Table of Contents
- 1 What is Financial?
- 2 What is Financial Management?
- 3 Definition of Financial Management
- 4 Functions of Financial Management
-
5 Objectives of Financial Management
- 5.1 Profit Maximization
- 5.2 Wealth Maximization
- 5.3 Proper Estimation of Total Financial Requirements
- 5.4 Proper Mobilization
- 5.5 Proper Utilization of Finance
- 5.6 Maintaining Proper Cash Flow
- 5.7 Survival of Company
- 5.8 Creating Reserves
- 5.9 Proper Coordination
- 5.10 Create Goodwill
- 5.11 Increase Efficiency
- 5.12 Financial Discipline
- 5.13 Reduce Cost of Capital
- 5.14 Reduce Operating Risks
- 5.15 Prepare Capital Structure
- 6 Scope of Financial Management
- 7 Importance of Financial Management
- 8 Limitations of Financial Management
-
9 FAQs About Financial Management
- 9.1 What is the Meaning of Financial?
- 9.2 What is the Meaning of Financial Management?
- 9.3 What is the definition of financial?
- 9.4 What is the definition of financial management?
- 9.5 What are the functions of financial management?
- 9.6 What are the objectives of financial management?
- 9.7 What are the scope of financial management?
- 9.8 What is the importance of financial management?
What is Financial?
Finance is defined as the provision of money at the time when it is required. Every enterprise, whether big, medium, or small, needs finance to carry on its operations and to achieve its target.
In fact, finance is so indispensable today that it is rightly said to be the blood of an enterprise. Without adequate finance, no enterprise can possibly accomplish its objectives.
What is Financial Management?
Financial management refers to that part of the management activity, which is concerned with the planning, & controlling of a firm’s financial resources. It deals with finding out various sources for raising funds for the firm. Financial management is practiced by many corporate firms and can be called Corporation finance or Business Finance.

In other words, Financial Management is an integral part of general management. It concerns managerial decision-making. It helps in the allocation of future financial requirements, allocation of resources, and appraisal of financial problems.
Definition of Financial Management
These are the following definition of financial management by authors:
[su_quote cite=”Hoagland”]Financial management deals with how corporations obtain funds and how it uses them.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”Archer and Ambrosio”]Financial Management is the application of planning and control functions to the finance function.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”Raymond Chambers”]Financial management may be considered to be the management of the finance function.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”J.F. Bradley”]Financial management is the area of business management devoted to the judicious use of capital and a careful selection of sources of capital in order to enable a business firm to move in the direction of reaching its goals.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”Joseph and Massie”]Financial Management is the operational activity of a business that is responsible for obtaining and effectively utilizing the funds necessary for efficient operations.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”Howard and Upton”]Financial Management is the application of the planning and control functions to the finance function.[/su_quote]
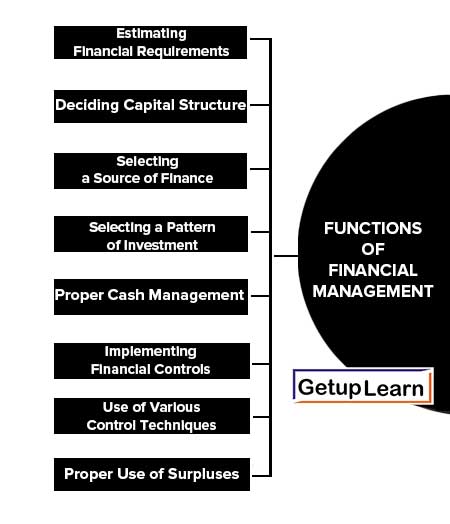
Functions of Financial Management
A financial manager has to concentrate on the following areas of the finance function. These are The functions of financial management explained below:
- Estimating Financial Requirements
- Deciding Capital Structure
- Selecting a Source of Finance
- Selecting a Pattern of Investment
- Proper Cash Management
- Implementing Financial Controls
- Use of Various Control Techniques
- Proper Use of Surpluses
Estimating Financial Requirements
The first task of the financial manager is to estimate the short-term and long-term financial requirements of his business. For this purpose, he will prepare a financial plan for the present as well as the future.
The amount required for purchasing fixed assets as well as the need for funds for working capital has to be ascertained.
The estimation should be based on sound financial principles so that neither there are inadequate nor excess funds for the concerned. The inadequacy will affect the working of the concern and excess funds may tempt management to indulge in extravagant spending.
Deciding Capital Structure
The capital structure refers to the kind and proportion of the different securities for raising funds. After deciding the quantum of funds required it should be decided which type of security should be raised. It may be wise to finance fixed securities through long-term debts. Long-term funds should be employed to finance working capital also.
