Table of Contents
-
1 Types of Banks
- 1.1 Public Sector Banks
- 1.2 Private Sector Banks
- 1.3 Co-operative Banks
- 1.4 Scheduled Banks
- 1.5 Non-Scheduled Banks
- 1.6 Commercial Banks
- 1.7 Foreign Banks
- 1.8 Industrial Banks
- 1.9 Agricultural Banks
- 1.10 Central Bank
- 1.11 Unit Banking
- 1.12 Branch Banking
- 1.13 Group Banking
- 1.14 Chain Banking
- 1.15 Correspondent Banking
- 2 FAQs About the Types of Banks
Types of Banks
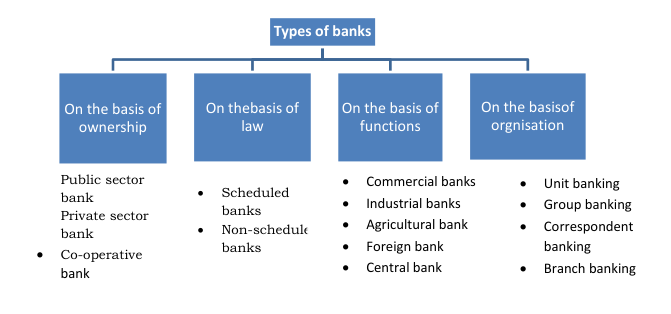
These are the four base of types of banks Basis of Ownership, Basis of Law, Basis of Functions, and Basis of Organization:
- Public Sector Banks
- Private Sector Banks
- Co-operative Banks
- Scheduled Banks
- Non-Scheduled Banks
- Commercial Banks
- Foreign Banks
- Industrial Banks
- Agricultural Banks
- Central Bank
- Unit Banking
- Branch Banking
- Group Banking
- Chain Banking
- Correspondent Banking
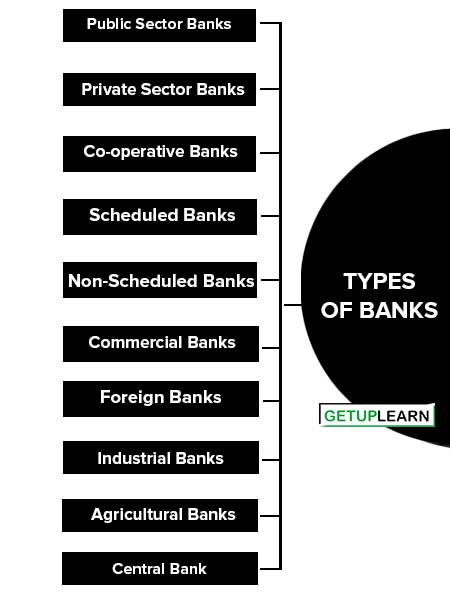
Types of Banks on Basis of Ownership
The bank’s classification on the basis of ownership:
Public Sector Banks
Public sector banks are those banks that are owned by the government. The main objective of these banks is social welfare.
Private Sector Banks
These are the banks that are owned and run by the private sector. Various banks in the country belong to this category like HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank, etc.
Co-operative Banks
These are the banks that are jointly run by a group of individuals. Each individual has an equal share in the bank. Profits are equally distributed among shareholders. Mutual help of the shareholder is the core objective.
Types of Banks According to Law
Banks classification according to law is explained below:
Scheduled Banks
These are those banks that are mentioned in the second schedule of the Reserve Bank of India Act 1934. These are like Joint Stock Companies or cooperative organizations.
Non-Scheduled Banks
These are those banks that are not mentioned under the second schedule of the reserve bank of India Act 1934.
Types of Banks According to Functions
Banks classification according to functions given below:
Commercial Banks
These are the most important constituents of the banking system governed by the banking companies act 1949. These banks are basically for earning profit. Commercial banks are the institutions that make short-term loans to businesses and in the process create money.
Foreign Banks
These are those banks that are incorporated in a foreign country. They have their branches in India. These banks deal in foreign exchange. These banks convert the currency of one country into the other for example Standard charted bank, Hong Kong Bank, and Bank of America.
Industrial Banks
These are those banks that offer long term and medium-term loans to the industries and also work for their development. These banks help industries to purchase capital assets. In India, many industrial banks are there like the Industrial Development Bank of India, Industrial Finance Corporation, and others.
Agricultural Banks
These are those banks that give credit to the agricultural sector of the economy. Short-term loans are given to farmers in order to purchase seeds, fertilizers, etc. Long-term loans are given for the improvement of farming facilities.
Agricultural cooperative banks deal with short-term credit. To fulfill agricultural needs at the national level, National Bank for Agriculture and rural development has been established.
Central Bank
The central bank is the apex bank in the Banking system in our country. The Reserve Bank of India is the central bank of our country. It issues currency notes and acts as a banker’s bank. It controls credit and regulates the credit system of banks.
The main objectives of this bank are to provide economic stability in the country. Central banks issues all types of currencies, control all other banks in the country, and function as a bank of government.
Types of Banks on Basis of Organization
The classification of commercial banks on the basis of their organization:
Unit Banking
Under the unit banking system banking operations are carried out from a single banking office rather than through a network of branches. Each banking company is a separate banking company, separately licensed having its own capital, board of directors, and Shareholders. In this banking system a particular bank functions in a limited area. Bank has no branch office.
Branch Banking
This type of banking system is the one in which a bank establishes a head office in some big city and operates all over the country. Some of them have branches in foreign countries. This system is too much prevalent in India.
Group Banking
It is the banking system in which two or more banks operate under the control of a holding company. These banks are known as subsidiaries of the corporation or holding. These banks may be unit banks or branch banks. The group banking system is most popular in the United States of America.
Chain Banking
Chain banking is the banking system where the same individual or group of individuals controls two or more banks. In this system, an undivided group of individuals buy the bulk of shares of two or more banks and thus control them.
Correspondent Banking
it is an arrangement that exists among banks throughout the country based on the practice of smaller banks carrying deposits with larger banks in exchange for the performance of various services. Services include cheque clearing, sale, and purchase of securities, and making advances for big loans. These large banks are called correspondent banking.
FAQs About the Types of Banks
What are the types of banks?
The following are the various types of banks: 1. Public Sector Banks 2. Private Sector Banks 3. Co-operative Banks 4. Scheduled Banks 5. Non-Scheduled Banks 6. Commercial Banks 7. Foreign Banks 8. Industrial Banks 9. Agricultural Banks 10. Central Bank.