Table of Contents
- 1 Meaning of Financial Management
- 2 Definition of Financial Management
- 3 Objectives of Financial Management
-
4 Nature of Financial Management
- 4.1 An Essential Part of Top Management
- 4.2 Less Descriptive and More Analytical
- 4.3 Continuous Function
- 4.4 Different from Accounting Function
- 4.5 Wide Scope
- 4.6 Centralized Nature
- 4.7 Measurement of Performance
- 4.8 Inseparable Relationship between Finance and Other Activities
- 4.9 Applicable to All Types of Organizations
- 5 Functions of Financial Management
- 6 FAQs Section
Meaning of Financial Management
The term financial management can be defined as the management of flow of funds and it deals with financial decision-making. It encompasses the procurement of funds in the most economical and prudent manner and the employment of these funds in the most optimum way to maximize the return for the owner.
Since raising funds and their best utilization is the key to the success of any business organization, financial management as a functional area has got a place of prime relevance in every firm. Financial management includes any decision made by a business that affects its finances.
Definition of Financial Management
In simple terms, Financial Management is a managerial activity of planning & controlling the firm’s financial resources. Let us see some of the important definitions of financial management:
Financial Management is the application of the planning & control functions to the finance function.
Howard & Upton
Financial management is an area of financial decisions harmonizing individual motives & enterprise goals.
Weston & Brigam
Financial Management is the operational activity of a business that is responsible for obtaining & effectively utilizing the funds necessary for efficient operations.
Joseph & Massie
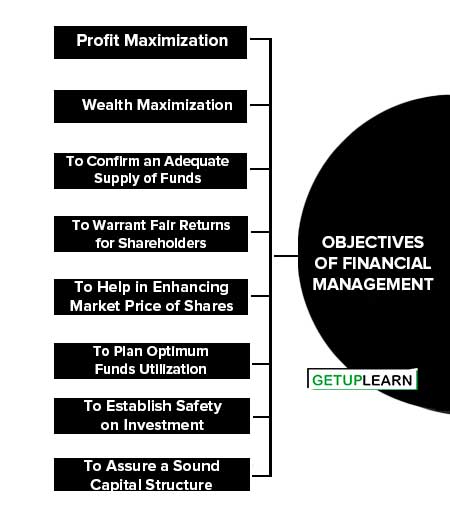
Objectives of Financial Management
Financial management is defined as a management task that deals with the effective utilization of the procured finance to meet organizational objectives. It plans, controls, organizes, and directs the activities related to finance in an organization.
The FM is generally concerned with the procurement, allocation & control of funds. The following are the objectives of Financial Management:
- Profit Maximization
- Wealth Maximization
- To Confirm an Adequate Supply of Funds
- To Warrant Fair Returns for Shareholders
- To Help in Enhancing Market Price of Shares
- To Plan Optimum Funds Utilization
- To Establish Safety on Investment
- To Assure a Sound Capital Structure
Profit Maximization
According to this approach, all activities that increase profits should be undertaken and that decrease profits should be avoided. Profit maximization implies that financial decision-making should be guided by only one test, which is, to select those assets, projects, and decisions which are profitable and reject those which are not.
Wealth Maximization
The second objective of financial management is value maximization or Net Present worth maximization. This approach is now universally accepted as an appropriate criterion for making financial decisions as it removes all the limitations of the profit maximization approach.
It is also known as the net present value (NPV) maximization approach. According to this approach, the worth of an asset is measured in terms of benefits received from its use less the cost of its acquisition.
Benefits are measured in terms of cash flows received from its use rather than accounting profit which was the basis of measurement of benefits in the profit maximization approach.
To Confirm an Adequate Supply of Funds
An adequate supply of funds to an organization should be ensured so as to meet its daily production requirements so that organizational goals and objectives are met in time. Failure of an adequate supply of funds curtails production which adversely affects the organization by causing delays in several inter-departmental functions.