Decisions about various sources of funds should be linked to the cost of raising funds. If the cost of raising funds is high, then such sources may not be useful. A decision about the kind of securities to be employed and the proportion in which these should be used is an important decision that influences the short-term and long-term planning of the enterprise.
Selecting a Source of Finance
After preparing a capital structure, an appropriate source of finance is selected. Various sources from which finance may be raised, include share capital, debentures, financial deposits, etc.
If finance is needed for short periods then banks, public deposits, and financial institutions may be appropriate. If long-term finance is required the share capital, debentures may be useful.
Selecting a Pattern of Investment
When funds have been procured then a decision about investment patterns is to be taken. The selection of investment patterns is related to the use of the funds. Does a decision have to be taken as to which assets are to be purchased? The fund will have to be spent first. Fixed assets and the appropriate portion will be retained for the working capital.
The decision-making techniques such as capital Budgeting, and opportunity cost analysis may be applied in making decisions about capital expenditures. While spending on various assets, the principles of safety, profitability, and liquidity should not be ignored.
Proper Cash Management
Cash management is an important task of a financial manager. He has to assess the various cash needs at different times and then make arrangements for arranging cash. Cash may be required to make payments to creditors, purchase raw materials, meet wage bills, and meet day-to-day expenses.
The sources of cash may be Cash sales, Collection of debts, and Short-term arrangements with the banks. The cash management should be such that neither there is a shortage of it and nor it is idle.
Any shortage of cash will damage the creditworthiness of the enterprise. The idle cash in the business means that it is not properly used. Through Cash Flow, Statement One is able to find out various sources and applications of cash.
Implementing Financial Controls
An efficient system of financial management necessitates the use of various control devices. Financial control devices generally used are:
- Return Investment
- Ratio Analysis
- Break-even Analysis
- Cost Control
- Cost and Internal Audit.
Use of Various Control Techniques
This will help the financial manager in evaluating the performance in various areas and take corrective measures whenever needed.
Proper Use of Surpluses
The utilization of profits or surpluses is also an important factor in financial management. A judicious use of surpluses is essential for the expansion and diversification plans and also for protecting the interest of the shareholders.
The plowing back of profit is the best policy for further financing. A balance should be struck in using the funds for paying dividends and retaining earnings for financing expansion plans.
Objectives of Financial Management
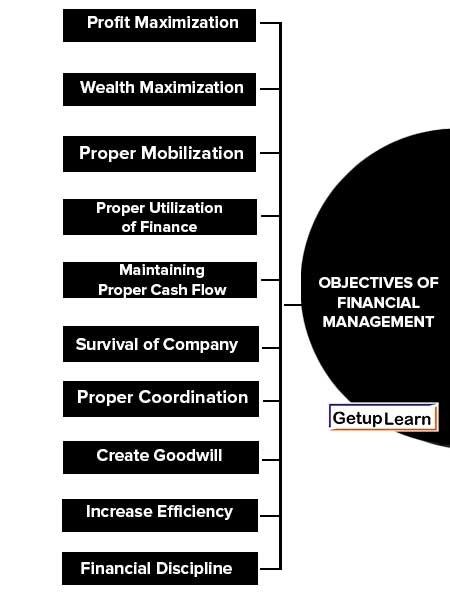
Financial management is generally concerned with the procurement, allocation, and control of financial resources of a concern. The objectives of the financial management are as follows:
- Profit Maximization
- Wealth Maximization
- Proper Estimation of Total Financial Requirements
- Proper Mobilization
- Proper Utilization of Finance
- Maintaining Proper Cash Flow
- Survival of Company
- Creating Reserves
- Proper Coordination
- Create Goodwill
- Increase Efficiency
- Financial Discipline
- Reduce Cost of Capital
- Reduce Operating Risks
- Prepare Capital Structure
Profit Maximization
The main objective of financial management is profit maximization. The finance manager tries to earn maximum profits for the company in the short term and the long term. He cannot guarantee profits in the long term because of business uncertainties.
However, a company can earn maximum profits even in the long term, if:
- The Finance manager takes proper financial decisions.
- He uses the finance of the company properly
Wealth Maximization
Wealth maximization (shareholders’ value maximization) is also a main objective of financial management. Wealth maximization means earning maximum wealth for the shareholders. So, the finance manager tries to give a maximum dividend to the shareholders.
He also tries to increase the market value of the shares. The market value of the shares is directly related to the performance of the company. The better the performance higher is the market value of shares and vice-versa. So, the finance manager must try to maximize shareholder value.
Proper Estimation of Total Financial Requirements
Proper estimation of total financial requirements is a very important objective of financial management. The finance manager must estimate the total financial requirements of the company. He must find out how much finance is required to start and run the company.
He must find out the fixed capital and working capital requirements of the company. His estimation must be correct. If not, there will be a shortage or surplus of finance.
