Table of Contents
- 1 What is a Bank?
- 2 Types of Banks
- 3 Principles of Commercial Banks
-
4 Services of Commercial Banks
- 4.1 Acceptance of Deposits
- 4.2 Advancing Loans
- 4.3 Investment of Funds
- 4.4 Remittance of Funds
- 4.5 Dealing in Foreign Exchange
- 4.6 Overdraft Facility
- 4.7 Discounting Bills of Exchange
- 4.8 Credit Cards
- 4.9 Debit Cards
- 4.10 Automatic Teller Machine (ATM)
- 4.11 Online Banking
- 4.12 Private Banking
- 4.13 Mobile Banking
- 5 FAQs About the What is a Bank?
What is a Bank?
A bank is an institution that accepts deposits of money from the public which is withdrawable by cheque and uses the deposits collected for lending. Hence, the following four parameters are essential to describe an institution as a bank.
- It has to accept deposits in the form of money.
- Deposits are to be accepted by the general public and not by the shareholders of the firm.
- Deposits are withdrawable on demand by cheque.
- The institution must use the deposits to give loans to the general public.
Hence, a bank is an intermediary that accepts deposits from the public who has disposable income or savings and routes the money in the form of a loan to the public who are in need of money. However, there are few institutions that accept deposits withdrawable by cheques from the public but use the deposits for its own purpose, they are not regarded as banks.
Such types of institutions are known as pure deposit systems. Post office savings bank is an example of a pure deposit system where the money collected from the public is utilized for governmental work. Similarly, there are few institutions that accept deposits from the public and give loans to the public and corporate but their deposits cannot be withdrawn by cheques.
They are known as pure financial intermediaries. Life Insurance Corporation of India and Unit Trust of India are a few examples of pure financial intermediaries. Hence to be a bank it has to fulfill all the above-mentioned criteria.
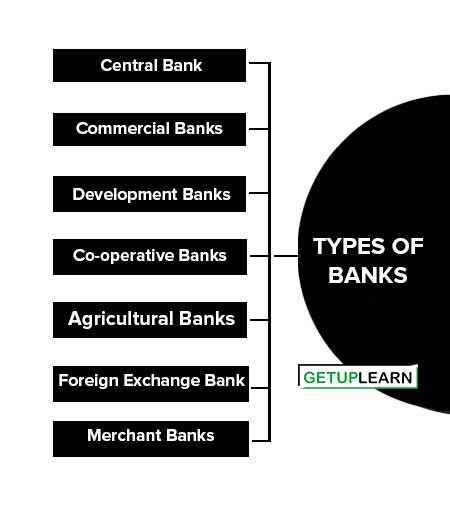
Types of Banks
The following are the different kinds or types of banks that exist in an economy:
- Central Bank
- Commercial Banks
- Development Banks
- Co-operative Banks
- Agricultural Banks
- Foreign Exchange Bank
- Merchant Banks
Central Bank
It is the apex bank of a country. The central bank regulates the entire banking system of a country. In India, the Reserve Bank of India is the central bank.
Commercial Banks
Among various types of banks, commercial banks are the most important banks in any country. In India, commercial banks are divided into two groups a) Nationalized or Public Sector Banks and b) Private Sector Banks. The private sector banks can further be segregated into Indian Banks and Foreign Banks.
Development Banks
These are the specialized financial institutions that supply medium to long-term finance to individuals and institutions. They are also known as Development Financial Institutions (DFIs). Whereas commercial banks mainly provide short-term and medium-term finance, development banks provide medium to long-term credit.
A few of the DFIs of India are the Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI), State Financial Corporations (SFCs), National Small Industries Corporation (NSIC), Small Industrial Bank of India (SIDBI), Northeast Development Financial Institution (NEDFi) and so on.
Co-operative Banks
There are a few banks that are organized under the provisions of the law of the cooperative societies, they are called cooperative banks. The cooperative banks in India were set up to provide short-term loans to agriculturists for the purchase of seeds, harvesting, and for other cultivation expenses.
However, at present, cooperative banks are operating similarly to commercial banks in urban, semi-urban, and rural areas.
Agricultural Banks
This type of bank offers long-term credit to farmers for the development/purchase of agricultural land. National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) is an example of an agricultural bank in India.
Foreign Exchange Bank
This type of bank facilitated international trade. They offer a range of services such as buying and selling foreign exchange, discounting bills, providing advisory services related to international trade, and so on. In India, Export-Import Bank (EXIM Bank) is a foreign exchange bank.
Merchant Banks
Merchant banks primarily focused on providing service to business undertakings on various financial matters. It is mainly concerned with providing non-fund-based services with respect to arranging funds rather than providing them.
Merchant banks provide a wide range of services to their client with respect to the underwriting of new issues, corporate mergers and acquisitions, loan syndication, and so on.
Principles of Commercial Banks
Commercial banks are the most important banks in any country. They primarily accept deposits from the public and lend the money in the form of loans to individuals or institutions. In India State Bank of India is the biggest commercial bank.
