Table of Contents
- 1 What is Scientific Management?
- 2 Definition of Scientific Management
- 3 Objectives of Scientific Management
- 4 Features of Scientific Management
- 5 Principles of Scientific Management
- 6 Techniques of Scientific Management
- 7 Advantages of Scientific Management
- 8 Criticism of Scientific Management
-
9 FAQ Related to Scientific Management
- 9.1 What is the meaning of scientific management?
- 9.2 What is the definition of scientific management?
- 9.3 What are objectives of scientific management?
- 9.4 What are features of scientific management?
- 9.5 What are principles of scientific management?
- 9.6 What are techniques of scientific management?
- 9.7 What are advantages of scientific management?
What is Scientific Management?
Scientific Management is the substitution of exact scientific investigations and knowledge for the old individual judgment or opinion in all matters relating to the work done in the shop.
The scientific management theory basically encompasses the work performed on the production floor as these tasks are quite different from the other tasks performed within the organization.
Such as, these are repetitive in nature, and the individual workers performing their daily activities are divided into a large number of cyclical repetitions of the same or closely related activities.
Definition of Scientific Management
These are the same two simple definitions of scientific management by authors:
[su_quote cite=”Peter F..Drucker“]The core of scientific management is the organized study of work and the analysis of work into its simplest elements and the systematic improvement of the worker’s performance of each element.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”F.W. Taylorr“]Scientific Management is the substitution of exact scientific investigations and knowledge for the old individual judgment or opinion in all matters relating to the work done in the shop.[/su_quote]
Objectives of Scientific Management
These are some important objectives of scientific management:
- To achieve higher production and acceleration in the rate of productivity by the use of standardized tools, equipment and methods.
- Betterment in the quality of the products by research, quality control, and effective inspection.
- Decrease in the cost of production by systematic planning, regulation, and cost control techniques.
- Avoidance of wastage in the use of resources, time, and method of production.
- Placement of the right person on the right job through scientific selection and training.
- Setting up a sound system of wage payment so as to attain maximum efficiency.
- Ensuring a regular supply of goods to the consumers at reasonable prices.
Features of Scientific Management
Let’s discussed the features of scientific management down below:
- Systematic Approach
- Discard of Traditional Change
- Improves Efficiency of Workers
- Useful for Large Organisations
- Attempts to Minimize Wastes
- Change in the Attitude
- Give Weightage to Specialization
Systematic Approach
Scientific management is a systematic approach to management and its use ensures that all activities are completed in a systematic and scientific manner.
Discard of Traditional Change
The approach of scientific management completely discards traditional management. It calls for the discarding of old techniques and the adoption of new and modern techniques, with the aim of improving the efficiency of employees.
Improves Efficiency of Workers
The main aim of scientific management is to increase the efficiency of the workers. This is done through conducting various kinds of studies such as Time Studies, Fatigue studies, and Motion Studies.
Useful for Large Organisations
Since the Scientific Management System is quite expensive to implement, it is useful only for large organizations. Small organizations cannot afford this system hence it involves a costly affair.
Attempts to Minimize Wastes
Scientific management aims at minimizing the waste of time, materials, machines, etc. This is indeed very essential to achieve a higher level of performance and an easier and quicker way to achieve goals.
Change in the Attitude
It involves a complete change in the mental attitude of workers as well as the management.
Give Weightage to Specialization
Scientific management involves dividing each work into various small parts, each part is allotted to the person who is an expert in it. This results in better and more work being performed in much less time.
