Table of Contents
What is Capitalization?
Capitalization is that which “comprises of a company’s own capital which includes capital stock and surplus in whatever form it may appear and borrowed capital which consists of bonds or similar evidence of long-term debt”.
The total amount of funds available for an undertaking is broadly divided into owned capital and borrowed capital. Both of these funds should be neither too much nor too low.
Over Capitalization
A concern is said to be over-capitalized if its earnings are not sufficient to justify a fair return on the amount of share capital and debentures that have been issued. It is said to be over-capitalized when the total of owned and borrowed capital exceeds its fixed and current assets i.e. when it shows accumulated losses on the assets side of the balance sheet.
[su_quote cite=”Gerstenberg”]”A corporation is over-capitalized when its earnings are not large enough to yield a fair return on the number of stocks and not large enough to yield a fair return on the number of stocks and bonds that have been issued or when the amount of securities outstanding exceeds the current value of assets”.[/su_quote]
Over-capitalization is not synonymous with excess capital. Excess of capital may be one of the reasons for over-capitalization. A company is over-capitalized only because its capital and funds are not being effectively and profitably deployed with the result that there is a fall in the earning capacity of the company and in the rate of dividend to be paid to its shareholders as well as a fall in the market value of its shares.
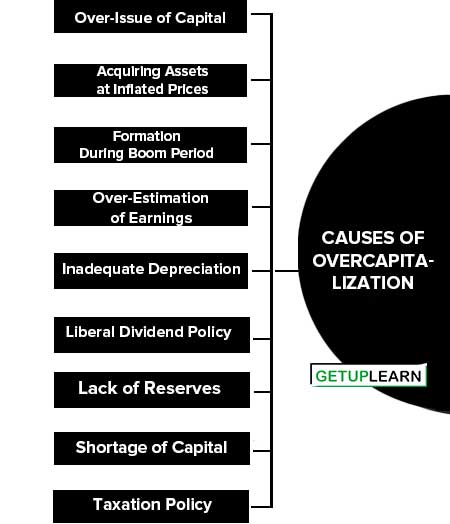
Causes of Overcapitalization
These are some of the important causes of overcapitalization are:
- Over-Issue of Capital
- Acquiring Assets at Inflated Prices
- Formation During Boom Period
- Over-Estimation of Earnings
- Inadequate Depreciation
- Liberal Dividend Policy
- Lack of Reserves
- Shortage of Capital
- Taxation Policy
Over-Issue of Capital
Defective financial planning may lead to excessive issues of shares or debentures. The issue would be superfluous and a constant burden on the earnings of the company.
Acquiring Assets at Inflated Prices
Assets may be acquired at inflated prices or at a time when the prices were at their peak. In both cases, the real value of the company is below its book value and the earnings are very low.
Formation During Boom Period
If the establishment of a new company or the expansion of an existing concern takes place during the boom period, it may be a victim of overcapitalization. The assets are acquired at fabulous prices.
But when boom conditions cease prices of products decline resulting in lower earnings. The original value of assets remains in books while earning capacity dwindles due to depression. Such a state of affairs results in overcapitalization.
Over-Estimation of Earnings
The promoters or the directors of the company may overestimate the earnings of the company and raise capital accordingly. If the company is not in a position to invest these funds profitably, the company will have more capital than required. Consequently, the rate of earnings per share will be less.
Inadequate Depreciation
The absence of a suitable depreciation policy would make the asset values superfluous. If the depreciation or replacement provision is not adequately made, the productive worth of the assets is diminished which will definitely depress the earnings. Lowered earnings bring about a fall in share values, which represents over-capitalization.
Liberal Dividend Policy
The company may follow a liberal dividend policy and may not retain sufficient funds for self-financing. It is not a prudent policy as it leads to over-capitalization in the long run, when the book value of the shares falls below their real value.
Lack of Reserves
Certain companies do not believe in making adequate provisions for various types of reserves and distribute the entire profit in the form of dividends. Such a policy reduces the real profit of the company and the book value of the shares lags much behind its real value. It represents over-capitalization.
Heavy promotion and organization expenses: “A certain degree of overcapitalization,” says Beacham, “may be caused by heavy issue expenses”. If expenses incurred for promotion, issue and underwriting of shares, promoters’ remuneration, etc., prove to be higher compared to the benefits they provide, the enterprise will find itself over-capitalized.
Shortage of Capital
If a company has small share capital it will be forced to raise loans at a heavy rate of interest. This would reduce the net earnings available for dividends to shareholders. Lower earnings bring down the value of shares leading to over-capitalization.
Taxation Policy
High rates of taxation may leave little in the hands of the company to provide for depreciation and replacement and dividends to shareholders. This may adversely affect its earning capacity and lead to over-capitalization.
