Table of Contents
What is Central Bank?
The central bank of any country is the apex institution of its monetary system as well as the financial system because the monetary system is the major constituent of the country’s financial system.
As the apex body, the central bank organizes runs, supervises, regulates, and develops the monetary system and thus the financial system of the country. Formulating and implementing the monetary policy are the main responsibilities of the central bank.
Central banks, in general, are very old institutions. For instance, The Bank of England was set up in 1694, and the Bank of France is more than 200 years old. As for the Federal Reserve Bank, it was set up in 1913. Coming to RBI it was set up in 1935.
It though may appear young due to its late inception when compared to the developed world, but as Governor Dr. Bimal Jalan said though it may appear like a ‘toddler or at most a young adult’, it is one of the oldest central banks in the developing world.
The central bank of India was established on April 1, 1935, under the Reserve Bank of India Act. It was entrusted with the responsibility to create financial stability in India and is charged with regulating the country’s currency and credit systems. RBI uses monetary policy as a major tool to discharge its fundamental responsibilities stated above.
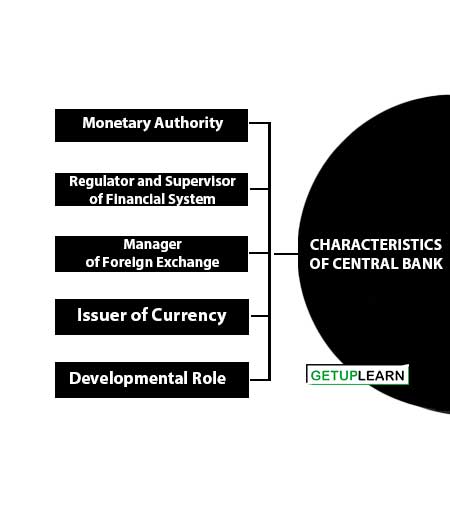
Characteristics of Central Bank
The main characteristics of central bank are:
- Monetary Authority
- Regulator and Supervisor of Financial System
- Manager of Foreign Exchange
- Issuer of Currency
- Developmental Role
RBI formulates implements and monitors the monetary policy. The objective of formulating monetary policy is to maintain price stability and ensure an adequate flow of credit to productive sectors as well as an adequate money supply in the economy.
Regulator and Supervisor of Financial System
RBI prescribes broad parameters of banking operations within which the country’s banking and financial system functions.
The objective of formulating common rules and regulations for the overall banking industry is to maintain public confidence in the system, protect depositors’ interests and provide cost-effective banking services to the public.
Manager of Foreign Exchange
Adequate foreign exchange reserves and efficient foreign exchange rates establish sound creditability status in the globalized world. RBI is responsible for managing foreign exchange reserves and their conversion rates.
This management of reserves is regulated under the Foreign Exchange Management Act, of 1999. The objective is to facilitate external trade, and payment and promote orderly development and maintenance of the foreign exchange market in India.
Issuer of Currency
RBI is having the sole responsibility of issuing currency. Besides Issues only, it also exchanges or destroys currency and coins not fit for circulation. The objective is to give the public an adequate quantity of supplies of currency notes and coins of good quality.
Developmental Role
RBI performs a wide range of promotional functions to support national objectives. For this Reserve Bank has helped in the setting up of various institutions such as the Industrial Financial Corporation of India (IFCI) and the State Financial Corporations (SFC); the Unit Trust of India (UTI) in 1964, the Industrial Development Bank of India (IDBI) also in 1964, the Agricultural Refinance Corporation of India in 1963, NABARD in 1982 and the Industrial Reconstruction Corporation of India in 1972.
These institutions were set up by the Reserve Bank directly or indirectly to promote saving habits among individuals and mobilize these savings to provide industrial finance as well as agricultural finance. The basic objective is to equal the development of all sectors of an economy.
Methods of Credit Control
The Central Bank controls credit through monetary policy. Credit is expanded or contracted as per the need by the Reserve Bank. It is called credit control. For this purpose, the R.B.I. uses different methods of monetary policy.
After independence, the RBI used the controlled expansion policy so that economic expansion and stabilization could be achieved. The R.B.I. uses different methods to control credit. These are the methods of credit control:
Quantitative Credit Control
The Quantitative Instruments are also known as the General Tools of monetary policy. These tools are related to the Quantity or Volume of the money.
They are designed to regulate or control the total volume of bank credit in the economy while Qualitative instruments regulate and provide credit to selected borrowers for a selected purpose, depending upon the use to which the control tries to regulate the quality of credit – the direction towards the credit flows.
Bank Rate Policy (BRP)
The Bank Rate Policy (BRP) is a very important tool for controlling the volume or the quantity of credit in a country. The bank rate refers to the rate at which the central bank (i.e. RBI) is preparing to discount bills. It is the standard rate prescribed by RBI at which the bank is prepared to buy or rediscount bills of exchange or other commercial paper.