Estimating the financial requirements is a very difficult job. The finance manager must consider many factors, such as the type of technology used by the company, the number of employees employed, the scale of operations, legal requirements, etc.
Proper Mobilization
Mobilization (collection) of finance is an important objective of financial management. After estimating the financial requirements, the finance manager must decide about the sources of finance.
He can collect finance from many sources such as shares, debentures, bank loans, etc. There must be a proper balance between owned finance and borrowed finance. The company must borrow money at a low rate of interest.
Proper Utilization of Finance
Proper utilization of finance is an important objective of financial management. The finance manager must make optimum utilization of finance. He must use the finance profitability. He must not waste the finance of the company.
He must not invest the company’s finance in unprofitable projects. He must not block the company’s finance in inventories. He must have a short credit period.
Maintaining Proper Cash Flow
Maintaining proper cash flow is a short-term objective of financial management. The company must have a proper cash flow to pay the day-to-day expenses such as the purchase of raw materials, payment of wages and salaries, rent, electricity bills, etc.
If the company has a good cash flow, it can take advantage of many opportunities such as getting cash discounts on purchases, large-scale purchasing, giving credit to customers, etc. A healthy cash flow improves the chances of survival and success of the company.
Survival of Company
Survival is the most important objective of financial management. The company must survive in this competitive business world. The finance manager must be very careful while making financial decisions. One wrong decision can make the company sick, and it will close down.
Creating Reserves
One of the objectives of financial management is to create reserves. The company must not distribute the full profit as a dividend to the shareholders. It must keep a part of its profit as reserves. Reserves can be used for future growth and expansion. It can also be used to face contingencies in the future.
Proper Coordination
Financial management must try to have proper coordination between the finance department and other departments of the company.
Create Goodwill
Financial management must try to create goodwill for the company. It must improve the image and reputation of the company. Goodwill helps the company to survive in the short term and succeed in the long term. It also helps the company during bad times.
Increase Efficiency
Financial management also tries to increase the efficiency of all the departments of the company. Proper distribution of finance to all the departments will increase the efficiency of the entire company.
Financial Discipline
Financial management also tries to create a financial discipline. Financial discipline means:- To invest finance only in productive areas. This will bring high returns (profits) to the company. To avoid wastage and misuse of finance.
Reduce Cost of Capital
Financial management tries to reduce the cost of capital. That is, it tries to borrow money at a low rate of interest. The finance manager must plan the capital structure in such a way that the cost of capital is minimized.
Reduce Operating Risks
Financial management also tries to reduce operating risks. There are many risks and uncertainties in a business. The finance manager must take steps to reduce these risks. He must avoid high-risk projects. He must also take proper insurance.
Prepare Capital Structure
Financial management also prepares the capital structure. It decides the ratio between owned finance and borrowed finance. It brings a proper balance between the different sources of capital. This balance is necessary for liquidity, economy, flexibility, and stability.
Scope of Financial Management
Financial management is one of the important parts of overall management, which is directly related to various functional departments like personnel, marketing, and production. Financial management covers a wide area with multidimensional approaches.
These are the scope of financial management given below:
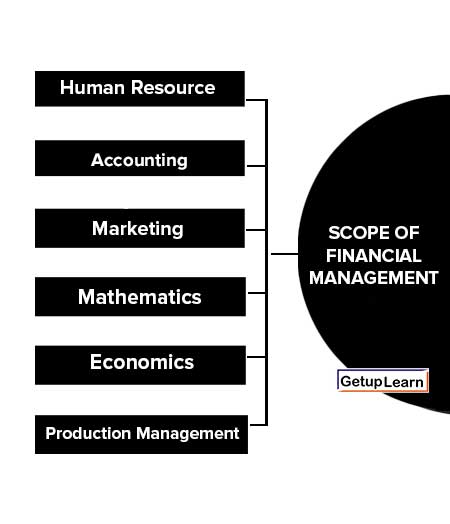
Human Resource
Financial management is also related to the human resource department, which provides manpower to all the functional areas of the management.
The financial manager should carefully evaluate the requirement of manpower for each department and allocate the finance to the human resource department as wages, salary, remuneration, commission, bonus, pension, and other monetary benefits to the human resource department. Hence, financial management is directly related to human resource management.
Accounting
Accounting records include the financial information of the business concern. Hence, we can easily understand the relationship between financial management and accounting.
Marketing
Produced goods are sold in the market with innovative and modern approaches. For this, the marketing department needs finance to meet their requirements.
Mathematics
Modern approaches to financial management applied a large number of mathematical and statistical tools and techniques. Economic order quantity, theories, ratio analysis, and working capital analysis are used as mathematical and statistical tools and techniques in the field of financial management.
Economics
Economic concepts like micro and macroeconomics are directly applied to financial management approaches.
