Table of Contents
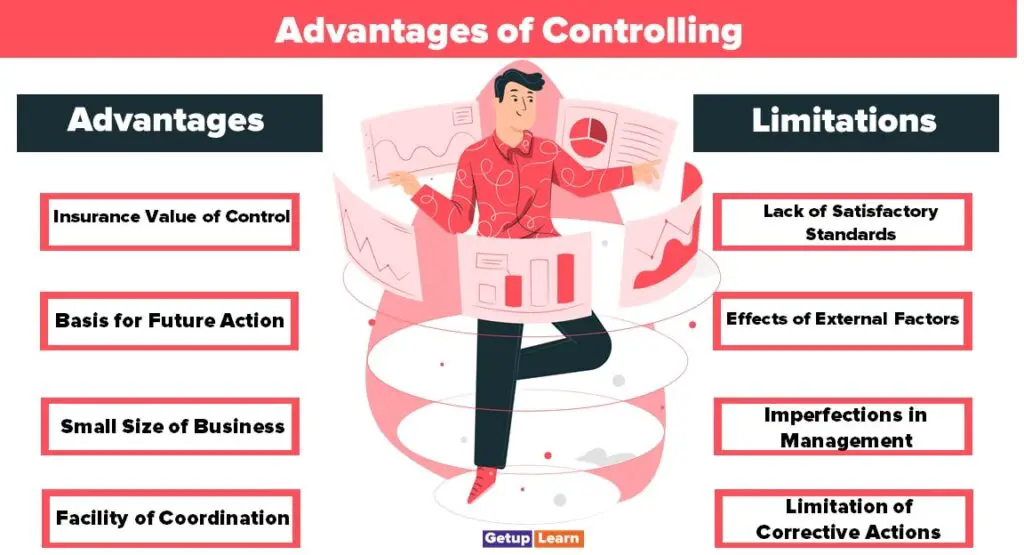
Advantages of Controlling
Controlling is an essential aspect of a Manager’s function. These are the important advantages of controlling:
- Insurance Value of Control
- Basis for Future Action
- Small Size of Business
- Indicator for Managerial Weakness
- Facility of Coordination
- Simplifies Supervision
- Extension of Decentralisation
Insurance Value of Control
Control eliminates the risk of non-conformity of actual performance with the main goals of the organisation. Control is the function which regulates the operation to ensure the attainment of the set objectives.
Regular measurement of work in progress with proper adjustments in operations puts the performance on the right track and helps in the attainment of goals.
Basis for Future Action
Control provides the information and facts to the management for planning and organising when the work is completed and the result is evaluated. In fact, evaluation of results helps the management to re-plan for non-repetitive operations and reward, punish and discipline the workers.
It would be better to say that long-term planning for the future is not possible unless and until control information is available in time to the managers for the operation of the work.
Small Size of Business
A small business can operate its activities smoothly and efficiently with a few workers. But for a large-scale business in modern times, it is quite impossible to work without proper policies, procedures and quality of different varieties of goods.
That is why in a large organisation there is always a need for a scientific system of control to solve day-to-day problems.
Indicator for Managerial Weakness
Control plays the role of an indicator and keeps an eye on the functions of managers for the attainment of goals. In the organisation there will be certain unforeseen and unknown problems which cannot be traced out by mere planning, organising and staffing efforts.
It is the control process that can trace these out. That is why it is known as an indicator of managerial weakness. Control not only finds out the weakness of managers but also provides solutions and remedial action to solve the problems.
Facility of Coordination
Control plays a very important role in Co-coordinating business activities and workers. It blinds all the workers and other activities and motivates them to move towards the common objectives through coordination.
Control will play the role of a middleman between the workers and management to provide the required information in time to the workers. Further, if proper coordination through control exists in the organisation then wastage of time, effort and money can easily be eliminated.
Simplifies Supervision
The systematic system of control helps in finding out the deviation existing in the organisation which also simplifies the task of the supervisor in managing his subordinates. So through control, it becomes simpler for the supervisor to supervise and guide the workers to follow the right track and fulfil the required goals.
Extension of Decentralisation
A Control system helps the top management to extend the frontiers of decentralisation without the loss of control. When proper procedures, policies, methods, targets etc, are clearly communicated to the sub-ordinates, they develop self-confidence and need not always refer to their supervisors with problems.
Thus senior management people will not waste their time on such problems and would rather utilise their time and energy for further planning and organisational work.
Limitations of Controlling
Let’s discuss the limitations of controlling in management explained below:
- Lack of Satisfactory Standards
- Effects of External Factors
- Imperfections in Management
- Problem in Setting of Individual Responsibilities
- Limitation of Corrective Actions
- More Expansive Device
- Human Reactions to Control
Lack of Satisfactory Standards
It is quite difficult to fix satisfactory standards for many activities, particularly those which involve intangible performances such as results of management, development, human relations and public relations.
The cost of other activities cannot be accurately indicated by any pre-set standards. Activities of the workers for service of advisory nature and other activities relating to the behaviour of the workers do not indicate quantitative output and identify their level of attainment. Therefore controlling becomes difficult.
Effects of External Factors
Internal factors could be checked and put in the right perspective in time, by the proper system of control, but it is impossible to check and control external factors.
For example, changes in the Government and its policy, new inventions or discoveries, changes in the fashions and liking of the consumers etc., cannot be checked by the system of control.
Imperfections in Management
As explained above, intangible performance always brings difficulties at the time of setting standards. This is also responsible for making the task complicated for the measurement of results or evaluations.
If one fails to measure the performance in quantitative and qualitative terms, the results of behavioural and staff activities have to be evaluated by line managers on their own thinking and managerial judgement. Further economic consideration is not possible if we measure everything and everybody’s work.
Problem in Setting of Individual Responsibilities
Assignment of individual responsibilities for negative deviation from the standard is difficult. This washout the system of control completely. In some cases, it is difficult to assign the responsibility of negative deviation to an individual.
The effective impact of control in most cases depends on how responsible the workers one has in the organisation.
Limitation of Corrective Actions
It is true that if all deviations and errors could be corrected in time, the chances of loss would be relatively less in the organisation. To some extent, it is true that there are certain organisations which have taken corrective and quick actions and were successful in avoiding errors.
But often problems arise when management does not take corrective action in time to avoid deviations.
More Expansive Device
Making the control more systematic and effective requires careful and timely investigation of different business activities. It enables the unit to find out the causes of variations with the actual provisions made in the budgets.
In order to investigate all the activities one has to appoint more skilled people, which requires more money to reward the workers for their work. It, therefore, becomes a costly affair in terms of money and time.
Human Reactions to Control
Control creates tension in the minds of workers and their actions and thinking is affected. The pressure of work gives negative results and reduces the quantity and quality of work. false reports about the performance too.
The worker ignores long-term goals and gives If the system of control is introduced in the organisation in detail, close check of individual performance exists, then it produces adverse results among lower-level managers.
What are the advantages of controlling?
The following are the advantages of controlling:
1. Insurance Value of Control
2. Basis for Future Action
3. Small Size of Business
4. Indicator for Managerial Weakness
5. Facility of Coordination
6. Simplifies Supervision
7. Extension of Decentralisation.
What are the limitations of controlling?
The following are the limitations of controlling:
1. Lack of Satisfactory Standards
2. Effects of External Factors
3. Imperfections in Management
4. Problem in Setting of Individual Responsibilities
5. Limitation of Corrective Actions
6. More Expansive Device
7. Human Reactions to Control.