Table of Contents
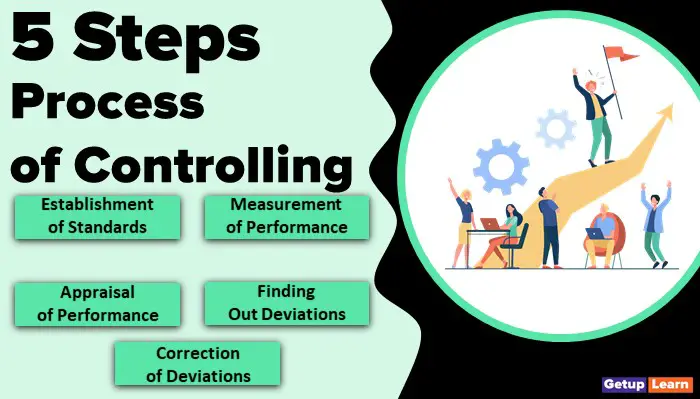
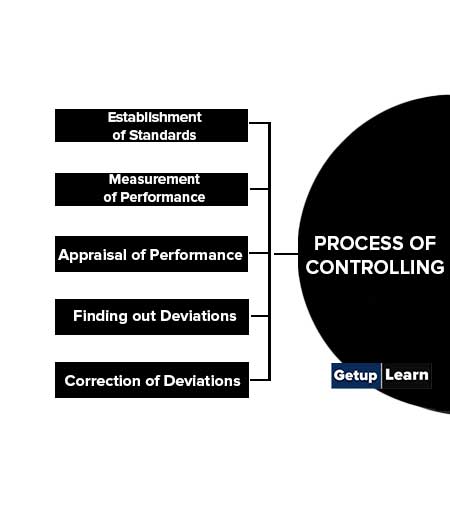
Process of Controlling
The basic process of controlling consists of the following five steps:
- Establishment of Standards
- Measurement of Performance
- Appraisal of Performance
- Finding out Deviations
- Correction of Deviations
Establishment of Standards
Standards serve as a basis for measuring performance. They may be expressed in quantitative or qualitative terms. A standard is a criterion against which results can be measured. In quantitative terms, they are expressed in numbers which are to be produced by workers while in terms of the money they refer to the cost of production, cost of distribution per unit etc.
It is the duty of the planner to set the standards and state clearly to those workers from whom the results are expected so that they do not face difficulty in achieving the goals. They must be valid, understandable and acceptable.
Measurement of Performance
The second important element in the process of control is the measurement of determination of the actual performance. Measurement of actual performance does not mean knowing what has happened but also what is likely to happen. It means that deviations are predicted in advance which helps the management to take corrective action in advance for the achievement of goals.
For the management, it becomes essential to measure performance as soon as the operations are completed. Not only this but it can also be measured while the activity is in the course of operation. From this, the appraisal would be possible in time.
Appraisal of Performance
Third step of process of controlling. We compare the actual performance with the standards. It can be easily compared if the standards are properly determined and methods are clearly communicated for the measurement of performance. The manager should concentrate on those main deviations which are noticed while making the appraisal of performance.
But he should not waste his time and energy on small deviations. This approach will give the correct, quick and favourable results. At the same time, simple and effective action also avoids uneconomic watching and wastage of time and attention.
Finding out Deviations
While comparing the actual and standard performance, it is wiser to find out the extent, nature and basic causes for deviations. A competent manager does not find any difficulty in locating the deviation points while measuring the actual performance properly.
To find out the cause of deviations he will have to depend on proper, accurate and timely information. A manager after getting the information from various departments would conveniently tell whether errors have occurred in the operations or project designing and from them, he can easily find out the causes of deviations and the workers who are responsible for such errors. This is another step process of controlling.
Correction of Deviations
The last but not least element in the process of control is the correction of deviations. For the correction of deviations, management should take necessary action and implement them so that in future these errors and deviations are minimized.
Correction in deviations involves improvement in technology, direction, supervision, setting new goals, restructuring the organisation and revision of targets, set in advance. If corrective action is not taken properly in time against the major deviations then it will lead to heavy losses. This is last step process of controlling.
Qualities of Good Controlling System
Controls at every level focus on inputs, processes and outputs. It is very important to have effective controls at each of these three stages. Effective control systems tend to have certain common characteristics. These are the qualities of good controlling system given below:
- Accuracy
- Timeliness
- Flexibility
- Acceptability
- Integration
- Economic Feasibility
- Strategic Placement
- Corrective Action
- Emphasis on Exception
Accuracy
Effective controls generate accurate data and information. Accurate information is essential for effective managerial decisions. Inaccurate controls would divert management efforts and energies on problems that do not exist or have a low priority and would fail to alert managers to serious problems that do require attention.
Timeliness
There are many problems that require immediate attention. If information about such problems does not reach management in a timely manner, then such information may become useless and damage may occur. Accordingly controls must ensure that information reaches the decision makers when they need it so that a meaningful response can follow.
Flexibility
The business and economic environment is highly dynamic in nature. Technological changes occur very fast. A rigid control system would not be suitable for a changing environment. These changes highlight the need for flexibility in planning as well as in control.
Strategic planning must allow for adjustments for unanticipated threats and opportunities. Similarly, managers must make modifications in controlling methods, techniques and systems as they become necessary. An effective control system is one that can be updated quickly as the need arises.
Acceptability
Controls should be such that all people who are affected by it are able to understand them fully and accept them. A control system that is difficult to understand can cause unnecessary mistakes and frustration and may be resented by workers.
Accordingly, employees must agree that such controls are necessary and appropriate and will not have any negative effects on their efforts to achieve their personal as well as organizational goals.
Integration
When the controls are consistent with corporate values and culture, they work in harmony with organizational policies and hence are easier to enforce. These controls become an integrated part of the organizational environment and thus become effective.
Economic Feasibility
The cost of a control system must be balanced against its benefits. The system must be economically feasible and reasonable to operate.
For example, a high security system to safeguard nuclear secrets may be justified but the same system to safeguard office supplies in a store would not be economically justified. Accordingly the benefits received must outweigh the cost of implementing a control system.
Strategic Placement
Effective controls should be placed and emphasized at such critical and strategic control points where failures cannot be tolerated and where time and money costs of failures are greatest.
The objective is to apply controls to the essential aspect of a business where a deviation from the expected standards will do the greatest harm. These control areas include production, sales, finance and customer service.
Corrective Action
An effective control system not only checks for and identifies deviation but also is programmed to suggest solutions to correct such a deviation. For example, a computer keeping a record of inventories can be programmed to establish if-then‖ guidelines.
For example, if inventory of a particular item drops below five percent of maximum inventory at hand, then the computer will signal for replenishment for such items.
Emphasis on Exception
A good system of control should work on the exception principle, so that only important deviations are brought to the attention of management, In other words, management does not have to bother with activities that are running smoothly.
This will ensure that managerial attention is directed towards error and not towards conformity. This would eliminate unnecessary and uneconomic supervision, marginally beneficial reporting and a waste of managerial time.
What is the process of controlling?
The following is the steps of process of controlling:
1. Establishment of Standards
2. Measurement of Performance
3. Appraisal of Performance
4. Finding out Deviations
5. Correction of Deviations.
What is the qualities of good controlling system?
The following are the qualities of good controlling system:
1. Accuracy
2. Timeliness
3. Flexibility
4. Acceptability
5. Integration
6. Economic Feasibility
7. Strategic Placement
8. Corrective Action
9. Emphasis on Exception.