Production Management
Production performance needs finance because the production department requires raw materials, machinery, wages, operating expenses, etc. The financial manager must be aware of the operational process and finance required for each process of production activities.
Importance of Financial Management
The importance of financial management is being discussed under the following points:
- Increase Value of Firm
- Promoting Savings
- Reduces Chances of Failure
- Maximization of Returns
- Makes Base for Planning and Control
- Optimum and Effective Utilization of Resources
- Useful for Stakeholders
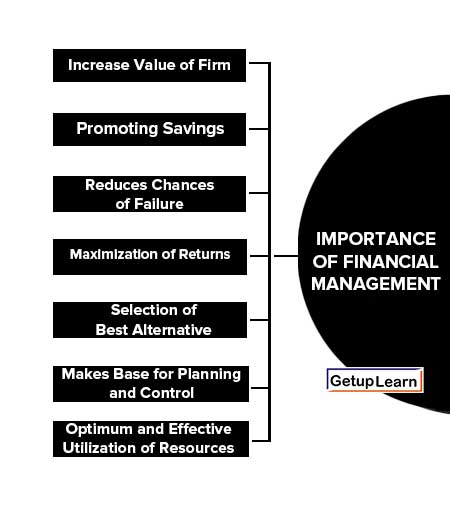
Increase Value of Firm
Financial management is very important in the field of increasing the wealth of the investors and the business concern.
Promoting Savings
Effective financial management helps to promote and mobilize individual and corporate savings.
Reduces Chances of Failure
Implementation of a proper system of financial management brings financial discipline to the organization. Every project is overlooked and carried out by detailed investigation which reduces the chances of failure.
Maximization of Returns
Good financial planning maximizes returns on investment as financial management is of scientific and analytical nature.
Makes Base for Planning and Control
As it is noted that each department depends upon the financial department to start its functioning. Various budget plans are drafted on the basis of financial availability.
Optimum and Effective Utilization of Resources
Financial planning ensures the optimum utilization of financial resources. Each and every stage is carefully planned under this beginning from generating funds to allocation and disposal of profits.
Useful for Stakeholders
Various stakeholders like business managers, investors, financial institutions, economists, politicians, etc. are always interested in knowing the financial position of the company as they maintain financial relations with the business in some way.
Limitations of Financial Management
These are some limitations of financial management:
- Sometimes it becomes difficult to compute the effect of financial decisions on various other departments. It is a very complex procedure that requires careful analysis.
- It requires deep knowledge of finance to perform various finance functions. No professional can be an expert in each and every aspect of finance behavior which limits their skills.
- In India, financial management is still in its developing stage. We lack expertise and knowledge which limits the full use of the subject.
- Sometimes financial decisions may get affected by the personal point of view of the finance officer. It is human nature which sometimes gets biased which may sometimes adversely affect the financial decision.
- Proper implementation of financial management is of expensive nature. It is not possible for small enterprises to appoint and get the services of experts nor do they implement a proper system of financial management.
FAQs About Financial Management
What is the Meaning of Financial?
The term finance can be defined as the management of the flow of money through an organization, whether it will be a corporation, school, bank, or government agency.
What is the Meaning of Financial Management?
“Financial management deals with procurement of funds and their effective utilization in the business”
What is the definition of financial?
Finance is the art and science of managing money. By Khan and Jain
What is the definition of financial management?
Financial management is an area of financial decision-making, harmonizing individual motives and enterprise goals. By Weston and Brigham
What are the functions of financial management?
The following are the functions of financial management:
1. Estimating Financial Requirements
2. Deciding Capital Structure
3. Selecting a Source of Finance
4. Selecting a Pattern of Investment
5. Proper Cash Management
6. Implementing Financial Controls
7. Use of Various Control Techniques
8. Proper Use of Surpluses.
What are the objectives of financial management?
The following are the objectives of financial management:
1. Profit Maximization
2. Wealth Maximization
3. Proper Estimation of Total Financial Requirements
4. Proper Mobilization
5. Proper Utilization of Finance
6. Maintaining Proper Cash Flow
7. Survival of Company
8. Creating Reserves
9. Proper Coordination
10. Create Goodwill
11. Increase Efficiency
12. Financial Discipline
13. Reduce the Cost of Capital
14. Reduce Operating Risks
15. Prepare Capital Structure.
What are the scope of financial management?
The following is the scope of financial management:
1. Human Resource
2. Accounting
3. Marketing
4. Mathematics
5. Economics
6. Production Management.
What is the importance of financial management?
These are the importance of financial management:
1. Increase the Value of Firm
2. Promoting Savings
3. Reduces Chances of Failure
4. Maximization of Returns
5. Makes Base for Planning and Control
6. Optimum and Effective Utilization of Resources
7. Useful for Stakeholders.