Table of Contents
- 1 What is Organization?
- 2 Meaning of Organization
- 3 Definition of Organization
- 4 Importance of Organization
- 5 Characteristics of Organization
- 6 Process of Organization
- 6.1 Review of Objectives and Policies
- 6.2 Determination of Activities
- 6.3 Grouping of Activities
- 6.4 Establishing Departments
- 6.5 Job Specification and Man Specifications
- 6.6 Distributing Jobs
- 6.7 Delegating Authority
- 6.8 Determining Responsibilities
- 6.9 Defining Scalar Chain
- 6.10 Coordination System
- 6.11 Actual Executing
- 7 Principles of Organization
- 7.1 Unity of Objectives
- 7.2 Division of Work and Specialization
- 7.3 Span of Supervision
- 7.4 Chain of Command
- 7.5 Unity of Command
- 7.6 Principle of Exception
- 7.7 Clear Definition of Authority and Responsibility
- 7.8 Unity of Direction
- 7.9 Balance between Authority and Responsibility
- 7.10 Absoluteness of Responsibility
- 7.11 Flexibility
- 7.12 Simplicity
- 7.13 Efficiency
- 7.14 Continuity
- 8 FQA Related to Organization
What is Organization?
A social unit of people that is structured and managed to meet a need or to pursue collective goals.
All organizations have a management structure that determines relationships between the different activities and the members and subdivides and assigns roles, responsibilities, and authority to carry out various tasks. Organizations are open systems they affect and are affected by their environment.
Meaning of Organization
These are the two bases of the meaning of organization:
Organization as Function
Organizing includes various functions. It includes defining the activities, grouping them, delegating authorities, guiding and directing them, coordinating, etc.
Organization as Structure
The structure of the organization includes collecting men, materials, machines, etc., and establishing relationships among them.
Definition of Organization
These are some simple-to-understand definitions of organization by authors:
[su_quote cite=”McFarland”]An identifiable group of people contributing their efforts towards the attainment of goals is called an organization.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”Louis A Allen“]”Organization is the process of identifying and grouping the work to be performed, defining and delegating responsibility and authority, and establishing relationships for the purpose of enabling people to work most effectively together in accomplishing objectives.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”Mooney and Railey”]Organization is the form of every human association for the attainment of a common purpose.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”Koontz and O’Donnell”]Organization involves the grouping of activities necessary to accomplish goals and plans, the assignment of these activities to appropriate departments, and the provision of authority, delegation, and coordination.[/su_quote]
Importance of Organization
The basic purpose of the organizational function is to ensure the optimum utilization of the available resources in an organization. The organizing function is so crucial that even a small mismatch between jobs, people, and authority can lead to big trouble.
The following are the importance of organization:
- It helps in establishing a clear relationship between the different positions.
- It provides the hierarchy of roles and responsibilities in an organization.
- The organization defines the degree to which authority can be delegated and responsibility can be assigned.
- It facilitates the attainment of the organization’s objective friction.
- It helps in understanding the similarity of jobs leading to departmentation.
- It is a science of defining positions and an art of establishing relations between them.
- More simplicity in structure means a more integrated system.
Characteristics of Organization
The following are the important characteristics of organization:
- Division of Labor
- Common Purpose
- Communication
- Authority Responsibility Structure
- People
- Environment
- Coordination
- Rules and Regulations
Division of Labor
The entire work of an organization is divided into functions and sub-functions. Division of labor leads to specialization because men acquire greater skill and knowledge when they perform a single operation again and again.
Division of labor helps to overcome wastage of efforts and duplication of work. Effective and proper division of labor leads to an increase in the quality and quantity of output.
Common Purpose
The basis of any organization is to achieve some common goal. The structure is bound together by the pursuit of specific and well-defined objectives.
An objective cannot be achieved without an organization, likewise, an organization cannot exist for long without goals and objectives. The structure of an organization should reflect these objectives so as to make the entire organization bound by a common purpose.
Communication
Effective communication is vital for success in management. Every organization has its own methods and channels of communication.
