Table of Contents
- 1 What is Controlling?
- 2 Meaning of Controlling
- 3 Definition of Controlling
- 4 Importance of Controlling
- 5 Limitations of Controlling
- 6 Controlling Process
- 7 Characteristics of Controlling
- 8 Techniques of Controlling
- 9 Elements of Controlling
- 10 FAQ Related to the Controlling
- 10.1 What is the meaning of controlling?
- 10.2 What is the definition of controlling?
- 10.3 What is the importance of controlling?
- 10.4 What is the controlling process?
- 10.5 What are the characteristics of controlling?
- 10.6 What are the elements of controlling?
- 10.7 What are the limitations of controlling?
- 10.8 What are the techniques of controlling?
What is Controlling?
Controlling is a process whereby managers determine the practical standards of the activities to be performed in an organisation. They evaluate the actual performance and find out the deviations by comparing actual performance with the predetermined standards.
By analyzing and finding out the reasons for deviations they take corrective measures to overcome them so that their recurrence in future can be checked.

Meaning of Controlling
Controlling is the last function of management. If there is an imperfection in the planning and actual performance, control will be needed. The deviations are set right by the controlling function. This function ensures desired results. Planning identifies the activities and controls and regulates the activities.
The success or failure of planning depends upon the result of the success or failure of controlling. It is an important function because it helps to check the errors and to take corrective action so that deviation from standards is minimized and stated goals of the organization are achieved in the desired manner.
Control is the process through which managers assure that actual activities conform to planned activities. According to modern concepts, control is a foreseeing action whereas the earlier concept of control was used only when errors were detected. Control in management means setting standards, measuring actual performance and taking corrective action.
Definition of Controlling
Below that we have given simple and easy definition of controlling:
[su_quote cite=”Mary Cushing Niles“]Controlling is the maintaining of a balance in activities directed towards a goal or a set of goals.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”Joseph Massie“]Controlling is the process that measures current performance and guides it towards some predetermined goals.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”Philip Kotler“]Controlling is the process of taking steps to bring actual results and desired results closer together.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”Theo Haimann“]Controlling is the process of checking whether or not proper progress is being made towards the objectives and goals and acting if necessary, to correct any deviation.” Controlling ensures that there is effective and efficient utilization of organizational resources so as to achieve the organizational goals. Controlling has two basic purposes a) It facilitates coordination b) It helps in planning.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”Harold Koontz“]Controlling is the measurement and correction of performance in order to make sure that enterprise objectives and the plans devised to attain them are accomplished[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”Koontz and O’Donnell”]Managerial control implies the measurement of accomplishment against the standard and the correction of deviations to assure the attainment of objectives according to plans.[/su_quote]
Importance of Controlling
A Good control system provides timely information to the manager which is very much useful for taking various operations. The road signals at a road crossing illustrate the significance of control.
Road signals are necessary to ensure accident-free and smooth traffic management controls are essential in any organization for its smooth functioning.
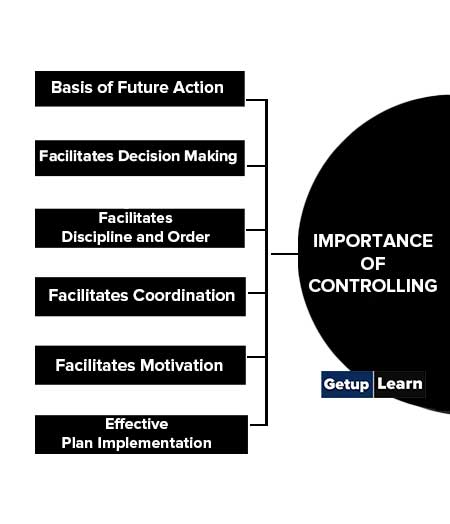
These are the importance of controlling explained one by one:
- Basis of Future Action
- Facilitates Decision Making
- Facilitates Discipline and Order
- Facilitates Coordination
- Facilitates Motivation
- Effective Plan Implementation
Basis of Future Action
Control provides the basis for future actions. It will reduce the chances of mistakes being repeated in future by suggesting preventive steps.
Facilitates Decision Making
The process of control is complete only when corrective measures have been taken. This requires taking the right decision as to what type of follow-up action is to be taken.
Facilitates Discipline and Order
The existence of a control system has a positive impact on the behaviour of the employees. They are cautious while performing their duties as they know they are being observed by their superiors.
