Table of Contents
What is Leverage?
Leverage can be defined as “the employment of an asset or source of funds for which the firm has to pay a fixed cost or fixed return”.
Because of the incurrence of fixed costs, the net income and the earnings available to the equity shareholders as well as the risk get affected. Leverage is favorable when the earnings less the variable costs exceed the fixed costs or when the earnings before interest and taxes exceed the fixed return requirement. Leverage is unfavorable in the reverse situation.
Meaning of Leverage in Financial Management
The dictionary sense of the term leverage refers to “an increased means of accomplishing some purpose.” For example, leverage helps us in lifting heavy objects, which may not be otherwise feasible. Nevertheless, in the area of finance, the term leverage has a special connotation. It is used to describe the firm’s ability to use fixed-cost assets or funds to blow up the return to its owners.
James Van Horne has defined leverage as “the employment of an asset or funds for which the firm pays a fixed cost or fixed return.” Thus, according to him, leverage results as an outcome of the firm employing an asset or source of funds, which has a fixed charge (or return).
The former may be termed as 93 “fixed operating cost”, while the latter may be termed as “fixed financial cost”. It should be noted that fixed cost or return is the pivot of leverage. If it is not obligatory for a firm to pay a fixed cost or a fixed return, there will be no leverage.
Since fixed cost or return has to be paid or incurred irrespective of the level of output or sales, the size of such cost or return has a substantial influence over the amount of profits available for the shareholders. When the level of sales changes, leverage helps in quantifying such influence.
It may therefore be defined as a relative change in profits due to a change in sales. A high degree of leverage implies that there will be a stout change in profits due to a relatively minute change in sales and viceversa. Thus, the higher the leverage, the higher the risk and the higher the expected return.
Types of Leverage in Financial Management
These are the three types of leverage in financial management:
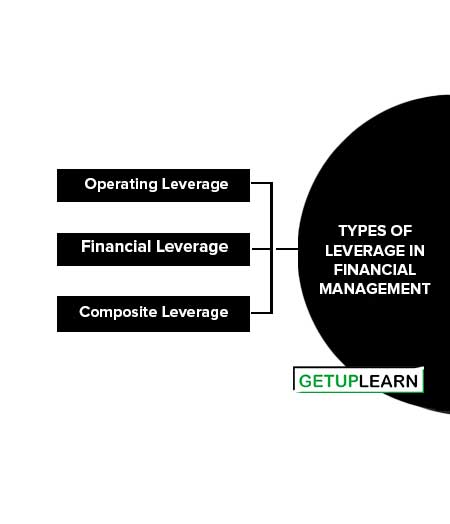
Operating Leverage
Operating leverage is the ratio that shows the between contribution (sales revenue less variable cost) and earnings before interest and tax or EBIT.
The operating leverage may be defined as the tendency of the operating profit to vary disproportionately with sales. It is assumed to exist when a firm has to pay fixed costs regardless of the level of output or sales. The firm is said to have a high degree of operating leverage if it employs a greater amount of fixed costs and a small number of variable costs.
On the other hand, a firm will have a low operating leverage when it employs a greater amount of variable costs and a smaller amount of fixed costs. Thus, the degree of operating leverage depends upon the number of fixed elements in the cost structure.
Sales Revenue – Variable cost = Contribution
Contribution – Fixed Cost = EBIT
| Contribution Operating Leverage = —————– EBIT |
Operating Leverage = Contribution/EBIT
This ratio gives an idea about the presence of fixed cost and its volume as compared to the variable cost used in the business as depicted above.
Financial Leverage
Financial leverage may be defined as the propensity of the residual net income to vary disproportionately with operating profit. It indicates the change that takes place in the taxable income as a result of a change in the operating income. It signifies the survival of fixed interest/fixed dividend-bearing securities in the total capital structure of the company.
Thus, the use of fixed interest/dividend-bearing securities such as debt and preference capital along with the owner’s equity in the total capital structure of the company is described as financial leverage.
EBIT – Interest Charges on the Loans = EBT
| EBIT Financial Leverage = —————– EBT |
This ratio gives an idea about the presence of loans and their volume as compared to equity capital in the business.
Composite Leverage
operating leverage measures a percentage change in operating profit due to a percentage change in sales. It explains the degree of operating risk. Financial leverage measures the percentage change in taxable profit (or EPS) on account of the percentage change in operating profit (i.e., EBIT). Thus, it explains the degree of financial risk.