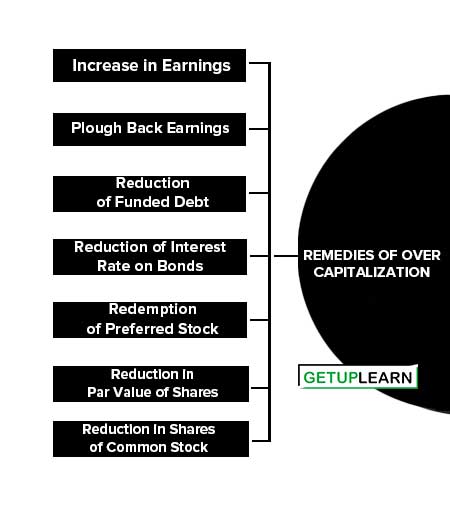
Remedies of Over Capitalization
These are the remedies of over capitalization explained below:
- Increase in Earnings
- Plough Back Earnings
- Reduction of Funded Debt
- Reduction of Interest Rate on Bonds
- Redemption of Preferred Stock
- Reduction in Par Value of Shares
- Reduction in Shares of Common Stock
Increase in Earnings
The earning capacity of the company should be raised by enhancing the efficiency of human and non-human resources belonging to the company. All types of wasteful expenditure should be avoided.
Plough Back Earnings
The remedy for over-capitalization resulting from the overvaluation of assets of the company lies in squeezing the water out of the stock by plowing back earnings into the business for replacements and extensions.
Reduction of Funded Debt
It is desirable to correct overcapitalization by reducing long-term debt. The debentures and bonds should be redeemed to restore parity between the book value of the company and its real value. True reduction of capitalization would be affected if the debt is retired from earnings.
Reduction of Interest Rate on Bonds
The old debenture holders may agree to take new debentures at a lower rate of interest when the premium is given on new debentures. But here, the scheme may not be successful without affecting reorganization.
Redemption of Preferred Stock
Redemption of Preferred Stock if It Carries a High Dividend: This can be tried in cases where the preferred stock is cumulative. Funds for the redemption would probably have to be procured from the sale of common stock at low prices.
It is a fine method if the equity shareholders are ready to give their consent to it.
Reduction in the Number of Equity Shares of Common Stock: There are difficulties in its implementation due to the average stockholders’ proportionate interest in the equity, it is sometimes effectuated.
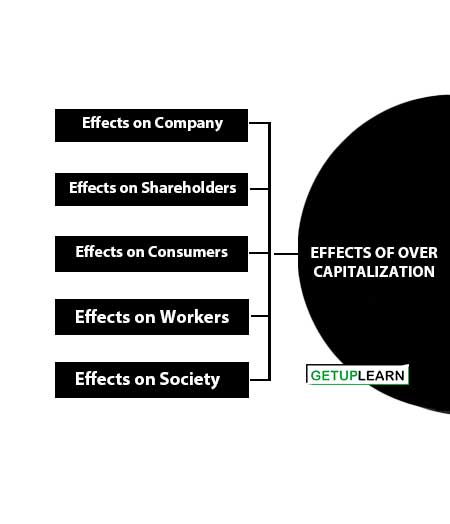
Effects of Over Capitalization
These are the 5 effects of over capitalization:
- Effects on Company
- Effects on Shareholders
- Effects on Consumers
- Effects on Workers
- Effects on Society
Effects on Company
-
Destroys the goodwill and creditworthiness: Over-capitalization marked by low earning capacity destroys the reputation and goodwill of the company with a deterrent effect on its prospects of the business.
-
Difficulty in raising additional funds: It causes a decline in share values which brings down the credit-standing and financial reputation of the company. Thus, it finds difficulty in mobilizing additional funds.
-
Borrowings at a higher rate of interest: An over-capitalized company that is not able to raise capital from the shareholders may get loans at a higher rate of interest due to which the position may further deteriorate.
- Resort to unfair practices: It may force the management of the company to follow unhealthy practices of window dressing of earnings. For example, it may not provide sufficient depreciation and also neglect the maintenance and replacement of assets. This will decrease the earning capacity of the company and discourage genuine investors from investing in the company.
The shareholders of an over-capitalized company are losers in all transactions:
- The return on their investment is uncertain, irregular, and nominal.
- The market value of their holdings is reduced.
- Their holdings have a small value as collateral security.
- If the shares are sold, no fair consideration is obtained.
- Speculation is encouraged in the shares and the real investors have to suffer on that account.
- When an over-capitalized company tries to set its house in order through reorganization, the shareholders are the worst sufferers. The reorganization would usually take the form of a reduction of capital for writing off past losses. At the time of liquidation too, the shareholders have to satisfy themselves with much less than their original investment.
Effects on Consumers
Over-capitalization is unfair to consumers also. Over-capitalized companies desirous of increasing their earnings would unjustifiably raise the price of their products and ignore or lower the quality of the goods.
