Table of Contents
What is Cash Management?
Cash management is one of the key areas of working capital management. Apart from the fact that it is the most liquid current asset, cash is the common denominator to which all current assets can be reduced because the other major liquid assets; i.e. receivable and inventory get eventually converted into cash. This underlines the significance of cash management.
Cash is an important current asset for the operations of the business. It is the basic input needed to keep the business running on a continuous basis. Cash is the money that a firm can disburse immediately without any restriction. The term cash includes coins, currency, and cheques held by the firm, and balances in its bank accounts.
Sometimes near-cash items, such as marketable securities or bank term deposits, are also included in cash. The basic characteristic of near-cash assets is that they can readily be converted into cash. Generally, when a firm has excess cash, it invests it in marketable securities. This kind of investment contributes some profit to the firm.
Meaning of Cash Management
Cash management is one of the key areas of working capital management. Cash is the most liquid current assets. Cash is the common denominator to which all current assets can be reduced because the other major liquid assets, i.e. receivable and inventory get eventually converted into cash.
This underlines the importance of cash management. Cash management refers to the management of cash balance and the bank balance including the short terms deposits. For cash management purposes, the term cash is used in this broader sense, i.e., it covers cash, cash equivalents, and those assets which are immediately convertible into cash.
A financial manager is required to manage the cash flows (both inflows and outflows) arising out of the operations of the firm. Cash Management deals with the optimization of cash as an asset and for this purpose, the financial manager has to take various decisions from time to time.
He has to deal as the cash flow director of the firm even if a firm is highly profitable. Its cash inflows may not exactly match the cash outflows. He has to manipulate and synchronize the two for the advantage of the firm by investing excess cash if any, as well as arranging funds to cover the deficiency.
Objectives of Cash Management
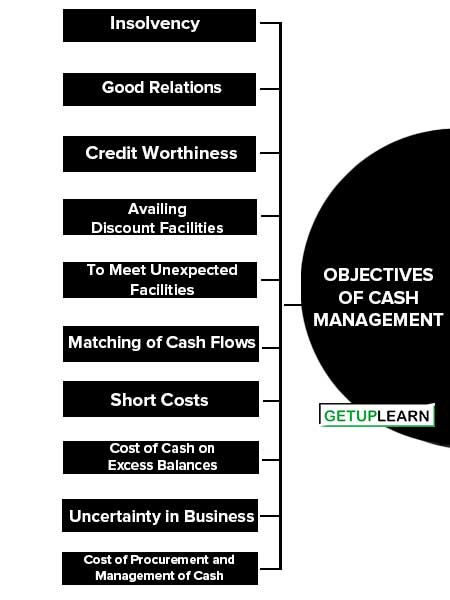
There are two bases of (1) Meeting the Payments Schedule, and (2) Minimizing Funds Committed to Cash Balances. The objectives of cash management are:
- Insolvency
- Good Relations
- Credit Worthiness
- Availing Discount Facilities
- To Meet Unexpected Facilities
- Matching of Cash Flows
- Short Costs
- Cost of Cash on Excess Balances
- Uncertainty in Business
- Cost of Procurement and Management of Cash
Meeting Payments Schedule
The basic objective of cash management is to meet the payment schedule. In the normal course of business, firms have to make payments of cash to suppliers of raw materials, employees, and so on regularly. At the same time, the firm will be receiving cash on a regular basis from cash sales and debtors.
Thus, every firm should have adequate cash to meet the payment schedule. In other words, the firm should be able to meet the obligations when they become due. The firm can enjoy certain advantages associated with maintaining adequate cash. They are:
- Insolvency
- Good Relations
- Credit Worthiness
- Availing Discount Facilities
- To Meet Unexpected Facilities
Insolvency
The question of insolvency does not arise as the firm will be able to meet its obligations.
Good Relations
The adequate cash balance in the business firm helps in developing good relations with creditors and suppliers of raw materials.
Credit Worthiness
The maintenance of adequate cash balances increases the creditworthiness of the firm. Consequently, it will be able to purchase raw materials and procure credit with favorable terms and conditions.
Availing Discount Facilities
The firm can avail of the discounts offered by the creditors for payments before the due date.
To Meet Unexpected Facilities
The firm can easily meet the unexpected cash expenditure in situations like strikes, competition from customers, etc. with little strain. So, every firm should have adequate cash balances for effective cash management.