These channels are necessary for mutual cooperation and understanding among the members of an organization. The channels are communication may be upward, downward, vertical, formal, or informal.
In an organization, there is a proper arrangement of positions into a graded series. There is a clear definition of authority in each position.
It specifies who is to direct whom and who is responsible for what result. The structure helps an individual in the organization to know what his role is and how he is related to other roles.
People
An organization is made up of a group of people who constitute the dynamic human element of an organization. Therefore, authority provisions and grouping of activities must take into account the customs and limitations of people.
Environment
An enterprise functions in a very dynamic environment which comprises social, political, economic, and legal factors. Thus, the structure is designed to adapt itself to the changing environment.
Coordination
An organizational structure provides for the effective coordination of different activities and parts of an organization so that it functions as an integrated whole.
People in an organization perform different functions but all of them have only one aim i.e. to accomplish the enterprise’s objectives for which the organization provides a suitable method to ensure that there is proper coordination of different activities.
Rules and Regulations
Rules and regulations are provided for the orderly functioning of people in every organization. These may be in writing or implied from customary behavior.
Process of Organization
The organization is the most important function of management. It is an executive function. After planning, management has to do the organizing. There are different activities included in organizing that explain the process of the organization.
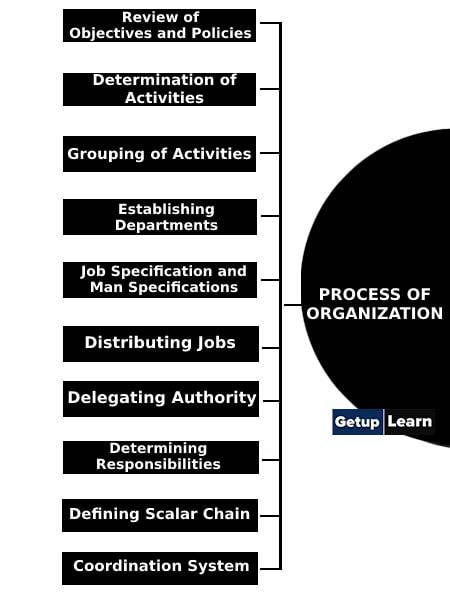
The following are the steps in the process of organization:
- Review of Objectives and Policies
- Determination of Activities
- Grouping of Activities
- Establishing Departments
- Job Specification and Man Specifications
- Distributing Jobs
- Delegating Authority
- Determining Responsibilities
- Defining Scalar Chain
- Coordination System
- Actual Executing
Review of Objectives and Policies
The organization is a tool for achieving objectives. Objectives are determined by top management. So it is necessary to take review objectives and policies. Therefore it is the first step in the process of the organization.
By knowing the exact objectives, it is possible to establish the exact structure of the organization. The objectives are to be explained to the people involved in the organization. On the basis of it, meaningful work division becomes possible.
Determination of Activities
The next step in the process of organizing is to identify and list out the different activities and jobs which are undertaken in an enterprise. An exhaustive list of all activities is prepared.
It is a primary and basic exercise that lay down the foundation for all the further steps of organizing. The list is verified with the help of a checklist and is finalized.
Grouping of Activities
The listed out activities are grouped on the basis of inter-relation and inter-linkage. The main activity with its related sub-activities is divided into groups. Grouping and sub-grouping depend upon size, nature, and competition.
It is a classification of activities for interconnecting and smoothly coordinating activities. It is essential for effective supervision and even avoiding repetition.
Establishing Departments
Establishing departments is the next step in the process of organizing. Classifications of groups are further grouped into sub-sections, sections, sub-departments, departments, and divisions as per the requirement of a business.
The advertising section, sales section, sales promotion section, after-sales service section, customer redressal section, credit section, market research section, etc. sections may be grouped into Marketing Department.
After-sales service section may have sub-section such as repairs, spare part supply, customer relation, replacement, home service, etc. Establishing the departments also depends on the size, policy, and financial provisions of a business.