Effects on Workers
In order to make up deficient earnings, the over-capitalized concerns may reduce the workers’ wages and withdraw the costly amentia admissible to them. Lower wages and adverse working conditions would demoralize the workers and decrease operational efficiency.
Effects on Society
- An over-capitalized company increased prices and reduces the quality of goods. Thus, the public is a loser both as regards price and quality.
- An over-capitalized company may try to increase its profits by reducing the wages of workers. This may spoil industrial relations.
- The closure of over- capitalized company may become the cause of general panic and alarm. This would affect the interests of the creditors. The workers would also lose their jobs.
- Over-capitalization results in the misapplication of society’s resources.
- The shares of an over-capitalized concern provide scope for speculation on the stock exchange. It is undesirable from a social point of view.
Undercapitalization
Undercapitalization is just the reverse of over-capitalization. The state of under-capitalization is where the value of assets is much more than it appears in the books of the company. In well-established companies, there is a large appreciation in assets, but such appreciation is not shown in the books.
As against over-capitalization, under-capitalization is associated with effective utilization of investments, an exceptionally high rate of dividend, and enhanced prices of shares. In other words, the capital of the company is less in proportion to its total requirements under the state of under-capitalization.
[su_quote cite=”Gerstenberg”]A corporation may be under-capitalized when the rate of profits it is making on the total capital is exceptionally high in relation to the return enjoyed by similarly situated companies in the same industry or when it has too little capital with which to conduct its business.[/su_quote]
Under-capitalization is a condition where the real value of the company is more than its book value. The assets bring profits but it would appear to be much larger than warranted by book figures of the capital. In such cases, the dividend will naturally be high and the market value of shares will be much higher.
Under-capitalization and inadequacy of capital are regarded as inter-changeable terms but there is a difference between these two terms. Under-capitalization does not mean inadequacy of capital.
Profits are high in such companies and a part of the profits are plowed back into the business directly or indirectly. The value of assets is shown at a lower price than their real value. It means that there are secret reserves in under-capitalized companies.
Causes of Under Capitalization
Now, The causes of under capitalization are:
- Acquisition of Assets During Recession
- Under-Estimation of Requirements
- Conservative Dividend Policy
- Efficient Management
- Creation of Secret Reserves
Acquisition of Assets During Recession
Assets might have been acquired at low costs during necessary conditions in the market. And now higher incomes are being earned by their use.
Under-Estimation of Requirements
There may be an underestimation of the capital requirements of the company by the promoters. This may lead to capitalization which is insufficient to conduct its operations.
Conservative Dividend Policy
The management may follow a conservative dividend policy leading to a higher rate of plowing back of profits. This would increase the earning capacity of the company.
Efficient Management
The management of a company may be highly efficient. It may issue the minimum share capital and may meet the additional financial requirements through borrowings at lower rates of interest.
Creation of Secret Reserves
A company may have large secret reserves due to which its profitability is higher.
Remedies for Undercapitalization
The following remedial undercapitalization of a company:
- Under-capitalization may be remedied by increasing the par value and/or number of equity shares by revising upward the value of assets. This will lead to a decrease in the rate of earnings per share.
- Management may capitalize the earnings by issuing bonus shares to the equity shareholders. This will also reduce the rate of earnings per share without reducing the total earnings of the company.
- Where under-capitalization is due to insufficiency of capital, more shares and debentures may be issued to the public.
FAQs About the Capitalization
What is the meaning of capitalization?
Capitalization is that which “comprises of a company’s own capital which includes capital stock and surplus in whatever form it may appear and borrowed capital which consists of bonds or similar evidence of long-term debt”.
What are the causes of overcapitalization?
The following are the causes of overcapitalization:
1. Over-Issue of Capital
2. Acquiring Assets at Inflated Prices
3. Formation During the Boom Period
4. Over-Estimation of Earnings
5. Inadequate Depreciation
6. Liberal Dividend Policy
7. Lack of Reserves
8. Shortage of Capital
9. Taxation Policy.
What are the remedies of over capitalization?
The remedies for over capitalization are:
1. Increase in Earnings
2. Plough Back Earnings
3. Reduction of Funded Debt
4. Reduction of Interest Rate on Bonds
5. Redemption of Preferred Stock
6. Reduction in Par Value of Shares
7. Reduction in Shares of Common Stock.
What are the effects of over capitalization?
The following are the effects of over capitalization:
1. Effects on Company
2. Effects on Shareholders
3. Effects on Consumers
4. Effects on Workers
5. Effects on Society.
What are the causes of under capitalization?
The causes of under capitalization are:
1. Acquisition of Assets During the Recession
2. Under-Estimation of Requirements
3. Conservative Dividend Policy
4. Efficient Management
5. Creation of Secret Reserves.