A change in the bank rate will necessarily bring out a resultant change in the cost of credit available to commercial banks. If the RBI increases the bank rate then the cost of credit will increase and thus the volume of commercial banks borrowing has been reduced from the RBI.
On the other hand, if the RBI reduces the bank rate, the cost of credit will be easy and cheaper. This will increase the credit creation in the economy. Thus bringing the change in bank rate will affect the availability of credit in the economy.
Open Market Operation (OMO)
The open market operation refers to the purchase and/or sale of short-term and long-term of Government securities by the Central Bank in the open market. If the RBI sells securities in an open market, institutions or individuals will buy these securities which reduces the cash reserves with the banking system and credit created by it.
Contrary to this when the RBI buys securities from commercial banks in the open market. The cheques issued by the central bank to the sellers are deposited with the central banks. It increases the cash reserves with the banking system which will further increase the credit creation capacity of commercial banks.
Variation in the Reserve Ratios (VRR)
Commercial Banks have to keep a certain percentage of their total deposits in the form of Cash Reserves. Some parts of these cash reserves have to be kept in the form of cash with themselves, known as Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR).
Apart from these, some part of cash reserves has to be kept with the RBI for the purpose of maintaining liquidity and controlling credit in an economy, known as the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR). Any change in any of the above will affect the lending capacity of commercial banks.
RBI increases these reserves during inflation to reduce credit creation in the economy. But during a period of recession or depression, it lowers these reserves by making more cash reserves available to commercial banks for credit expansion.
Qualitative Instruments of Credit Control
The Qualitative Instruments are also known as the Selective Tools of monetary policy. These tools are not directed toward the quality of credit or the use of credit. These methods are meant to give the central bank the ability to affect particular segments of the economy on a selective basis.
They are used for discriminating between different uses of credit. The Selective Tools of credit control comprise of following instruments:
- Fixing Margin Requirements
- Consumer Credit Regulation
- Publicity
- Credit Rationing
- Moral Suasion
- Control Through Directives
- Direct Action
Fixing Margin Requirements
The margin requirement refers to the difference between the market value of the security and its maximum loan.
An increase in margin requirement will decrease the amount of loan and thus reduces the money supply in the economy. On the contrary decrease in margin requirement will increase the amount of loan and thus raises the money supply in the economy.
Consumer Credit Regulation
Under this method, consumer credit supply is regulated through hire-purchase and installment sale of consumer goods. Under this method, the down payment, installment amount, loan duration, etc is fixed in advance. This can help in checking credit use and then inflation in a country.
Publicity
This is yet another method of selective credit control. Through it, Central Bank (RBI) publishes various reports stating what is good and what is bad in the system.
This published information can help commercial banks to direct credit supply in the desired sectors. Through its weekly and monthly bulletins, the information is made public and banks can use it for attaining goals of monetary policy.
Credit Rationing
Under this method, the central Bank fixes a limit for the credit facilities available to commercial Banks. The available credit is rationed among the applicants according to the purpose of the credit.
This method controls even bill rediscounting. For certain purposes, the upper limit of credit can be fixed and banks are told to stick to this limit. This can help in lowering banks’ credit exposure to unwanted sectors.
Moral Suasion
Moral suasion is a general term for describing a variety of informal or nonlegal methods used by the central bank to persuade commercial banks to behave in a particular manner. It is simply pressure exerted by the RBI on the Indian banking system without any strict action for compliance with the rules.
Under moral suasion, central banks can issue directives, guidelines, and suggestions for commercial banks regarding reducing credit supply for speculative purposes.
Control Through Directives
Under this method, the central bank issue frequent directives to commercial banks. These directives guide commercial banks in framing their lending policy.
Through a directive, the central bank can influence credit structures, and supply of credit to certain limits for a specific purpose e.g. issuance of directives to commercial banks for not lending loans to speculative sectors such as securities, etc beyond a certain limit.
Direct Action
Under this method, the RBI can impose an action against a bank. If certain banks are not adhering to the RBI’s directives, the RBI may refuse to rediscount their bills and securities. Secondly, RBI may refuse credit supply to those banks whose borrowings are in excess of their capital.
A central bank can penalize a bank by changing some rates. At last, it can even put a ban on a particular bank if it does not follow its directives and work against the objectives of the monetary policy.
FAQs About the Central Bank
What are the characteristics of central bank?
The following are the characteristics of central bank:
1. Monetary Authority
2. Regulator and Supervisor of Financial System
3. Manager of Foreign Exchange
4. Issuer of Currency
5. Developmental Role.
What are the methods of credit control?
The two main methods of credit control:
1. Quantitative Credit Control
3. Qualitative Instruments of Credit Control.