Job Specification and Man Specifications
Before the actual distribution of activities and jobs, job specifications and main specifications are undertaken. An expert team is appointed for this purpose. It analyses different jobs and identifies their characteristics.
A team also identifies man-specifications i.e. required skills and qualities for performing a particular job. It facilitates the distribution of jobs and activities which leads to the matching of jobs and employees.
Distributing Jobs
On the basis of job specifications and man specifications, different jobs and activities are distributed among employees of an enterprise.
Skills, qualifications, experience, traits, training and qualities of an employee are major considerations for assigning jobs. This is the most important phase of the process. Hence it is done thoughtfully and scientifically.
Granting necessary powers to employees is essential for performing their jobs. Hence authority is delegated as per the requirement of a job assigned to an employee. Every job requires a certain kind of authority.
An employee can perform his job-related duties effectively with authority. Of course, the quantum of authority to be delegated is decided in advance by the management. A line and span of authority are also explained to an employee which defines his liberty.
Determining Responsibilities
Authority is followed by responsibility. Once necessary authority is delegated to an employee, corresponding responsibilities are clearly determined for his job. Determinations of responsibility help him to use his authority more cautiously and carefully.
Fixation of responsibility makes him more aware of his performance. The Quantum of responsibility shall correspond with the quantum of authority. Otherwise, it may affect his performance adversely.
Defining Scalar Chain
Defining relation among employees is an important phase of the organizing process, by which superior and subordinate relation is determined. Who shall issue orders to whom, who shall receive orders from whom, and who shall report to whom, this relation among employees is clearly defined.
These relations between superiors and subordinates constitute a scalar chain in an organization. It ensures discipline and timely execution of orders.
Coordination System
A separate coordinating system is established because different jobs and activities are distributed among employees for higher efficiency and better performance. Basically all jobs/activities are interconnected to each other.
Hence proper coordination of different jobs which are distributed among different employees and groups is essential for the attainment of the ultimate objectives of a business. All these job groups are coordinated on the basis of interconnections among different jobs.
Actual Executing
After completing all the above steps, it constitutes an effective organization that is set for actual functioning. It means that an organization starts its work and executes orders or directives.
It initiates actions by superiors and subordinates for fulfilling pre-determined goals. In fact, this is the last step of the process of organizing. All these steps are interdependent, so it is necessary to think about them collectively.
There may be a merging of some steps and the process may be shortened or maybe the addition of any new step. It depends on the philosophy of the enterprise.
Principles of Organization
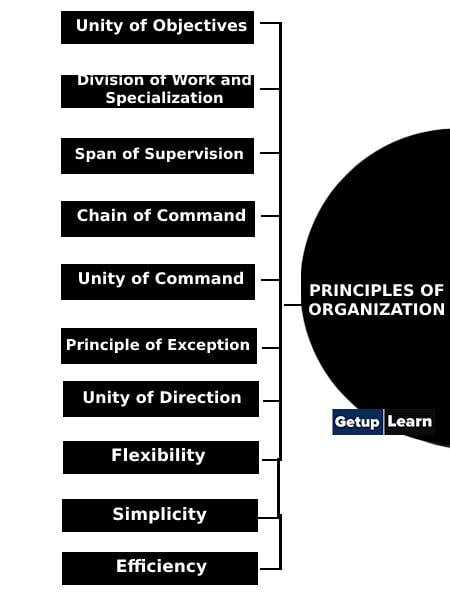
The principles are guidelines for planning an efficient and sound organizational structure. Therefore, for good organization, a clear understanding of these principles is essential. The important principles of organization are:
- Unity of Objectives
- Division of Work and Specialization
- Span of Supervision
- Chain of Command
- Unity of Command
- Principle of Exception
- Clear Definition of Authority and Responsibility
- Unity of Direction
- Balance between Authority and Responsibility
- Absoluteness of Responsibility
- Flexibility
- Simplicity
- Efficiency
- Continuity
Unity of Objectives
The objectives of an enterprise should be stated in clear and precise terms because it is the objectives of an enterprise that help in determining the type of organization structure.