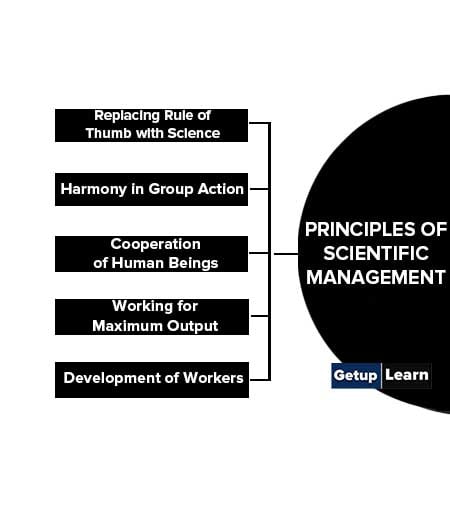
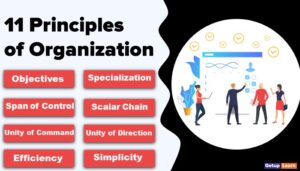
Principles of Scientific Management
The following are the principles of Scientific Management developed by Taylor on the basis of his experiments:
- Replacing Rule of Thumb with Science
- Harmony in Group Action
- Cooperation of Human Beings
- Working for Maximum Output
- Development of Workers
Replacing Rule of Thumb with Science
Taylor emphasized the use of organized knowledge in scientific management and wanted it to replace the rule of thumb. Scientific methods denote precision, while the rule of thumb emphasizes intuition and experience to determine the work methods and tools.
The basic cores of scientific management are fair work, standardization of work, etc. It is essential that these are measured properly and not based on estimates. This concept can be applied to all aspects of management.
Harmony in Group Action
Harmony in a group activity is one of the most important principles of scientific management where Taylor emphasized that there should be harmony in group action rather than discord. This would help in proper understanding and maximum contribution on the part of the group.
Cooperation of Human Beings
Scientific management stresses the cooperation of human beings rather than chaotic individualism. It is based on mutual confidence, utmost good faith, cooperation, and goodwill.
Mutual understanding and positive thinking would develop good cooperation between workers and management. He suggested the substitution of peace for war and the replacement of suspicion with mutual confidence and cooperation.
Working for Maximum Output
Taylor was against inefficiency and deliberate curtailment of production. He always emphasized the continuous increase in productivity instead of restricted production either by workers or management.
He pointed out that both management and workers could gain from it. Management could secure higher profits and workers could expect higher wages.
Development of Workers
Another principle of Scientific management is developing all workers to the fullest extent possible for their own and their enterprise’s highest prosperity.
This involves scientific selection and training of the workers, which would improve productivity and help a worker to adapt himself according to changing situations.
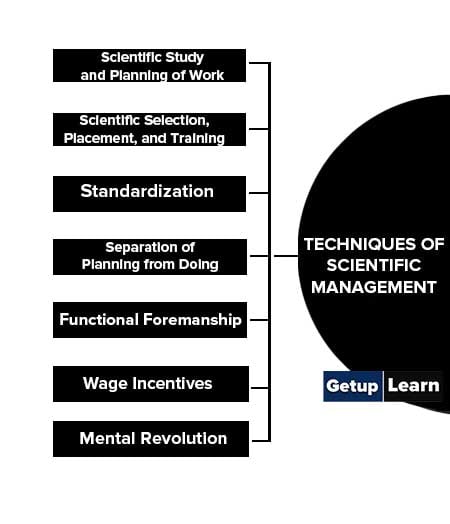
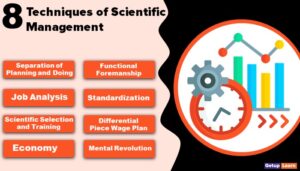
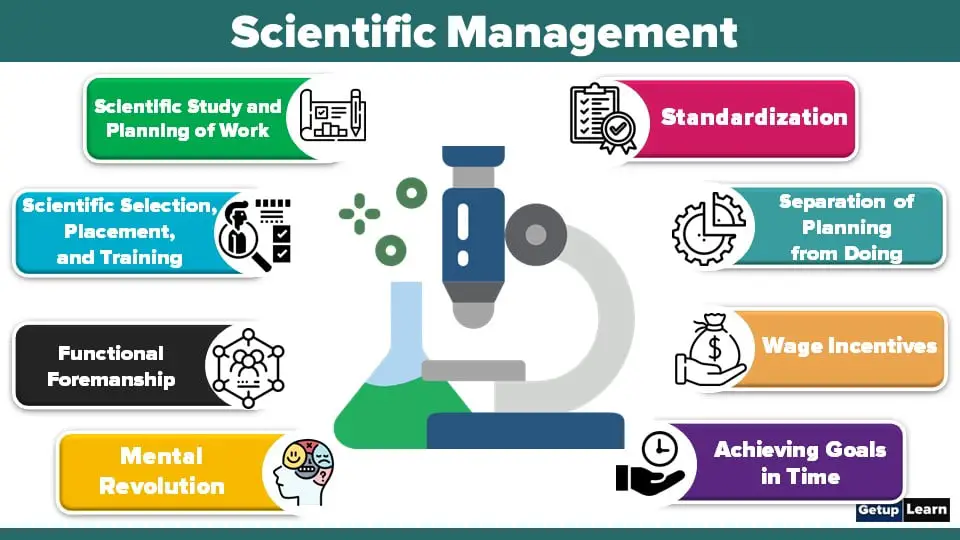
Techniques of Scientific Management
Based on his experience on the shop floor Taylor has suggested the following techniques of scientific management:
- Scientific Study and Planning of Work
- Scientific Selection, Placement, and Training
- Standardization
- Separation of Planning from Doing
- Functional Foremanship
- Wage Incentives
- Mental Revolution
Scientific Study and Planning of Work
The management should study each element of work scientifically and decide the daily standard output for each worker. For this purpose time and motion, the study should be conducted. Time study will help to determine the standard time required to do a job.
Motion study will help to remove unnecessary movements of workers in doing the job. With the help of this technique, the management can give a precise idea to the workers on what is to be done and how it can be done efficiently.
