, borrowings, etc.
- A finance manager ensures that scarce financial resources are maximally utilized in the best possible manner at the least cost in order to get maximum returns on investment.
Importance of Financial Planning
Financial Planning is the process of framing objectives, policies, procedures, programs, and budgets regarding the financial activities of a concern. This ensures effective and adequate financial and investment policies. These are the importance of financial planning:
- Adequate funds have to be ensured.
- Financial Planning helps in ensuring a reasonable balance between outflow and inflow of funds so that stability is maintained.
- Financial Planning ensures that the suppliers of funds are efficiently investing in companies that exercise financial planning.
- Financial Planning helps in making growth and expansion programs which helps in long- run survival of the company.
- Financial Planning reduces uncertainties with regard to changing market trends which can be faced easily through enough funds.
- Financial Planning helps in reducing the uncertainties which can be a hindrance to the growth of the company. This helps in ensuring stability and profitability in concern.
Steps in Financial Planning
The following are the steps in financial planning:
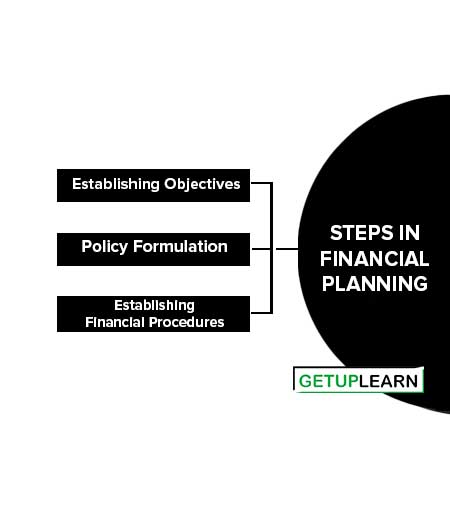
Establishing Objectives
Financial planning starts with the establishment of financial goals/objectives for the overall firm and the various departments like cost reduction, increasing market share by 10 percent, and so on. Financial planners should establish both short-term and long sum objectives. The long-run goal of any firm is to use capital in the correct proportion.
Policy Formulation
Financial policies are guidelines for all actions which deal with procuring, administering, and disbursing the funds of business firms. These policies may be classified into several broad categories.
Some of them are given below:
- Policies govern the amount of capital required for firms to achieve their financial objectives.
- Policies that determine the control by the parties who furnish the capital.
- Policies that guide the management in the selection of sources of funds.
Establishing Financial Procedures
Once the plan is implemented, the firm needs to review and monitor the progress. Both online monitoring and post-activity monitoring are beneficial to control any deviations.
Tools of Financial Planning
Financial Planning includes various tools which can be used for financial analysis; some of them are as follows:
-
Financial Statements: Financial statements such as the forecasted balance sheet, the statement of income, and the cash flow statement assist in the financial planning of a firm.
-
Ratio Analysis: This tool helps investors, analysts, and management to evaluate the business performance and compare it with its competitors.
-
Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis: It establishes the relationship among the cost incurred, volume produced, and profits generated by the firm.
- Budgeting: It involves forecasting future fund requirements for different activities of the firm. This helps the fundraising process of the firm.
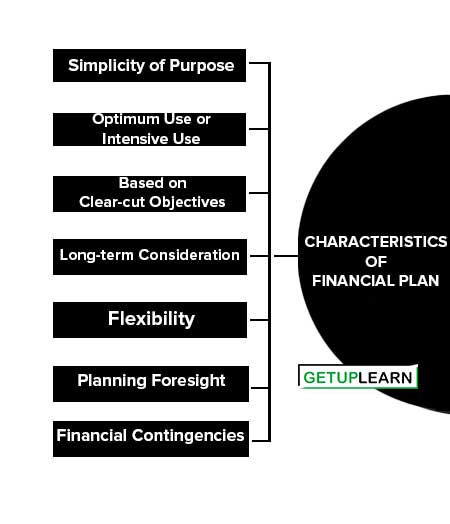
Characteristics of Financial Plan
The following are the characteristics of financial plan:
- Simplicity of Purpose
- Optimum Use or Intensive Use
- Based on Clear-cut Objectives
- Long-term Consideration
- Flexibility
- Planning Foresight
- Financial Contingencies
Simplicity of Purpose
A financial plan should be drafted in terms of the purpose for which the enterprise is organized. It should contain a simple financial structure that can be implemented and managed easily and understood clearly by all.
In short, the financial plan should not be too complicated to understand and implement by the executive managers.
Optimum Use or Intensive Use
Wasteful use of capital is almost as bad as inadequate capital. A financial plan should be such that it will provide for an intensive use of funds. Funds should not remain idle and there should not be any paucity of it. Financial planners should keep in view the proper utilization of funds in the context of the overall objective of maximization of wealth.
Again they should see that there is a proper balance in maintenance between long-term and short-term funds since the surplus of one will not be able to offset the shortage of the other.