Minimizing Funds Committed to Cash Balances
The second important objective of cash management is to minimize cash balance. In minimizing the cash balances two conflicting aspects have to be reconciled. A high level of cash balances will ensure prompt payment together with all advantages, but at the same time, cash is a non-earning asset and larger balances of cash impair profitability.
On the other hand, a low level of cash balance may lead to the inability of the firm to meet the payment schedule. Thus the objective of cash management would be to have an optimum cash balance. The factors determining the cash needs of the industry are explained as follows:
- Matching of Cash Flows
- Short Costs
- Cost of Cash on Excess Balances
- Uncertainty in Business
- Cost of Procurement and Management of Cash
Matching of Cash Flows
The first and very important factor determining the level of cash requirement is matching cash inflows with cash outflows. If the receipts and payments are perfectly coinciding or balance each other, there would be no need for cash balances. The need for cash management, therefore, is due to the non-synchronization of cash receipts and disbursements.
For this purpose, the cash inflows and outflows have to be forecast over a period of time say 12 months with the help of a cash budget. The cash budget will pinpoint the months when the firm will have an excess or shortage of cash.
Short Costs
Short costs are defined as the expenses incurred as a result of a shortfall of cash such as an unexpected or expected shortage of cash balances to meet the requirements.
The short costs include transaction costs associated with raising cash to overcome the shortage, borrowing costs associated with borrowing to cover the shortage i.e. interest on the loan, loss of trade-discount, penalty rates by banks to meet a shortfall in compensating, cash balances and costs associated with deterioration of the firm’s credit rating, etc. which is reflected in higher bank charges on loans, the decline in sales and profits.
Cost of Cash on Excess Balances
One of the important factors determining cash needs is the cost of maintaining cash balances i.e. excess or idle cash balances. The cost of maintaining an excess cash balance is called excess cash balance cost. If large funds are idle, the implication is that the firm has missed opportunities to invest and thereby lost interest.
This is known as excess cost. Hence cash management is necessary to maintain an optimum balance of cash.
Uncertainty in Business
Uncertainty plays a key role in cash management because cash flows cannot be predicted with complete accuracy.
The first requirement of cash management is a precautionary cushion to cope with irregularities in cash flows, unexpected delays in collections and disbursements, defaults and expected cash needs the uncertainty can be overcome through accurate forecasting of tax payments, dividends, capital expenditure, etc., and the ability of the firm to borrow funds through an overdraft facility.
Cost of Procurement and Management of Cash
The costs associated with establishing and operating cash management staff and activities determine the cash needs of a business firm. These costs are generally fixed and are accounted for by salary, storage, handling of securities, etc.
Managing Cash Flows
Managing cash flows is a crucial aspect of any business, regardless of its size or industry. Effective cash flow management ensures the business can cover its operational expenses, pay off debts on time, and invest in growth opportunities. Here are a few ways to manage cash flows effectively:
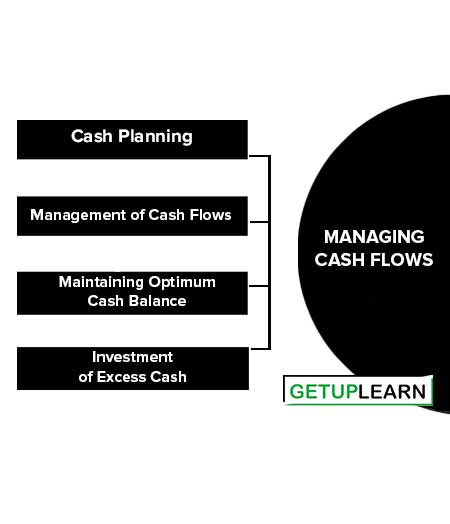
Cash Planning
Cash is the most important as well as the least unproductive of all current assets. Though it is necessary to meet the firm’s obligations, idle cash earns nothing. Therefore, it is essential to have sound cash planning neither excess nor inadequate.
Management of Cash Flows
This is another important aspect of cash management. Synchronization between cash inflows and cash outflows rarely happens. Sometimes, the cash inflows will be more than outflows because of receipts from debtors, and cash sales in huge amounts.
At other times, cash outflows exceed inflows due to the payment of taxes, interest, dividends, etc. Hence, the cash flows should be managed for better cash management.