Facilitates Coordination
Control helps in the Coordination of the activities of various departments of the enterprise. It provides them with unity of direction.
Facilitates Motivation
A control system is most effective when it motivates people to high performance. Since most people respond to a challenge, successfully meeting a tough standard may provide a greater sense of accomplishment.
Effective Plan Implementation
Controlling and planning are interdependent. Control is the only means to ensure that the plans are being implemented control points out shortcomings of not only planning but also other functions of management. Comparison can be done through various Performance reports, Personal observations.
Read More About: ✅Advantages of Controlling and Limitations of Controlling✅
Read More About: ✅14 Nature of Controlling✅
Limitations of Controlling
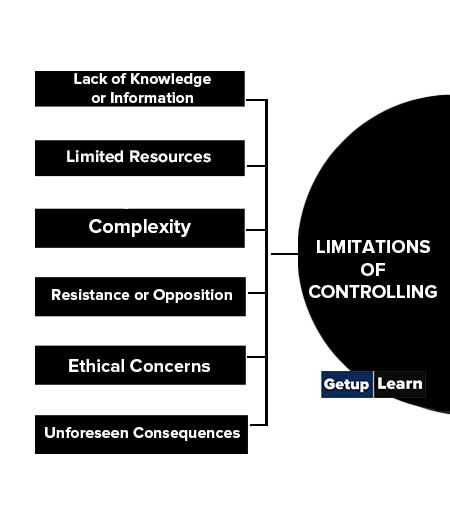
There are several limitations of controlling various contexts. Some common limitations include:
- Lack of Knowledge or Information
- Limited Resources
- Complexity
- Resistance or Opposition
- Ethical Concerns
- Unforeseen Consequences
Lack of Knowledge or Information
In order to effectively control a situation, an individual or organization must have a thorough understanding of the factors involved. If key information is missing or unclear, it can be difficult to make informed decisions about how to best exercise control.
Limited Resources
Controlling can require a significant amount of resources, such as time, money, and personnel. If these resources are limited, it may be challenging to effectively exert control over a situation.
Complexity
Some situations are inherently complex and difficult to control due to the number of variables and factors at play. In these cases, it may be challenging to predict how different actions will impact the outcome.
Resistance or Opposition
When attempting to exert control over a situation, an individual or organization may face resistance or opposition from those who are affected by the changes being implemented. This can make it difficult to effectively exercise control.
Ethical Concerns
In some cases, the use of control may raise ethical concerns, such as when it involves the infringement of an individual’s rights or freedoms. It is important to carefully consider the ethical implications of any control measures before implementing them.
Unforeseen Consequences
Even when control measures are carefully planned and implemented, there is always the risk of unintended consequences. These can arise due to a variety of factors, including unpredictable changes in the environment or the emergence of new variables.
Read More About: ✅Effective Control System✅
Controlling Process
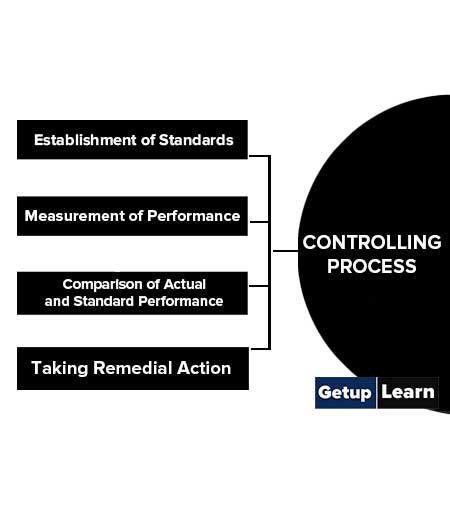
These are the steps which involve in the controlling process:
- Establishment of Standards
- Measurement of Performance
- Comparison of Actual and Standard Performance
- Taking Remedial Action
Establishment of Standards
Standards are the plans or the targets which have to be achieved in the course of business function. It acts as a basis for evaluations of actual performance. Standards can be set in quantitative or qualitative terms. Quantitative or measurable standards can be informed of cost, output, time, profit etc.
Qualitative or nonmeasurable standards can be in form of the performance of a manager, the attitude of workers improving the motivational level of employees. Standards should be flexible i.e. capable of being changed according to the circumstances.
Measurement of Performance
This step involves measuring the actual performance of various individuals, groups or units. Measurement of tangible standards is easy as it can be expressed in quantitative terms. The frequency of measurement depends on the nature of the task being controlled Qualitatively.
