Table of Contents
What are Financial Products?
Today, the importance of financial services is gaining momentum all over the world. In these days of complex finance, people expect a Financial Service Company to play a very dynamic role not only as a provider of finance but also as a departmental store of finance.
With the injection of the economic liberation policy into our economy and the opening of the economy to multinationals, the free market concept has assumed much significance. As a result, the clients both corporates and individuals are exposed to the phenomena of volatility and uncertainty and hence they expect the financial service company to innovate new products and services so as to meet their varied requirements.
As a result of innovations, new instruments, and new products are emerging in the capital market. The capital market and the money market are getting widened and deepened. Moreover, there has been a structural change in the international capital market with the emergence of new products and innovative techniques of operation in the capital market.
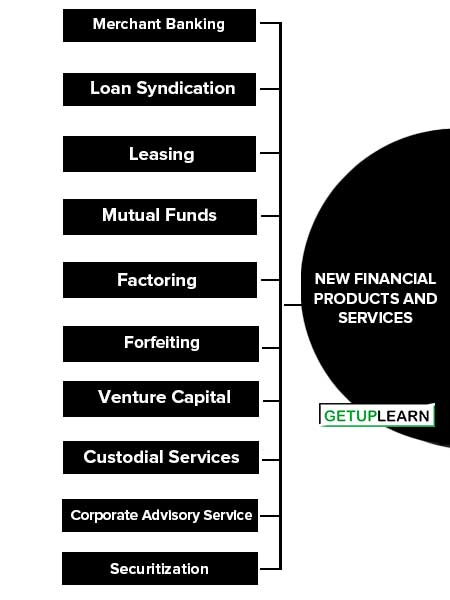
New Financial Products and Services
Many financial intermediaries including banks have already started expanding their activities in the financial services sector by offering a variety of new products. As a result, sophistication and innovations have appeared in the arena of financial intermediation. Some of the new financial products and services are discussed below:
- Merchant Banking
- Loan Syndication
- Leasing
- Mutual Funds
- Factoring
- Forfeiting
- Venture Capital
- Custodial Services
- Corporate Advisory Service
- Securitization
- Derivative Security
Merchant Banking
A merchant banker is a financial intermediary who helps to transfer capital from those who possess it to those who need it.
Merchant banking includes a wide range of activities such as management of customers’ securities, portfolio management, project counseling, and appraisal, underwriting of shares and debentures, loan syndication, acting as a banker for refund orders, handling interest and dividend warrants, etc.
Thus, a merchant banker renders a host of services to corporates and thus promotes industrial development in the country.
This is more or less similar to ‘consortium financing’. But, this work is taken up by the merchant banker as a lead manager. It refers to a loan arranged by a bank called lead manager for a borrower who is usually a large corporate customer or a Government Department.
The other banks who are willing to lend can participate in the loan by contributing an amount suitable to their own lending policies. Since a single bank cannot provide such a huge sum as a loan, a number of banks join together and form a syndicate. It also enables the members of the syndicate to share the credit risk associated with a particular loan among themselves.
Leasing
A lease is an agreement under which a company or a firm, acquires a right to make use of a capital asset like machinery, on payment of a prescribed fee called “rental charges”. The lessee cannot acquire any ownership of the asset, but he can use it and have full control over it. he is expected to pay for all maintenance charges and repairing and operating costs.
In countries like the U.S.A., the U.K., and Japan equipment leasing is very popular and nearly 25% of plant and equipment is being financed by leasing companies. In India also, many financial companies have started equipment leasing businesses. Commercial banks have also been permitted to carry on this business by forming subsidiary companies.
Mutual Funds
A mutual fund refers to a fund raised by a financial service company by pooling the savings of the public. It is invested in a diversified portfolio with a view to spreading and minimizing risk.
The fund provides 11: investment avenues for small investors who cannot participate in the equities of big companies. It ensures low risk, steady returns, high liquidity, and better capital appreciation in the long run.
Factoring
Factoring refers to the process of managing the sales ledger of a client by a financial service company. In other words, it is an arrangement under which a financial intermediary assumes credit risk in the collection of book debts for its clients. The entire responsibility of collecting the book debts passes on to the factor.
His services can be compared to a del credo agent who undertakes to collect debts. But, a factor provides credit information, collects debts, monitors the sales ledger, and provides finance against debts. Thus, he provides a number of services apart from financing.
Forfeiting
Forfeiting is a technique by which a forfeiture (financing agency) discounts an export bill and pays ready cash to the exporter who can concentrate on the export front without bothering about the collection of export bills.
The forfeiture does so without any recourse to the exporter and the exporter is protected against the risk of non-payment of debts by the importers.
Venture Capital
Venture capital is another method of financing in the form of equity participation. A venture capitalist finances a project based on the potentialities of a new innovative project. It is in contrast to the conventional “security-based financing”.
Much thrust is given to new ideas or technological innovations. Finance is being provided not only for ‘start-up capital’ but also for ‘development capital’ by the financial intermediary.
Custodial Services
It is another line of activity that has gained importance, of late. Under this, a financial intermediary mainly provides services to clients, particularly to foreign investors, for a prescribed fee. Custodial services provide agency services like safe keeping of shares and debentures, collection of interest and dividends, and reporting of matters on corporate developments and corporate securities to foreign investors.
Corporate Advisory Service
Financial intermediaries particularly banks have set up corporate advisory service branches to render services exclusively to their corporate customers.
For instance, some banks have extended computer terminals to their corporate customers to that they can transact some of their important banking transactions by sitting in their own offices. As new avenues of finance like Euro loans, GDRs, etc. are available to corporate customers, this service is of immense help to the customers.
Securitization
Securitization is a technique whereby a financial company converts its ill-liquid, non-negotiable, and high-value financial assets into securities of small value that are made tradable and transferable. A financial institution might have a lot of its assets blocked up in assets like real estate, machinery, etc. which are long-term in nature and which are non-negotiable.
In such cases, securitization would help the financial institution to raise cash against such assets by means of issuing securities of small value to the public. Like any other security, they can be traded in the market.
It is best suited to housing finance companies whose loans are always long-term in nature and whose money is locked up for a considerably long period in real estate. Securitization is the only answer to convert these ill-liquid assets into liquid assets.
Derivative Security
A derivative security is a security whose value depends upon the values of other basic variables backing the security. In most cases, these variables are nothing but the prices of traded securities. A derivative security is basically used as a risk management tool and it is resorted to cover the risk due to price fluctuations by the investments manager.
Just like a forward contract which is a derivative of a spot contract, a derivative security is derived from other trading securities backing it. Naturally, the value of derivative security depends upon the values of the backing securities.
Derivative helps to break the risks into various components such as credit risk, interest rates risk, exchange rates risk, and so on. It enables the various risk components to be identified precisely and priced and even traded if necessary. Financial intermediaries can go for derivatives since they will have greater importance in the near future. In India, some forms of derivatives are in operation.
FAQs About the New Financial Products and Services
What are the new financial products?
The following are the new financial products:
1. Merchant Banking
2. Loan Syndication
3. Leasing
4. Mutual Funds
5. Factoring
6. Forfeiting
7. Venture Capital
8. Custodial Services
9. Corporate Advisory Service
10. Securitization.