Maintaining Optimum Cash Balance
Every firm should maintain an optimum cash balance. The management should also consider the factors determining and influencing the cash balances at various points in time. The cost of excess cash and the danger of inadequate cash should be matched to determine the optimum level of cash balances.
Investment of Excess Cash
The firm has to invest the excess or idle funds in short-term securities or investments to earn profits as idle funds earn nothing. This is one of the important aspects of the management of cash.
Thus, the aim of cash management is to maintain adequate cash balances on the one hand and to use excess cash in some profitable way on the other hand.
Importance of Cash Management
Cash Management consists of taking the necessary actions to maintain adequate levels of cash to meet operational and capital requirements and to obtain the maximum yield on short-term investments of pooled, idle cash. A good cash management program is a very significant component of the overall financial management of a municipality.
Such a program benefits the city or town by increasing non-tax revenues, improving the control and superintendence of cash, increasing contacts with members of the financial community, and lowering borrowing costs, while at the same time maintaining the safety of the municipality’s funds. The following are the importance of cash management to the company:
- Managing Credit Cash Flow
- Preparing for Emergencies
- Cash for Takeovers
- Fluctuating Commodity Prices
- Cash for Debt Payments
Managing Credit Cash Flow
Cash Management is particularly important for those companies that make sales as well as purchases on credit since creditors can demand money anytime therefore it is important for a company to manage cash.
Preparing for Emergencies
Cash management is also necessary to deal with contingencies such as fire, breakdown of machinery, payment of compensation in case of any lawsuit going against the company, etc.
Cash for Takeovers
In this dynamic business world there is always a scope for a takeover that is the company can buy another company if it thinks that it is undervalued, cash will play a key role in a successful takeover.
Fluctuating Commodity Prices
Since global commodity prices are fluctuating companies need cash in order to take advantage of the decline in the raw material prices of the company’s product.
Cash for Debt Payments
Cash management assumes greater importance when a company has taken debt because interest payments are fixed and the company has to pay it, any delay in interest payment or principal repayment of debt can even result in the company becoming bankrupt, therefore cash should be there for payment of the such expense.
Methods of Cash Management
Cash management involves several methods to ensure that a business maintains an optimal level of cash, enough to meet its operating expenses, but not so much as to be wasteful. Some methods of cash management include:
Projection of Cash Flows and Planning
The cash planning and the projection of cash flows are determined with the help of the cash budget. The cash budget is the most important tool in cash management. It is a device to help a firm to plan and control the use of cash. It is a statement showing the estimated cash inflows and cash outflows over the firm’s planning horizon.
In other words, the net cash position i.e., surplus or deficiency of a firm is highlighted by the cash budget from one budgeting period to another period.
Determining Optimal Level of Cash
Determining Optimal Level of Cash Holding in the Company: One of the important responsibilities of a finance manager is to maintain sufficient cash balances to meet the current obligations of a company. Determining to optimum level of cash balance is influenced by a tradeoff between risk and profitability.
Every business enterprise holds cash balances for transaction purposes and to meet precautionary, speculative and compensative motives. With the help of a cash budget, the finance manager predicts the inflows and outflows of cash during a particular period of time and thereby determines the cash requirements of the company.
While determining the optimum level of cash balance (neither excess nor inadequate cash balances) the finance manager has to bring a tradeoff between the liquidity and profitability of the firm. The optimum level of cash balances of a company can be determined in various ways. They are:
- Inventory Model (Economic Order Quantity) to cash management
- Stochastic Model
- Probability Model
- The BAT Model
Strategies for Cash Management
Once cash flow projections are made and appropriate cash balances are established, the finance manager should take steps toward the effective utilization of available cash resources. Let’s understand the strategies for cash management:
- Quick Deposit of Customer Cheques
- Establishing Collection Centres
- Lock-Box Method
- Delaying Outward Payment
- Making Pay Roll Periods Less Frequent
- Solving Disbursement by Use of Drafts
- Playing Float
- Centralized Payment System
- Bank Transferring
Strategies Towards Accelerating Cash Inflows
In order to accelerate the cash inflows and maximize the available cash the firm has to employ several methods such as reducing the time lag between the movement of payment to the company is mailed and the movement of the funds are ready for redeployment by the company.
