The advocates of this school perceive management as a process involving certain functions such as planning, organizing, directing and controlling. That’s why it is called a ‘functional approach’ or ‘management process’ approach.
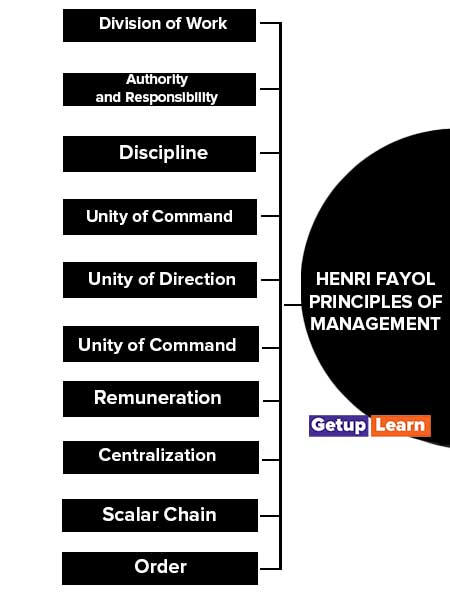
Fayol’s contributions were first published in book form titled ‘Administration Industrielle at General in the French Language, in 1916. He defined management in terms of certain functions and then laid down fourteen principles of management which according to him have universal applicability.
Thus, he was a pioneer in the field of management education. In brief, Fayol’s views on management command acceptability even today because they are much in tune with the requirements of management in the present-day world.
Table of Contents
-
1 Administrative Approach to Management
- 1.1 Division of Work
- 1.2 Authority and Responsibility
- 1.3 Discipline
- 1.4 Unity of Command
- 1.5 Unity of Direction
- 1.6 Subordination of Individual Interest to General Interests
- 1.7 Remuneration
- 1.8 Centralisation
- 1.9 Scalar Chain
- 1.10 Order
- 1.11 Equity
- 1.12 Stability and Security
- 1.13 Initiative
- 1.14 Esprit De Corps
- 2 FAQ Related to Administrative Approach to Management
Administrative Approach to Management
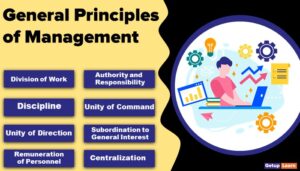
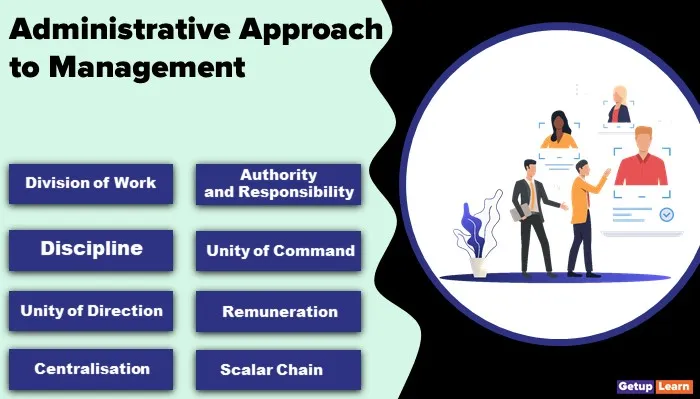
The 14 principles of administrative management outlined by Fayol in his book are as below:
- Division of Work
- Authority and Responsibility
- Discipline
- Unity of Command
- Unity of Direction
- Subordination of Individual Interest to General Interests
- Remuneration
- Centralisation
- Scalar Chain
- Order
- Equity
- Stability and Security
- Initiative
- Esprit De Corps
Division of Work
The division of work not only improves work efficiency, but also the effectiveness in production. During the industrialisation period, the increased demand for products led to increased complexity and job.
This necessitated the division of work into small activities in such a manner to get final outcome after synchronising all these activities. Each division of work can be assigned to a specialised person to get better performance. Thus, the strategy to handle the work became the principle to manage large operations.
Authority and responsibility should go hand in hand. Authority means the power of giving orders and exercising the power to mobilise resources. The person doing the job is usually held responsible for the outcome.
Therefore, Fayol advocated that the division of work needs to accompany the authority related to the job for effective decision-making in order to make the person accountable for the job, the authority given and the outcome.
Discipline
To implement planning effectively, discipline in an organisation must be maintained. The division of work leads to the decentralisation of the work centre leading to many points of decision-making.
The authority delegation also requires strong discipline in order to avoid the utilisation of authority in an unfair manner. Hence, strong discipline facilitates the route of effective implementation of organisational policies.
Unity of Command
It means that every employee of the organisation must get command from one superior. In the case of multidiscipline departments, the unity of command is essential to avoid any conflict of interest.
Unity of Direction
There should be unity in the direction of related or similar nature jobs. The leadership and communication system should be supportive and cooperative. The instructions, guidelines and manuals should be linked to each other to avoid conflict between organisational and departmental objectives.
Subordination of Individual Interest to General Interests
Every organisation must integrate individual interests with organisational interests. The individual interest should be given a subordinate position to the organisational interest.
Remuneration
Employees should be given fair wages for their performance and contribution to the organisation. The concept of incentives and bonuses must be part of remuneration in order to compensate employees for every additional effort. Every employee must be ensured some minimum remuneration to be paid in special cases.
Centralisation
The delegation of authority should be partially made to the lower management for operational activities only. The centralisation of power is inevitable for effective control and discipline in an organisation.
Scalar Chain
There should be a scalar chain for communication. The policy, instruction, orders, rules etc. should flow from top to bottom. At the same time, feedback, performance and grievance must go to the top in order to sound policy formulation.
Order
There should be a place for everything and everything should be in its place. This means the sequence must be followed in true spirit. Every activity should have a hierarchical position in relation to others. There should be an order of activities.
Equity
There should be equal treatment for everyone irrespective of hierarchy. Equity advocates justice, fair treatment and kindness to human beings. The superior should be fair enough in making justice with kindness while performing in the organisation.
Stability and Security
There should be the stability of employees in the organisation. The attrition rate must be kept low by giving reasonable job security to the employees. It will add to the organisation’s development.
Initiative
Managers must encourage and motivate their subordinates to innovate and initiate new idea development by giving them freedom of expression. This requires empowering employees to go beyond some boundaries to get something new.
Esprit De Corps
This principle is based on the concept ‘Union is having strength’. The union does not mean groups or labour unionism, but developing team spirit. The team can achieve performance beyond the sum of individual ones.
What are the administrative approaches?
The following are the administrative approaches to management:
1. Division of Work
2. Authority and Responsibility
3. Discipline
4. Unity of Command
5. Unity of Direction
6. Subordination of Individual Interest to General Interests
7. Remuneration
8. Centralisation
9. Scalar Chain
10. Order
11. Equity
12. Stability and Security
13. Initiative
14. Esprit De Corps.
What is fayol’s administrative approach?
This approach is associated with the work of Henri Fayol, who proposed that management should be based on five functions: planning, organizing, commanding, coordinating, and controlling. He also proposed 14 principles of management, which are still widely used today, including the principle of scalar chain, which states that there should be a clear chain of command within the organization, and the principle of unity of command, which states that each employee should have only one direct supervisor.