Scientific Selection, Placement, and Training
The workers should be selected by using scientific methods and not relying on the intuition and judgment of the foreman. They should be placed on the right job by matching job requirements with their capacity and attitude.
Further, they should be trained on a regular basis to do the task in the best manner and give maximum output at minimum cost.
Standardization
Taylor advocated the importance of standardization of tools, equipment, raw materials, quality of work, and physical working conditions.
Separation of Planning from Doing
The planning function should be separated from the doing function to secure the benefits of division of work and specialization. Planning of work should be the responsibility of management.
The management should plan, organize and direct the work whereas the workers should implement the plans.
Functional Foremanship
Taylor was the first to introduce and practice the concept of functional foremanship. According to Taylor, instead of having one foreman, there should be four Supervisors in the shop room namely, the gang boss, the speed boss, the repair boss, and the inspector.
In the planning office, there should be four specialists namely the time and cost clerk, the instruction card clerk, the order of work and route clerk, and the shop disciplinarian. Under functional foremanship, each worker should receive orders directly from these eight different supervisors dealing with different aspects of his job.
Wage Incentives
Taylor suggested paying workers according to their efficiency. Workers producing more should be given higher wages. He devised a differential price rate plan which implies different rates of wages for different levels of efficiency of workers.
The efficient worker should get more wages than the average worker. The introduction of a wage incentive scheme will reward the efficient worker and punish the inefficient worker.
Mental Revolution
For getting the desired results of scientific management Taylor emphasized the need for a mental revolution i.e. a fundamental change of outlook on the part of both employer and employees. The workers should change their attitude, outlook, and behavior as to their duties, their work, their fellowmen, and their employer.
At the same time, the management should change its attitude, outlook, and behavior toward the workers and their problems. Instead of having a hostile attitude and engaging in continuous conflict, management and workers should cooperate with each other and work for their mutual benefit.
They should give up the perception that any gain by one is at the expense of another. Their relationship should be cordial, cooperative, and positive. There should be no hostility, distrust, or suspicion between them.
Advantages of Scientific Management
These are the following advantages of scientific management of an organization:
- Reduction in Cost of Production
- Better Quality Product
- Division of Labour
- Increased Wages
- Right Method of Selection & Training of Workers
- Provision for Better Working Environment
- Better Utilization of Resources
Reduction in Cost of Production
It increases production with the help of mechanization and the latest technology used in producing the goods. On account of large-scale production, the per unit cost of production is considerably reduced.