Quick Deposit of Customer Cheques
The inflow is accelerated through quick deposit of cheques in the banks, the moment they are received. Special attention should be given to depositing the cheques without any delay.
Establishing Collection Centres
In order to accelerate the cash inflows the organization may establish collection centers in various marketing centers of the country. These centers may collect cheques or payments from the customers and deposit them in the local bank.
Thus, these cheques are collected immediately at the collection center and the bank can transfer the surplus money, if any, to the company’s main bank. Thus, the decentralized collection system of the company reduced the time lag in cash remittances and collections.
Lock-Box Method
The new device which is popular in the recent past is the lock-box method which will help to reduce the time interval from the mailing of the cheque to the use of funds by the company. Under this arrangement, the company rents lock-box from post offices through its service area.
The customers are instructed to mail cheques to the lockbox. The company’s bank collects the mail from the lockbox several times a day and deposits them directly in the company’s account on the same day. This will reduce the time in mailing cheques, depositing them in the bank, and thereby reducing overhead costs to the company.
But one of the serious limitations of the system is that the banks will charge additional service costs to the company. However, this system is proved useful and economical to the firm.
Strategies for Slowing Cash Outflows
In order to accelerate cash availability in the company, the finance manager must employ some devices that could slow down the speed of payments outward in addition to accelerating collections. The methods of slowing down disbursements are as follows:
- Delaying Outward Payment
- Making Pay Roll Periods Less Frequent
- Solving Disbursement by Use of Drafts
- Playing Float
- Centralized Payment System
- Bank Transferring
Delaying Outward Payment
The finance manager can increase the cash turnover by delaying the payment of bills until the due date of the no-cost period. Thus, he can economize the cash resources of the firm.
Making Pay Roll Periods Less Frequent
The firm can economize its cash resources by changing the frequency of disbursing pay to its employees. For example, if the company is presently paying wages weekly, it can effect substantial cash savings if the pay is disbursed only once a month.
Solving Disbursement by Use of Drafts
A company can delay disbursement by use of drafts on funds located elsewhere. When the firm pays the amount through drafts, the bank will not make the payment against the draft unless the bank gets the acceptance of the issuer firm.
Thus the firm need not have a balance in its bank account till the draft is presented for acceptance. On the other hand, it will take several days for the draft to be actually paid by the company. Thus finance managers can economize large amounts of cash resources for at least a fortnight. The funds saved could be invested in highly liquid low-risk assets to earn income thereon.
Playing Float
Float is the difference between the company’s chequebook balance and the balance shown in the bank’s books of accounts. When the company writes a cheque, it will reduce the balance in its books of accounts by the amount of the cheque. But the bank will debit the amount of its customers only when the cheque is collected.
On the other hand, the company can maximize its cash utilization by ignoring its book balance and keeping its cash invested until just before the cheques are actually presented for payment. This technique is known as “playing the float”.
Centralized Payment System
A firm can delay payments through the centralized payment system. Under this system, payments will be made from a single central account. This will benefit the company.
Bank Transferring
By transferring funds from one bank to another bank firm can maximize its cash turnover.
FAQs About the Cash Management
What is the meaning of cash management?
Cash management is one of the key areas of working capital management. Cash is the most liquid current assets. Cash is the common denominator to which all current assets can be reduced because the other major liquid assets, i.e. receivable and inventory get eventually converted into cash.
What are the objectives of cash management?
The objectives of cash management are:
1. Insolvency
2. Good Relations
3. Credit Worthiness
4. Availing Discount Facilities
5. To Meet Unexpected Facilities
6. Matching of Cash Flows
7. Short Costs
8. Cost of Cash on Excess Balances
9. Uncertainty in Business
10. Cost of Procurement and Management of Cash.
What is the importance of cash management?
A good cash management program is a very significant component of the overall financial management of a municipality.
1. Managing Credit Cash Flow
2. Preparing for Emergencies
3. Cash for Takeovers
4. Fluctuating Commodity Prices
5. Cash for Debt Payments.
What are the strategies for cash management?
These are the strategies for cash management:
1. Quick Deposit of Customer Cheques
2. Establishing Collection Centres
3. Lock-Box Method
4. Delaying Outward Payment
5. Making Pay Roll Periods Less Frequent
6. Solving Disbursement by Use of Drafts
7. Playing Float
8. Centralized Payment System
9. Bank Transferring.