Table of Contents
-
1 Characteristics of Financial Plan
- 1.1 Simplicity of Purpose
- 1.2 Optimum Use or Intensive Use
- 1.3 Based on Clear-cut Objectives
- 1.4 Long-term Consideration
- 1.5 Flexibility
- 1.6 Planning Foresight
- 1.7 Financial Contingencies
- 1.8 Solvency and Liquidity
- 1.9 Profitability
- 1.10 Economy to Administer Financial Plan
- 1.11 Conservative
- 1.12 Varying Risks
- 1.13 Pragmatic Approach
- 1.14 Availability of Required Funds
- 1.15 Investors Preference or Temperament
- 1.16 Timing
- 1.17 Interaction with Stakeholders
- 1.18 Effective Implementation
- 1.19 Owners Control
- 1.20 Adequate Internal Financing
- 1.21 Industrial Suitability
- 1.22 Suitability Financial Plan to Company Reputation
- 1.23 Consideration of General Economic Conditions
- 1.24 Legal Compliance
- 2 FAQs Related to the Characteristics of Financial Plan
Characteristics of Financial Plan
Every concern had to formulate a financial plan that would suit the specific circumstances in which it is operating. A concern should bear in mind certain considerations or principles while formulating or devising its financial plan:
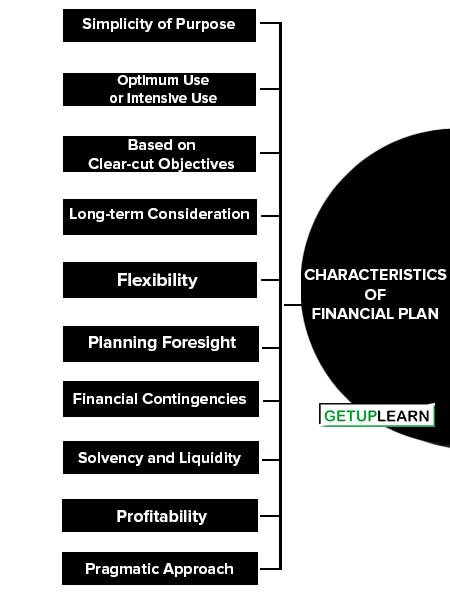
The following are the characteristics of financial plan:
- Simplicity of Purpose
- Optimum Use or Intensive Use
- Based on Clear-cut Objectives
- Long-term Consideration
- Flexibility
- Planning Foresight
- Financial Contingencies
- Solvency and Liquidity
- Profitability
- Economy to Administer Financial Plan
- Conservative
- Varying Risks
- Pragmatic Approach
- Availability of Required Funds
- Investors Preference or Temperament
- Timing
- Interaction with Stakeholders
- Effective Implementation
- Owners Control
- Adequate Internal Financing
- Industrial Suitability
- Suitability Financial Plan to Company Reputation
- Consideration of General Economic Conditions
- Legal Compliance
Simplicity of Purpose
A financial plan should be drafted in terms of the purpose for which the enterprise is organized. It should contain a simple financial structure that can be implemented and managed easily and understood clearly by all.
In short, the financial plan should not be too complicated to understand and implement by the executive managers.
Optimum Use or Intensive Use
Wasteful use of capital is almost as bad as inadequate capital. A financial plan should be such that it will provide for an intensive use of funds. Funds should not remain idle and there should not be any paucity of it. Financial planners should keep in view the proper utilization of funds in the context of the overall objective of maximization of wealth.
Again they should see that there is a proper balance in maintenance between long-term and short-term funds since the surplus of one will not be able to offset the shortage of the other.
Based on Clear-cut Objectives
Financial planning should be done by keeping in view the overall objectives of the company. It should aim to procure funds at the lowest cost so that the profitability of the business is improved.
Long-term Consideration
Financial planning should be formulated keeping in view the long-term requirements and not just the immediate or short-term requirements of the concern. This is because financial planning originally formulated would continue to operate for a long time after the formation of the concern.
Flexibility
The financial planning should be such that it can be modified or changed according to the changing needs of the business with the minimum possible delay. There may be scope for raising additional funds if fresh opportunities occur.
Flexibility in a plan will be helpful in coping with the demands of the future. Management should be ready to revise or completely change the firm’s short-run objectives, policies, and procedures in order to take advantage of changing conditions.
Planning Foresight
Foresight is essential for any plan of business operations so that capital requirements may be assessed as accurately as possible. Accurate forecasts are required to be made regarding the future scope of operations of the concern, technological developments, etc.
The making of accurate forecasts requires foresight on the part of financial planners. A financial plan visualized without foresight may fail to meet the present as well as the future requirements of funds and bring disaster to the concern.
Financial Contingencies
The financial planning should make adequate provisions of funds for meeting the contingencies likely to arise in the future. This principle does not mean that large amounts of funds should be kept idle as reserves for unforeseen contingencies.