Finance management should make a fair return on shareholders’ investment, which makes the organization stronger in terms of further procurement of funds through various procurement methods of finance from internal and external sources.
It should help in increasing the market price of shares through standardized financial practices, increasing organizational assets or decreasing debts, increasing a company’s potential to be taken over by other companies, increasing public image, and improving creditworthiness.
To Plan Optimum Funds Utilization
Financial Management should deal effectively with utilizing the funds at their optimum level. It should plan proper inflow and outflow of funds and utilization should be done in such a way where the wastage on the funds utilization is seen at negligible levels.
To Establish Safety on Investment
It should safely invest the funds in risk-free or high returns offering shares or other financial instruments, which proves the organizational investment pattern to be hassle-free for the investors through adding creditworthiness and making wise investment decisions.
To Assure a Sound Capital Structure
Financial management in an organization should be sound by ensuring proper inflow and outflow of funds and financial stability. The plan for expenditure and its working capital structure pattern should positively affect an organization in the long run by maintaining the organization’s credit with its customers, creditors, shareholders, and society.
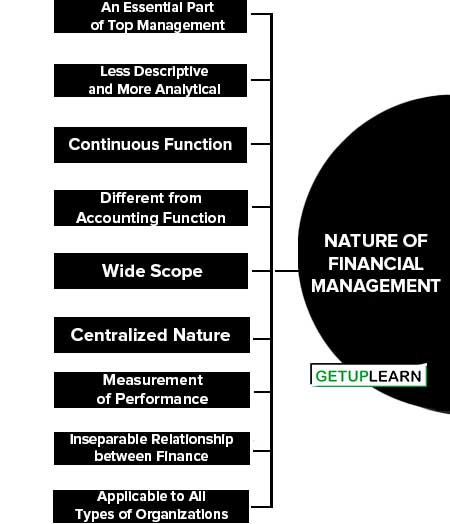
Nature of Financial Management
The important nature of financial management is explained below;
- An Essential Part of Top Management
- Less Descriptive and More Analytical
- Continuous Function
- Different from Accounting Function
- Wide Scope
- Centralized Nature
- Measurement of Performance
- Inseparable Relationship between Finance and Other Activities
- Applicable to All Types of Organizations
An Essential Part of Top Management
In modern business management, the financial manager is one of the active members of the top management team, and day by day his role is becoming more significant in solving complex management problems. This is because almost all kinds of business activities such as production, marketing, etc. directly or indirectly involve the acquisition and use of finance.
Less Descriptive and More Analytical
Financial management is less descriptive and more analytical. Due to the development of new statistical and accounting techniques of financial analysis, financial management chooses the best alternative out of the many possible alternatives.
Continuous Function
Financing is a continuous function. In addition to the raising of finance, there is a continuous need for planning and controlling the finances of an enterprise. A firm performs finance functions continuously in the normal course of the business.
Different from Accounting Function
There are key differences between the accounting and finance functions. Accounting generates information or data whereas in the finance function, the data are analyzed and used for the purpose of decision-making.
Wide Scope
There is a wide scope of financial management. It is concerned not only with the raising of finance but also with the allocation and efficient use of such finance.
Centralized Nature
Financial management is centralized in nature. It is neither, possible nor desirable to decentralize the financial responsibilities.
Measurement of Performance
Financial management is concerned with the wise use of finance. It fixes certain norms and standards against which the benefits of investment decisions are matched.
Inseparable Relationship between Finance and Other Activities
There exists an inseparable relationship between finance on the one hand and production, marketing, and other activities on the other. All other activities are related to finance.
Applicable to All Types of Organizations
It is applicable to all forms of organization whether corporate or non-corporate such as sole proprietorship and partnership firms etc.