Comparison of Actual and Standard Performance
Comparison of actual performance with the planned targets is very important. Deviations can be defined as the gap between actual performance and the standards laid down.
The manager has to find out the extent of the deviation and the cause of the deviation. The manager has to exercise control by exception. He has to target those deviations which are critical and important for business.
Taking Remedial Action
Once the causes and extent of deviation are known, the manager has to detect those errors and take remedial measures so that these deviations don’t occur again. Remedial or corrective actions can be replanning of standards, classification of duties, training of workers etc.
Successful management involves active participation by managers in the above basic managerial functions. These functions are interrelated and most managers use a combination of all of them simultaneously to solve the problems facing their companies.
Read More About: ✅Process of Controlling: Good Controlling System✅
Characteristics of Controlling
These are characteristics of controlling explained below:
- Continuous Process
- Management Function
- Control is Exercised at All Levels
- Control is Forward Looking
- Dynamic Process
- Control is a Self-Corrective Process
- Closely Related to Planning
Continuous Process
Controlling is a Continuous Process: Control is a never-ending activity on the part of managers. This includes continuous analysis of goals, the establishment of standards, measurement of performance, and remedial action with the help of organisational policies and procedures.
Management Function
Controlling is a Management Function: Control as a management function implies, the measurement of accomplishment of events against the standard of plans and correcting the deviations in order to attain the objectives according to the plan. In fact, this is a follow-up action towards other management functions.
The utility of this function is such that it is performed by all levels of managers in the business unit to keep close control of all aspects of business which are assigned to them.
Control is Exercised at All Levels
Controlling is Exercised at All Levels: The word “control” exists and works at each and every level of management, even though its nature and extent may be different at different levels to the top management, it helps in exercising administrative control which is based on certain plans and policies for the common objectives.
In the same way, the middle level of management is also responsible for controlling and implementing plans and policies in the organisation. Finally, the lower level management is responsible to keeps control of the operations that are involved in actual performance.
Control is Forward Looking
Controlling is Forward Looking: Another characteristic feature of control is that it always looks forward. It relates to the future as a manager and has no control over the happenings in the past.
They can only correct future actions for further operations of work. It is the past experience of control, which guides a manager to improve his action for the attainment of common objectives of the organisation.
Dynamic Process
Controlling is a Dynamic Process: It is a dynamic process and is flexible. It requires regular review and check of standards and performances which leads to proper corrective actions and modifications in plans and policies, according to the changing conditions and atmosphere, tests and needs of the business.
Control is a Self-Corrective Process
Control is a Self-Corrective Process: In the process of control, we generally compare our actual performance with planned performance and verify the deviations which have taken place in actual performance from those which have been fixed by the planners.
Thus it tells us that control exists only when the work is completed because we can compare the performance only then. If there are deviations in actual performance when compared with proposed performance, then the control should take corrective measures to avoid errors and deviations in future.
Control is Closely Related to Planning: We know the meaning of planning. It decides in advance what do to, what to do when to do and by whom it is to be done. It makes impossible things possible, which would not otherwise happen. For this, certain objectives are famed and are referred to as standards against which actual performance is checked.
Read More About: ✅14 Importance of Controlling✅
Techniques of Controlling
Controlling is a process used in management and organizational theory to ensure that an organization’s resources are used effectively and efficiently in order to achieve its goals and objectives. There are several techniques that can be used to control an organization.
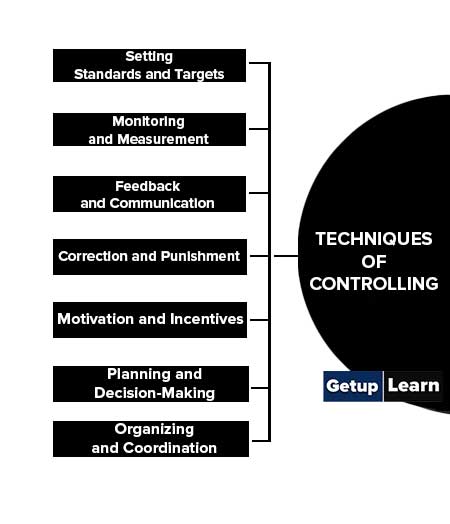
These are the techniques of controlling in management:
- Setting Standards and Targets
- Monitoring and Measurement
- Feedback and Communication
- Correction and Punishment
- Motivation and Incentives
- Planning and Decision-Making
- Organizing and Coordination
Setting Standards and Targets
Setting clear and measurable standards and targets for performance allows organizations to track progress and identify areas for improvement.