Better Quality Product
By resorting to measures of standardization and effective supervision, better quality products are ensured.
Division of Labour
The principle of specialization adopted under scientific management ensures the benefits derived from the division of labor. The work is simplified and is carried out in the most economical and efficient manner.
Avoidance of Disputes between Labour & Management
Scientific management is instrumental in developing healthy cooperation between the management and the labor thereby encouraging cordial and harmonious relations between the two.
Increased Wages
Scientific management aims at higher productivity and the workers get increased wages. Taylor suggested a differential incentive plan for increased wages to efficient workers. The higher wages are helpful in increasing the standard of living of the workers.
Right Method of Selection & Training of Workers
Taylor advocated the standardization of tools and couplings, a cost system, and several other items. Efforts should be made to provide a standardized working environment and methods of production to the workers.
Standardization would help to reduce spoilage and wastage of materials, improve the quality of work, reduce the cost of production and reduce fatigue among the workers.
Provision for Better Working Environment
Scientific management provides a proper atmosphere of work to the workers. Proper working hours followed by rest pauses, adequate lighting, ventilation, ensuring proper safety, provision of many other amenities, etc. are ensured to workers.
Better Utilization of Resources
Scientific management techniques ensure optimum utilization of available resources viz., materials, machines, equipment, money, workers, etc. It removes waste and inefficiency of every kind.
Criticism of Scientific Management
Taylor’s philosophy of scientific management was criticized on the following grounds:
- Taylor treated workers just as a factor of production. He neglected the social and psychological needs of workers. Thus, he ignored the ‘human’ element.
- Taylor concentrated on improving productivity on the shop floor. His philosophy is confined to operative personnel only. It is not concerned with the overall organization and improving its effectiveness.
- Functional foremanship would result in specialization and create confusion in the minds of workers.
- Adoption of principles of scientific management may result in the exploitation of workers. Hence, it may be opposed by workers and their unions.
- Scientific management is anti-democratic. It does not seek the participation of workers in the decision-making process.
What is the meaning of scientific management?
Scientific Management is the substitution of exact scientific investigations and knowledge for the old individual judgment or opinion in all matters relating to the work done in the shop. By F.W. Taylorr
What is the definition of scientific management?
Scientific Management is the substitution of exact scientific investigations and knowledge for the old individual judgment or opinion in all matters relating to the work done in the shop. By Peter F..Drucker
What are objectives of scientific management?
Following are the objectives of scientific management:
To achieve higher production and acceleration in the rate of productivity by the use of standardized tools, equipment and methods.
1. Betterment in the quality of the products by research, quality control, and effective inspection.
2. Decrease in the cost of production by systematic planning, regulation, and cost control techniques.
3. Avoidance of wastage in the use of resources, time, and method of production.
4. Placement of the right person on the right job through scientific selection and training.
5. Setting up a sound system of wage payment so as to attain maximum efficiency.
6. Ensuring a regular supply of goods to consumers at reasonable prices.
What are features of scientific management?
The following are the features of scientific management:
1. Systematic Approach
2. Discard of Traditional Change
3. Improves Efficiency of Workers
4. Useful for Large Organisations
5. Attempts to Minimize Wastes
6. Change in the Attitude
7. Give Weightage to Specialization.
What are principles of scientific management?
The following are the principles of scientific management:
1. Replacing Rule of Thumb with Science
2. Harmony in Group Action
3. Cooperation of Human Beings
4. Working for Maximum Output
5. Development of Workers
What are techniques of scientific management?
The following are techniques of scientific management:
1. Scientific Study and Planning of Work
2. Scientific Selection, Placement, and Training
3. Standardization
4. Separation of Planning from Doing
5. Functional Foremanship
6. Wage Incentives
7. Mental Revolution.
What are advantages of scientific management?
The following are the advantages of scientific management:
1. Reduction in Cost of Production
2. Better Quality Product
3. Division of Labour
4. Increased Wages
5. Right Method of Selection & Training of Workers
6. Provision for Better Working Environment
7. Better Utilization of Resources.