Both these leverages are closely related to the firm’s capacity to meet its fixed costs (both operating and financial). In case both leverages are combined, the result obtained will unveil the effect of change in sales over the change in taxable profit (or EPS).
Composite leverage thus expresses the relationship between revenue on account of sales (i.e. contribution or sales less variable cost) and the taxable income. It helps in finding out the resulting percentage change in taxable income on account of the percentage change in sales. This can be computed as follows:
| Composite leverage = Operating leverage x Financial leverage = C/OP x OP/PBT = C/PBT |
Where C = Contribution (i.e. sales – variable cost)
OP = Operation Profit or Earning before Interest and Tax
PBT = Profit before Tax but after Interest
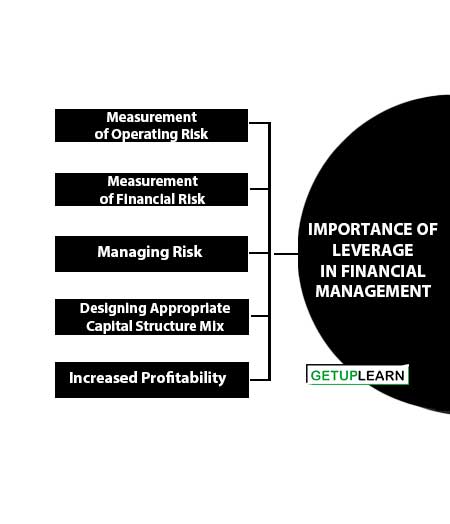
Importance of Leverage in Financial Management
Leverage refers to the use of fixed costs in an attempt to increase profitability. Leverage affects the level and variability of the firm’s after-tax earnings and hence, the firm’s overall risk and return. The following are the importance of leverage in financial management:
- Measurement of Operating Risk
- Measurement of Financial Risk
- Managing Risk
- Designing Appropriate Capital Structure Mix
- Increased Profitability
Measurement of Operating Risk
Operating risk refers to the risk of the firm not being able to cover its fixed operating costs. Since operating leverage depends on fixed operating costs, larger fixed operating costs indicate a higher degree of operating leverage and thus, a higher operating risk for the firm. High operating leverage is good when sales are rising but bad when they are falling.
Measurement of Financial Risk
Financial risk refers to the risk of the firm not being able to cover its fixed financial costs. Since financial leverage depends on fixed financial costs, high fixed financial costs indicate a higher degree of operating leverage and thus, high financial risk. High financial leverage is good when operating profit is rising and bad when it is falling.
Managing Risk
The relationship between operating leverage and financial leverage is multiplicative rather than additive. Operating leverage and financial leverage can be combined in a number of different ways to obtain a desirable degree of total leverage and level of total firm risk.
Designing Appropriate Capital Structure Mix
To design an appropriate capital structure mix or financial plan, the amount of EBIT under various financial plans should be related to earnings per share. It is one widely used means of examining the effect of leverage to analyze the relationship between EBIT and earnings per share.
Increased Profitability
Leverage is an effort or attempt by which a firm tries to show high results or more benefits by using fixed costs assets and fixed return sources of capital. It ensures maximum utilization of capital and fixed assets in order to increase the profitability of a firm. It helps to know the reasons for not having more profit by a company.
Operating Lease
As against the finance lease, where the lessor expects to recover his investment from a single lease, under an operating lease, the asset is leased out for a shorter duration to a number of successive lessees. The lessor recovers his Investment in the asset over a period from the lease rentals received from several lessees.
The lessor looks after the maintenance and proper upkeep of the asset, As in the case of a finance lease, the ownership remains with the lessor. AS-19 defines an operating lease as a lease other than a finance lease.
A lease is classified as an operating lease if it does not transfer substantially all the risks and rewards incident to ownership. An operating lease is also known as a service lease. An operating lease is preferable in cases where:
- The rate of obsolescence of the asset is very high.
- The asset will be required for a short duration.
- The lessee wants to tide over a temporary financial problem.
FAQs About the Leverage in Financial Management
What are the types of leverage?
Types of leverage in financial management are:
1. Operating Leverage
3. Financial Leverage
4. Composite Leverage.
What is the importance of leverage?
The importance of leverage in financial management is:
1. Measurement of Operating Risk
2. Measurement of Financial Risk
3. Managing Risk
4. Designing Appropriate Capital Structure Mix
5. Increased Profitability.