Based on Clear-cut Objectives
Financial planning should be done by keeping in view the overall objectives of the company. It should aim to procure funds at the lowest cost so that the profitability of the business is improved.
Long-term Consideration
Financial planning should be formulated keeping in view the long-term requirements and not just the immediate or short-term requirements of the concern. This is because financial planning originally formulated would continue to operate for a long time after the formation of the concern.
Flexibility
The financial planning should be such that it can be modified or changed according to the changing needs of the business with the minimum possible delay. There may be scope for raising additional funds if fresh opportunities occur.
Flexibility in a plan will be helpful in coping with the demands of the future. Management should be ready to revise or completely change the firm’s short-run objectives, policies, and procedures in order to take advantage of changing conditions.
Planning Foresight
Foresight is essential for any plan of business operations so that capital requirements may be assessed as accurately as possible. Accurate forecasts are required to be made regarding the future scope of operations of the concern, technological developments, etc.
The making of accurate forecasts requires foresight on the part of financial planners. A financial plan visualized without foresight may fail to meet the present as well as the future requirements of funds and bring disaster to the concern.
Financial Contingencies
The financial planning should make adequate provisions of funds for meeting the contingencies likely to arise in the future. This principle does not mean that large amounts of funds should be kept idle as reserves for unforeseen contingencies.
It simply means that while formulating the financial plans, the financial planners should make proper forecasts of the contingencies likely to arise in the future and make adequate provisions for funds for meeting the future contingencies.
Factors Affecting Financial Planning
Financial planning is a dynamic process that involves assessing an individual’s current financial situation, setting financial goals, and developing strategies to achieve those goals. Several factors can influence the financial planning process. The factors affecting financial planning are:
- Nature of Industry
- Size of Company
- Status of Company in Industry
- Sources of Finance Available
- Capital Structure of a Company
- Matching Sources With Utilization
- Flexibility
- Government Policy
Nature of Industry
The very first factor affecting the financial plan is the nature of the industry. Here, we must check whether the industry is a capital-intensive or labor-intensive industry. This will have a major impact on the total assets that a firm owns.
Size of Company
The size of the company greatly influences the availability of funds from different sources. A small company normally finds it difficult to raise funds from long-term sources at competitive terms. On the other hand, large companies like Reliance enjoy the privilege of obtaining funds both short-term and long-term at attractive rates.
Status of Company in Industry
A well-established company enjoys a good market share, for its products normally command investors’ confidence. Such a company can tap the capital market for raising funds in competitive terms for implementing new projects to exploit the new opportunities emerging from changing business environment.
Sources of Finance Available
Sources of finance could be grouped into debt and equity. Debt is cheap but risky whereas equity is costly. A firm should aim at the optimum capital structure that would achieve the least cost capital structure.
A large firm with a diversified product mix may manage a higher quantum of debt because the firm may manage higher financial risk with lower business risk. The selection of sources of finance is closely linked to the firm’s capability to manage risk exposure.
Capital Structure of a Company
The capital structure of a company is influenced by the desire of the existing management (promoters) of the company to retain control over the affairs of the company. The promoters who do not like to lose their grip over the affairs of the company normally obtain extra funds for growth by issuing preference shares and debentures to outsiders.
Matching Sources With Utilization
The prudent policy of any good financial plan is to match the term of the source with the term of the investment. To finance fluctuating working capital needs, the firm resorts to short-term finance. All fixed asset – investments are to be financed by long-term sources, which is a cardinal principle of financial planning.
Flexibility
The financial plan of a company should possess flexibility so as to effect changes in the composition of capital structure whenever the need arises. If the capital structure of a company is flexible, there will not be any difficulty in changing the sources of funds. This factor has become a significant one today because of the globalization of the capital market.
Government Policy
SEBI guidelines, finance ministry circulars, various clauses of the Standard Listing Agreement, and regulatory mechanisms imposed by FEMA and the Department of corporate affairs (Govt. of India) influence the financial plans of corporate today. Management of public issues of shares demands compliance with many statutes in India. They are to comply with a time constraint.
FAQs about the Financial Planning
What are the types of financial plans?
There are three types of financial plans:
1. Short-Term Financial Plan: One Year
2. Medium-Term Financial Plan: One to Five Years
3. Long-Term Financial Plan: More Than Five Years
What are the 7 characteristics of a sound financial plan?
The 7 characteristics of a sound financial plan are:
1. Simplicity of Purpose
2. Optimum Use or Intensive Use
3. Based on Clear-cut Objectives
4. Long-term Consideration
5. Flexibility
6. Planning Foresight
7. Financial Contingencies.
What are the factors affecting financial planning?
The factors affecting financial planning are:
1. Nature of Industry
2. Size of Company
3. Status of the Company in the Industry
4. Sources of Finance Available
5. Capital Structure of a Company
6. Matching Sources With Utilization
7. Flexibility
8. Government Policy.