In other words, only after the objectives have been laid, an organizational structure should be developed to achieve them.
Division of Work and Specialization
The organization structure should be designed in such a way, that as far as possible every individual should perform only a single function according to his aptitude and ability.
This is also called the principle of specialization. The performance of work will be better when a person performs it continuously.
Span of Supervision
According to this principle, no individual should be allowed to supervise more subordinates than he can effectively manage. For effective decision-making and communication, the number of levels of authority should be as few as possible.
Chain of Command
The line of authority should be clear and unbroken. It should run from top to bottom of the organization. Every individual in the organization should know to whom he will have to report and who will have to report to him.
Unity of Command
According to this principle, every individual in the organization should have only one superior to whom he will have to report. If a subordinate reports to two or more superiors, then there will be confusion in the organization and this will lead to indiscipline.
Principle of Exception
Every manager according to this principle is given authority to make routine decisions. Only in exceptional cases where it is beyond the scope of his authority, he should seek the help of higher authorities.
The authority and responsibility of each individual in the organization should be clearly defined so that each one knows what is expected of him. This will help in removing any overlapping of authority and gaps between responsibilities.
Unity of Direction
According to this principle, each group of actors with the same objective should have one head and one plan. This provides for better coordination among various activities to be undertaken by an organization.
There should be a proper balance between authority and responsibility. Responsibility should always be coupled with corresponding authority. Each individual should have sufficient authority to discharge the responsibility entrusted to him. This is otherwise called parity of authority and responsibility.
Absoluteness of Responsibility
In an organization, an individual cannot pass on his responsibility to others. Only authority can be delegated whereas responsibility cannot be delegated. Even when a manager has delegated his authority to a subordinate, he is held responsible for the work performed by his subordinate.
Flexibility
The organization structure should always be flexible in order to adapt and adjust itself to any environmental change. There should always be scope for expansion.
Simplicity
The organization structure should be clear and simple with a few levels of authority. This helps in free and effective communication and proper coordination.
Efficiency
The organization structure design should help the business unit to function effectively and efficiently to achieve its objectives with minimum effort and cost.
Continuity
This is another important principle of organization. Continuity of the business unit for a long period is essential to help people gain experience in positions of responsibility. It also helps in the growth and expansion of a business unit.
These principles are considered as the essential requirements of a sound organization and knowledge of these principles is the first prerequisite for sound organizing.
What is meaning of organization?
An identifiable group of people contributing their efforts towards the attainment of goals is called an organization.
What is a simple definition of organization?
Organization is the form of every human association for the attainment of a common purpose. By Mooney and Railey
What are the characteristics of organization?
Following are the characteristics of organization:
1. An defined objective, purpose or goal.
2. The activities needed to achieve the defined objective.
3. The classification of activities to make groups of similar activities.
4. The authority and responsibility needed for each activity.
5. Relationship between the activities.
What are the 8 characteristics of organization?
Following are the characteristics of organization:
1. Division of Labor
2. Common Purpose
3. Communication
4. Authority Responsibility Structure
5. People
6. Environment
7. Coordination
8. Rules and Regulations.
What are the steps of process of organization?
Following are the process of organization:
1. Review of Objectives and Policies
2. Determination of Activities
3. Grouping of Activities
4. Establishing Departments
5. Job Specification and Man Specifications
6. Distributing Jobs
7. Delegating Authority
8. Determining Responsibilities
9. Defining Scalar Chain
10. Coordination System
11. Actual Executing.
What are the principles of organization?
Following are the principles of organization:
1. Unity of Objectives
2. Division of Work and Specialization
3. Span of Supervision
4. Chain of Command
5. Unity of Command
6. Principle of Exception
7. Clear Definition of Authority and Responsibility
8. Unity of Direction
9. Balance between Authority and Responsibility
10. Absoluteness of Responsibility
11. Flexibility
12. Simplicity
13. Efficiency
14. Continuity.