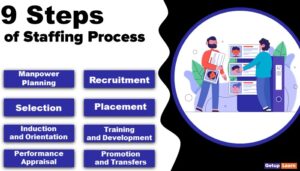
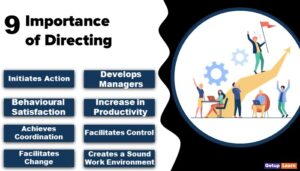
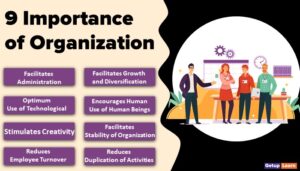
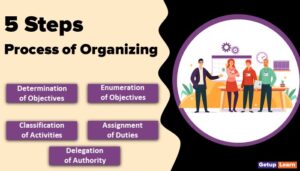
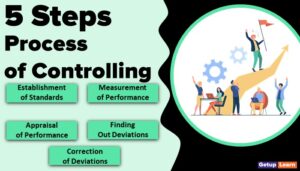
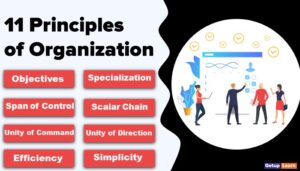
There are a number of ways available to complete a certain job. Planning chooses any one of the best alternatives out of the available ones. Economy and certainty are considered while selecting the best alternative. Thus, the nature of planning is briefly discussed below.
Table of Contents
-
1 Nature of Planning
- 1.1 Primary of Planning
- 1.2 Planning Contributes to Objectives
- 1.3 Planning an Intellectual Activity
- 1.4 Planning Results in Higher Efficiency
- 1.5 Planning is a Continuous Process
- 1.6 Planning is Flexible
- 1.7 Unity and Consistency
- 1.8 Planning is Common to All
- 1.9 Basis for All Managerial Functions
- 1.10 Getting Coordination
- 1.11 Considering Limiting Factors
- 2 FAQ Related to the Nature of Planning
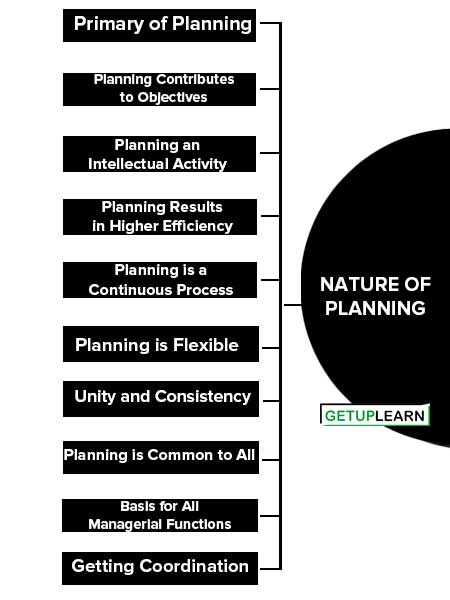
Nature of Planning
These are the nature of planning explained below:
- Primary of Planning
- Planning Contributes to Objectives
- Planning an Intellectual Activity
- Planning Results in Higher Efficiency
- Planning is a Continuous Process
- Planning is Flexible
- Unity and Consistency
- Planning is Common to All
- Basis for All Managerial Functions
- Getting Coordination
- Considering Limiting Factors
Primary of Planning
The functions of management include planning, organising, staffing, directing and controlling. Eminent writers may add other new ones to these functions or those which have not been included in these functions. Anyway, writers unanimously accept that planning is the primary function of all the other functions. The reason is that the manager wants to achieve the pre-determined objectives in a better way.
Planning Contributes to Objectives
There is a close connection between objectives and planning. Planning is based on objectives. If there is no link between planning and objectives, the former will only be a mental exercise and of no use. Planning contributes to the attainment of objectives.
Planning an Intellectual Activity
Planning includes the selection of the best alternative available and thinking before selecting of the best alternative. It involves the ability to foresee mishaps in future which might affect the smooth functioning of an organisation. So, planning is an intellectual activity.
Planning Results in Higher Efficiency
Planning efficiency is measured in terms of input and output ratios. Planning leads to maximum output with minimum expenditure.
This input and output relationship is not only determined by money, labour hours and production units but also by the degree of satisfaction available to the individual as well as the group. The high degree of human satisfaction motivates the workers to produce more within the specified time.
Planning is a Continuous Process
Planning, does not come to an end with the establishment of a business concern. Planning in other functions is also required. After the establishment of a business concern, certain decisions are taken. Planning is necessary to implement the decisions.
A number of decisions are taken during the lifetime of the business concern. So, planning is necessary throughout the running of the business concern as a continuous process.
Planning is Flexible
As already pointed out, while planning, any one of the available alternatives is selected. Planning selects the best alternative based on certain assumptions. If the assumptions are proved wrong, the selected alternative tends to be an incorrect one.
There is a possibility of a dead log in the functions of the management. Planning has one more alternative to suit future situations.
Unity and Consistency
Every department manager resort to planning at different times. The planning is related to the achievement of objectives. In other words, the managerial actions of different managers are unified in order to achieve the objectives. Policies and procedures of the organisation provide a basis for the consistency of executive behaviour and action in matters of planning.
Planning is Common to All
Planning work is done by every person who is working in a business unit. He may be a managing director or a foreman. Being of a higher place, the planning for a managing director is to frame the policies and procedures to be adopted. Being at a lower place, planning for a foreman is to allocate the work to his subordinates. So, planning is common to all.
Basis for All Managerial Functions
Planning is found at all levels of management. Top management looks after strategic planning. Middle management looks after administrative planning and lower-level management looks after operational planning.
Getting Coordination
Planning coordinates with various business activities. Without planning, nothing can be coordinated.
Considering Limiting Factors
Every plan is formulated after considering the limiting factors. The limiting factors may be money, skilled labour, quality materials, plant and machinery.
What is the nature of planning?
The following is the nature of planning:
1. Primary Planning
2. Planning Contributes to Objectives
3. Planning an Intellectual Activity
4. Planning Results in Higher Efficiency
5. Planning is a Continuous Process
6. Planning is Flexible
7. Unity and Consistency
8. Planning is Common to All
9. Basis for All Managerial Functions
10. Getting Coordination
11. Considering Limiting Factors.