It simply means that while formulating the financial plans, the financial planners should make proper forecasts of the contingencies likely to arise in the future and make adequate provisions for funds for meeting the future contingencies.
Solvency and Liquidity
Solvency means the ability of the concern to meet it long-term debt obligations and liquidity means the ability of the business to meet its short-term payments. The plan should take proper care of solvency because many of the companies have failed due to insolvency.
There should be adequate liquidity in the financial plans. This ensures creditworthiness and goodwill to the concern and funds become available to it on very reasonable terms. It acts as a shock absorber in the event of business operations deviating from the normal course.
It gives the financial plan a certain degree of flexibility. Above all, it will help in avoiding embarrassment to the management and a loss of reputation of the concern in the eyes of the public. Proper forecasting of future payments will be helpful in planning liquidity.
Profitability
A financial plan should maintain the required proportion between fixed charge obligations and liabilities in such a manner that the profitability of the organization is not adversely affected.
The most crucial factor in financial planning is the forecast of sales, for sales almost invariably represent the primary source of income and cash receipts. Besides, the operations of a business are geared to the anticipated volume of sales.
Economy to Administer Financial Plan
The financial plan should also ensure the economy. It should ensure that the cost of raising funds is optimum. This is possible by having a proper debt-equity mix in the capital structure. The cost of capital is an important element in the formulation of a financial plan. An excessive burden of fixed charges on its earnings might inflate its cost of capital.
Conservative
A financial plan should be conservative, in the sense that the fundraising capacity of the plan should not be over-exploited.
Varying Risks
The financial plan should provide for ventures with varying degrees of risk so that it might enable a company to achieve substantial earnings from risky ventures.
Pragmatic Approach
A plan should be such that it should serve a practical purpose. It should be realistic and capable of being put to use.
Availability of Required Funds
The source of finance which a corporation may select may be available at a given point in time. If certain sources are not available, the corporation may even prefer to violate the principle of suitability. Availability sometimes bears no relation to cost.
A corporation cannot always choose its source of funds. The availability of different kinds of funds often plays an important part in a firm’s decision to use debt or equity. This aspect may be considered while formulating a plan.
Investors Preference or Temperament
Preferences of different investors vary. Some who are bold and venturesome prefer equity shares. Some investors who are cautious go for debentures. As such, the financial plan should keep in mind the temperament or the preference of investors, i.e. the financial plan should be formulated in accordance with the preferences of investors.
Timing
Sound financial planning involves effective timing in the acquisition of funds. The key to effective timing is correct forecasting. This would depend upon the understanding of the management as to how business cycles behave during different phases of business operations.
Interaction with Stakeholders
With outside parties including investors and other suppliers of funds, communication is an essential prerequisite. The outside parties would then know that the management is trying to control its business effectively and what it is doing.
Effective Implementation
A firm should see to it that plans are actually carried out. The data should be available at any level in detail and in a certain frequency. This would enable a firm to take timely and corrective action whenever necessary.
Owners Control
The capital structure of a firm may be such to ensure that control does not pass into the hands of outsiders. For this purpose, the use of debt financing may be encouraged. However, the stock should be broadly distributed to facilitate the maintenance of control.
Adequate Internal Financing
Long-term financial planning should aim to reduce dependence on outside sources. This can be possible by retaining a part of profits for plowing back. The generation of own funds is the best way of financing operations. In the beginning, outside funds may be a necessity but financial planning should be such that dependence on such funds may be reduced in due course of time.
Industrial Suitability
The needs for funds are different for various industries. The asset structure, element of seasonality, and stability of earnings are not common factors for all industries. These variables influence or determine the size and structure of financial requirements.
Suitability Financial Plan to Company Reputation
This will influence a decision about the financial plan. The goodwill of the concern, credit rating in the market, past performances, and attitude of the management are some of the factors which will be considered in formulating a financial plan.
Consideration of General Economic Conditions
The prevailing economic conditions at the national level and international levels will influence a decision about a financial plan. These conditions should be considered before taking any decisions about sources of funds.
A favorable economic environment will help in raising funds without any difficulty. On the other hand, uncertain economic conditions may make it difficult for even a good concern to raise sufficient funds.
Legal Compliance
The Government policies regarding the issue of shares and debentures, payment of dividends and interest rates, entering into foreign collaborations, etc. will influence a financial plan.
The legislative restrictions on using certain sources, limited dividends, etc. will make it difficult to raise funds. So Government controls should be properly considered while selecting a financial plan.
What are the characteristics of financial plan?
The characteristics of financial plan are:
1. Simplicity of Purpose
2. Optimum Use or Intensive Use
3. Based on Clear-cut Objectives
4. Long-term Consideration
5. Flexibility
6. Planning Foresight
7. Financial Contingencies
8. Solvency and Liquidity
9. Profitability
10. Economy to Administer Financial Plan.