Monitoring and Measurement
Regular monitoring and measurement of performance allow organizations to identify deviations from standards and take corrective action.
Feedback and Communication
Providing regular feedback to employees and ensuring effective communication within the organization helps to ensure that everyone is working towards the same goals.
Correction and Punishment
When standards are not met, organizations may need to take corrective action or impose punishment in order to maintain control and ensure that standards are upheld.
Motivation and Incentives
Providing motivation and incentives can help to encourage employees to perform to the best of their abilities and meet or exceed standards.
Planning and Decision-Making
Careful planning and decision-making can help organizations stay on track and make the most effective use of their resources.
Organizing and Coordination
Organizing and coordinating the work of different departments and teams can help to ensure that resources are used effectively and efficiently.
Read More About: ✅16 Techniques of Controlling in Management✅
Elements of Controlling
Let’s discussed the elements of controlling:
Condition to Be Controlled
The first element is the characteristic or condition of the operating system which is to be measured. We select a specific characteristic because a correlation exists between it and how the system is performing.
The characteristic can be the output of the system during any stage of processing or it may be a condition that is the result of the system. For example, it may be the heat energy produced by the furnace or the temperature in the room which has changed because of the heat generated by the furnace.
In an elementary school system, the hours a teacher works or the gain in knowledge demonstrated by the students on a national examination are examples of characteristics that may be selected for measurement, or control.
Sensor
The second element of control, the sensor, is a means for measuring the characteristic or condition. For example, in a home heating system, this device would be the thermostat, and in a quality-control system, this measurement might be performed by a visual inspection of the product.
Comparator
The comparator determines the need for correction by comparing what is occurring with what has been planned. Some deviation from the plan is usual and expected, but when variations are beyond those considered acceptable, corrective action is required. It involves a sort of preventative action which indicates that good control is being achieved.
Activator
the activator is the corrective action taken to return the system to its expected output. The actual person, device, or method used to direct corrective inputs into the operating system may take a variety of forms.
It may be a hydraulic controller positioned by a solenoid or electric motor in response to an electronic error signal, an employee directed to rework the parts that failed to pass quality inspection or a school principal who decides to buy additional books to provide for an increased number of students.
As long as a plan is performed within allowable limits, corrective action is not necessary; however, this seldom occurs in practice.
Information is the medium of control because the flow of sensory data and later the flow of corrective information allow a characteristic or condition of the system to be controlled. To illustrate how information flow facilitates control, let us review the elements of control in the context of information.
What is the meaning of controlling?
Controlling is an important function of management which ensures the execution of work as per planning, finds the gap between standard performance and actual performance, analyses the reasons for deviations in standard and actual performance and takes corrective action so that performance could be achieved as per plan.
What is the definition of controlling?
This is the simplest definition of controlling:
Control is the maintaining of a balance in activities directed towards a goal or a set of goals.
What is the importance of controlling?
The following are the importance of controlling:
1. Basis of Future Action
2. Facilitates Decision Making
3. Facilitates Discipline and Order
4. Facilitates Coordination
5. Facilitates Motivation
6. Effective Plan Implementation.
What is the controlling process?
The following are the steps that involve in the controlling process:
1. Establishment of Standards
2. Measurement of Performance
3. Comparison of Actual and Standard Performance
4. Taking Remedial Action.
What are the characteristics of controlling?
The following are the characteristics of controlling:
1. Continuous Process
2. Management Function
3. Control is Exercised at All Levels
4. Control is Forward Looking
5. Dynamic Process
6. Control is a Self-Corrective Process
6. Closely Related to Planning.
What are the elements of controlling?
The following are the elements of controlling:
1. Condition to Be Controlled
2. Sensor
3. Comparator
4. Activator.
What are the limitations of controlling?
The following are the limitations of controlling:
1. Lack of Knowledge or Information
2. Limited Resources
3. Complexity
4. Resistance or Opposition
5. Ethical Concerns
6. Unforeseen Consequences.
What are the techniques of controlling?
The following are the techniques of controlling:
1. Setting Standards and Targets
2. Monitoring and Measurement
3. Feedback and Communication
4. Correction and Punishment
5. Motivation and Incentives
6. Planning and Decision-Making
7. Organizing and Coordination.