Table of Contents
What is Financial Innovation?
Financial innovation can be defined as the act of creating and then popularising new financial instruments as well as new financial technologies, institutions, and markets. It includes institutional, product, and process innovation.
Financial Innovation is something that is seen by an individual as a new way by which finance can generate returns, redistribute risk and fuel the economy. Among all the adventures of mankind, financial innovation is the one that is very unique.
Financial innovation like innovation elsewhere in business is an ongoing process whereby private parties experiment to try to differentiate their products and services, responding to both sudden and gradual changes in the economy.
Surely, innovation ebbs and flows with some periods exhibiting bursts of activity and others witnessing a slackening or even backlash. However, financial innovation should always be a regular ongoing part of a profit-maximizing economy.
-
Institutional innovations relate to the creation of new types of financial firms (such as specialist credit card firms like MBNA, discount broking firms such as Charles Schwab, internet banks, and so on).
-
Product innovation relates to new products such as derivatives, securitized assets, foreign currency mortgages, and so on.
- Process innovation relates to new ways of doing financial business including online banking, phone banking, and new ways of implementing information technology and so on.
Definition of Financial Innovation
These are the simple definitions of financial innovation given by the authors:
[su_quote cite=”Stephen A. Ross”]Financial innovation means new financial products (financial assets and derivative instruments) better suited to the circumstances of the time and to the markets in which they trade, and strategies that primarily use these financial products.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”Simon Nixon”]Financial innovation can solve many credit bottlenecks but only if policymakers wean themselves off their symbiotic relationship with banks.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”Getuplearn”]Advances over time in the financial instruments and payment systems used in the lending and borrowing of funds. These changes, which include innovations in technology, risk transfer, and credit and equity generation have increased available credit for borrowers and given banks new and less costly ways to raise equity capital.[/su_quote]
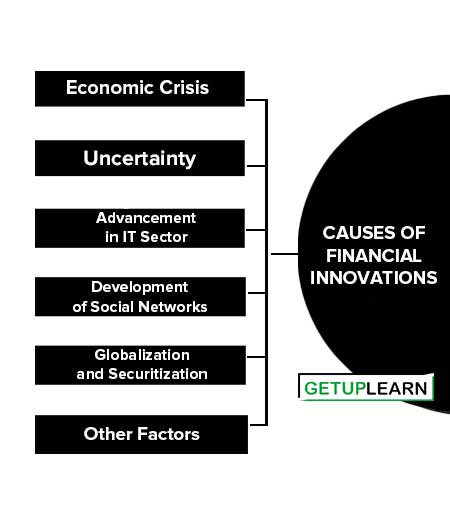
Causes of Financial Innovations
There are numerous factors that have led to financial innovation in the markets. Here are some causes of financial innovations:
- Economic Crisis
- Uncertainty
- Advancement in IT Sector
- Development of Social Networks
- Globalization and Securitization
- Other Factors
Economic Crisis
The economic crisis has led to reforming the regulation of the financial sector, and this may have some impact on financial innovation. Deregulation in the financial markets had led to the development of new instruments.
New instruments developed, led to further regulation in the financial markets. This had led financial institutions to compete in the international markets.
Uncertainty
With the growing market developments, there has been established a relationship between the risks associated with the assets and the interest and exchange rates.
Asset values have become volatile and in order to protect them financial institutions have developed a variety of products to hedge risks. Increased volatility of interest rates, inflation, equity prices, and exchange rates are therefore major factors.
Advancement in IT Sector
The advancements in the information and telecommunication sector have led to new financial innovations, the protection and management of which are challenging and require closer examination. IT revolution has drastically reduced the cost of financial transactions.
It has led to the development of certain financial products where pricing is needed on a real-time basis which is not possible without advanced data processing software. In short, advances in computer and telecommunication technologies have contributed a lot to financial innovation.
Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube are all being used to offer new financial services, increase interaction with the customer and collect new ideas from outside the financial institution. These media allow collecting, in real-time, feedback and ideas that can be used to start a company’s innovation processes.
There is very much data traffic, so there is an urgent need to create new organizational structures to effectively coordinate the various inflows of information and the tracking of the external idea towards absorption or rejection.
Globalization and Securitization
With international trade and investment, demand for international financial services has increased. Due to this development, a number of new financial products have emerged.
Other Factors
In addition to the above factors, other factors are also major drivers for financial innovations such as financial intermediary competition, greater sophistication and educational training among professional market participants, incentives to get around existing regulation and tax laws, and changing global patterns of financial wealth.
FAQs about the Financial Innovation
What is the meaning of financial innovation?
Financial innovation means new financial products (financial assets and derivative instruments) better suited to the circumstances of the time and to the markets in which they trade, and strategies that primarily use these financial products.
What is the definition of financial innovation?
Financial innovation can solve many credit bottlenecks but only if policymakers wean themselves off their symbiotic relationship with banks.
What are the causes of financial innovations?
The following are the causes of financial innovations:
1. Economic Crisis
2. Uncertainty
3. Advancement in IT Sector
4. Development of Social Networks
5. Globalization and Securitization
6. Other Factors.