Commercial banks are guided by a few specific principles. These principles need to be followed for the smooth and effective functioning of commercial banks. There are mainly six principles of commercial banking:
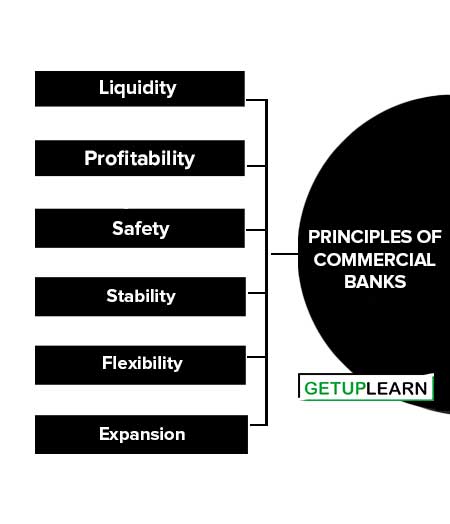
Liquidity
Liquidity refers to the capacity of the banks to meet the cash demands of their clients. In other words, commercial banks must have sufficient cash to meet the cash demand of their depositors. Hence they must maintain liquidity.
Bank has to maintain liquidity to gain the trust and confidence of its customers. To ensure liquidity, commercial banks are required to keep a certain portion of their deposits in the form of cash, as prescribed by RBI from time to time.
Profitability
Like any other organization, a commercial bank must earn profit for its existence. In order to earn a profit, a bank has to lend money to its clients in the form of loans and advances. However if the bank lends its entire deposits, it runs into liquidity risk.
Therefore the commercial bank must maintain a ‘trade-off’ between liquidity and profitability. A successful bank has to strike the right balance between profitability and liquidity.
Safety
A bank must ensure the safety of the money of its depositors. A bank accepts deposits from the public; hence safety of the money is one of the prime principles of banking.
A bank must ensure due diligence before offering loans to its clients. In case of default by a large number of clients, in repaying the loan amount, the bank will run the risk of insolvency.
Stability
Stability implies the growth of an organization at a steady rate. A sound banking system must operate rationally and judiciously. There should not be undue expansion or undue contraction of credit.
Flexibility
An efficient bank needs to be flexible. It should be able to expand or contract credit as per the requirement of the economy. In other words, it should disburse more loans during the depression and contract loans during inflation.
Expansion
A sound banking system should not only be concentrated only to urban or semi-urban areas but it should be expanded to the rural areas also. Expansion of the banking system to rural areas will increase the inducement to save for the rural people. All these will help in capital formation and economic development of a country.
Services of Commercial Banks
Commercial banks are the most important financial institutions in any country. They provide various services for the economic development of a country. The major services of commercial banks are as follows:
- Acceptance of Deposits
- Advancing Loans
- Investment of Funds
- Remittance of Funds
- Dealing in Foreign Exchange
- Overdraft Facility
- Discounting Bills of Exchange
- Credit Cards
- Debit Cards
- Automatic Teller Machine (ATM)
- Online Banking
- Private Banking
- Mobile Banking
Acceptance of Deposits
They accept deposits from the public. People prefer to deposit their savings in banks because banks offer interest on deposits.
Advancing Loans
Commercial banks offer loans to their customers in order to earn profit. After keeping a certain percentage as cash reserves, the bank provides short-term, medium-term, and long-term loans to needy borrowers.
Investment of Funds
Commercial banks are one of the prominent players in the money market and capital market. They invest their surplus funds in the market to generate maximum returns.
Remittance of Funds
Banks act as an intermediary in transferring funds from one place to another through various means such as cheques, drafts, online banking, etc.
Dealing in Foreign Exchange
Commercial banks deal with foreign currencies. They facilitate international by buying and selling foreign currencies.
Overdraft Facility
This facility allows customers to withdraw funds more than their deposits against a fee. The overdraft facility helps businesses to expand and grow.
Discounting Bills of Exchange
Commercial banks discount bills of exchange by paying the value of the bill upfront to the holder, after deducting a percentage as commission. The bank then gets the payment from the party who accepted the bill, when the bill matures.
Credit Cards
Credit cards are innovative instruments in the area of financial services offered by commercial banks. A credit card facilitates the cardholder to make purchases of goods and services without making immediate payments within a specified credit limit, which is fixed by the issuer of the card.
Debit Cards
Debit cards are also used to make purchases of goods and services at merchant establishments, however, the amount of money spent on purchases is debited from the account of the debit card holder. Debit cards usually require a personal identification number (PIN) to be used to verify the transaction.
Automatic Teller Machine (ATM)
Commercial banks have placed ATMs at various important locations to provide basic banking services such as withdrawal of cash, deposit of cash, account inquiries, etc.
Online Banking
It is a service that allows account holders to access data through the Internet. It is also known as Internet banking. In order to carry out online banking, the account holder needs to enter a specific login identity and password.
After logging in, the customer can perform various banking transaction such as paying bills, transferring money, downloading account statements, etc.
Private Banking
It is personalized financial and banking services offered specifically to high net-worth individuals (HNI).
Mobile Banking
Mobile banking enables a customer to do various bank transactions such as balance inquiries, bill payments, transferring money, and so on through their mobile handset.
FAQs About the What is a Bank?
What are the types of banks?
These are the types of banks: Central Bank 2. Commercial Banks 3. Development Banks 4. Co-operative Banks 5. Agricultural Banks 6. Foreign Exchange Bank 7. Merchant Banks.
What are the principles of commercial banks?
The principles of commercial banks are Liquidity 2. Profitability 3. Safety 4. Stability 5. Flexibility 6. Expansion.
What are the services of commercial banks?
The services of commercial banks are:
1. Acceptance of Deposits
2. Advancing Loans
3. Investment of Funds
4. Remittance of Funds
5. Dealing with Foreign Exchange
6. Overdraft Facility
7. Discounting Bills of Exchange
8. Credit Cards
9. Debit Cards
10. Automatic Teller Machine (ATM).