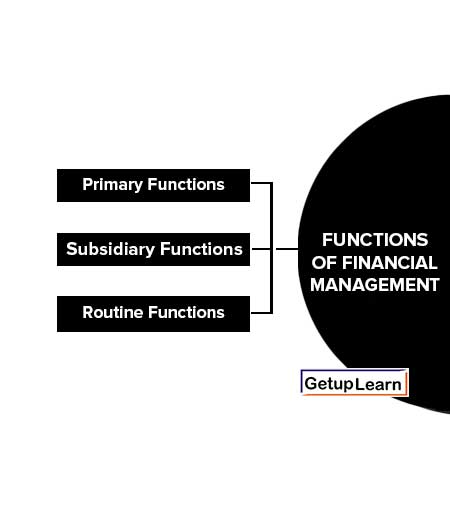
Functions of Financial Management
Financial management includes the performance of the finance function which is divided into three main functions for the sake of convenience of study.
These are the three major categories of functions of financial management:
- Primary Functions
- Subsidiary Functions
- Routine Functions
Primary Functions of Financial Management
As the name itself speaks, this function is of executive nature and requires a lot of skills and expert advice. Let’s study the primary functions of financial management:
- Financial Planning
- Acquisition of Funds
- Allocating Funds
- Financial Control
Financial Planning
This is the basic function under this. Financial planning is of a primary nature and forms the base for other departments. The finance manager has to draft financial plans for the enterprise.
How much should be borrowed from outside financial institutions and how much from internal sources? A perfect combination of debt and equity mix is carried out by a financial manager who bears less cost of capital.
Acquisition of Funds
This is the crucial stage of financial planning. Funds are acquired from various sources which were decided in the primary function. All the formalities of acquiring funds are shown under this. Every source has its own cost which is to be looked upon.
Allocating Funds
After acquiring funds, they are allocated to various assets, activities, projects, etc. This is a very important function because only after allocating funds project work will get started.
Financial Control
The finance manager make records, store information and make reports of various activities. This enables one to make comparative statements with past performances and the finance manager can take corrective functions if he feels so.
Subsidiary Functions of Financial Management
After performing primary functions, come subsidiary functions. Now look at the subsidiary functions of financial management:
- Maintaining Liquidity
- Review of Financial Function
- Coordination with Other Departments
Maintaining Liquidity
Liquidity means a firm’s financial position to meet its current liabilities. Businesses should be strong enough to meet their short-term liabilities. Cash inflows and outflows should be balanced properly to maintain liquidity.
Review of Financial Function
Financial performance should be reviewed and presented in front of the board. Such reports are made based on comparisons with past performances like inter-firm comparison, trend analysis, ratio analysis, and cost-volume-profit analysis.
Coordination with Other Departments
Finance is required in each and every activity. Hence, the finance function is related to every other department.
Routine Functions of Financial Management
Finance is also required in day-to-day routine business. Commonly performed incidental functions are:
- Conducting internal audit.
- Maintaining accounts and keeping records.
- Making public relations.
- Keeping in mind the present governmental regulations.
- Maintaining cash receipts, payments, and checking cash balances.
FAQs Section
What are the functions of financial management?
The following are the major three categories of functions of financial management:
1. Primary Functions: Financial Planning, Acquisition of Funds, Allocating, Funds Financial Control.
1. Subsidiary Functions: Maintaining Liquidity, Review of Financial Function, Coordination with Other Departments.
What are the objectives of financial management?
The objectives of financial management are:
1. Profit Maximization
2. Wealth Maximization
3. To Confirm an Adequate Supply of Funds
4. To Warrant Fair Returns for Shareholders
5. To Help in Enhancing the Market Price of Shares
6. To Plan Optimum Funds Utilization
7. To Establish Safety on Investment
8. To Assure a Sound Capital Structure.
What is the nature of financial management?
Here is the nature of financial management:
1. An Essential Part of Top Management
2. Less Descriptive and More Analytical
3. Continuous Function
4. Different from Accounting Function
5. Wide Scope
6. Centralized Nature
7. Measurement of Performance
8. Applicable to All Types of Organizations.