A business receives funds from various sources such as investors, lenders, and past profits. These funds are used for different purposes such as buying assets for production, maintaining inventory, and keeping cash on hand.
These funds are considered static over time, but changes in the flow of funds are known as funds flow. Finance is the management of these funds, including obtaining them and using them effectively. It involves managing the actual flow of money and any claims against it.

Financial management principles come from accounting, economics, and other fields, but are applied specifically to managing money in a business context. Finance is different from both accounting and economics, although it draws from both.
Table of Contents
-
1 Nature of Financial Management
- 1.1 Organization Management
- 1.2 Valuation of Firm
- 1.3 Balancing Risk and Return
- 1.4 For Business Growth and Survival
- 1.5 Functions in All Business Entities
- 1.6 Subsystem of Business Operations
- 1.7 Impact of External Factors
- 1.8 Interdisciplinary Nature
- 1.9 Role of Procedural Finance Functions
- 1.10 Characteristics and Industry Needs
- 2 FAQs about the Nature of Financial Management
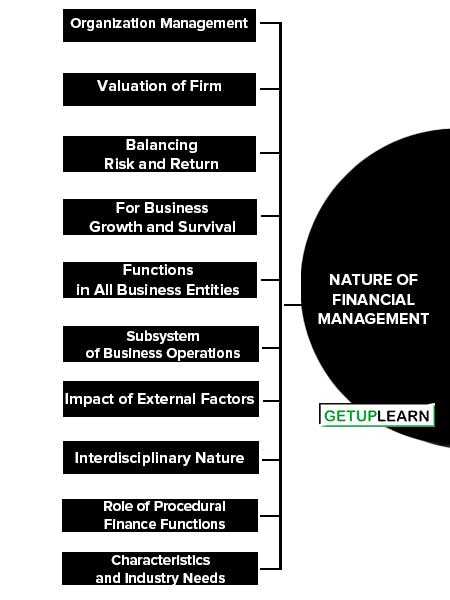
Nature of Financial Management
The nature of financial management is concerned with its functions, its foals, trade-offs with conflicting goals, its indispensability, its systems, its relation with other subsystems in the firm, its environment, its relationship with other disciplines, the procedural aspects, and its equation with other divisions with the organization:
The nature of financial management is explained below:
- Organization Management
- Valuation of Firm
- Balancing Risk and Return
- For Business Growth and Survival
- Functions in All Business Entities
- Subsystem of Business Operations
- Impact of External Factors
- Interdisciplinary Nature
- Role of Procedural Finance Functions
- Characteristics and Industry Needs
Organization Management
Financial management is an integral part of overall management. Financial considerations are involved in all business decisions.
Acquisition, maintenance, removal or replacement of assets, employee compensation sources, and costs of different capital, production, marketing, finance, and personnel decisions, almost all decisions for that matter have financial implications. So financial management is pervasive throughout the organization.
Valuation of Firm
The central focus of financial management is the valuation of the firm. That is financial decisions are directed at increasing/ maximizing/ optimizing the value of the firm. Fred. J. Weston and Eugene F. Brigham depict the above orientation.
Balancing Risk and Return
Financial management essentially involves risk-return trade-off decisions in investment involving choosing types of assets that generate returns accompanied by risks. Generally, the higher the risk, the higher the returns, and vice versa.
So, the financial manager has to decide the level of risk the firm can assume and satisfy with the accompanying return. Similarly, cheaper sources of capital have other disadvantages. So to avail the benefit of the low-cost funds, the firm has to put up with certain costs, disadvantages, or risks, so, the risk-return trade-off is there throughout. Implies this aspect o financial management also.
For Business Growth and Survival
Financial management affects the survival, growth, and vitality of the firm. Finance is said to be the life blood of business. It is to business what blood is to us. The amount, type, sources, conditions, and cost of finance squarely influence the functioning of the unit.
Functions in All Business Entities
Finance functions investment, raising of capital, and distribution of profit, are performed in all firms business or non-business, big or small, proprietary or corporate undertakings. Financial management is a concern of every concern.
Subsystem of Business Operations
Financial management is a subsystem of the business system which has other subsystems like production, marketing, etc. In systems arrangements, financial subsystems are to be well-coordinated with others, and other subsystems are well-matched with the financial subsystem.
Impact of External Factors
The financial management of a business is influenced by the external legal and economic environment. Investor preferences, stock market conditions, legal constraints, using particular types of funds or investing in a particular type of activity, etc., affect the financial decisions of the business. Financial management is, therefore, highly, influenced/ constrained by the external environment.
Interdisciplinary Nature
Financial management is related to other disciplines like accounting, economics, taxation operations research, mathematics, statistics, etc. It draws heavily from these disciplines. The relationship between financial management and supportive disciplines is depicted.
Role of Procedural Finance Functions
There are some procedural finance functions-like record keeping, credit appraisal and collection, inventory replenishment, and issue, etc. These are routinized and are normally delegated to the bottom management.
Characteristics and Industry Needs
The nature of the finance function is influenced by the special characteristic of the business. In a predominantly technology-oriented business, it is R&D functions that get more dominance; in a consumer fashion product business it is marketing and marketing research which get more priority, and so on.
Here, finance assumes a low profile importance. But one should not forget that the strength of a chain depends on its weakest link.
FAQs about the Nature of Financial Management
What is the nature of financial management?
The following is the nature of financial management:
1. Organization Management
2. Valuation of Firm
3. Balancing Risk and Return
4. For Business Growth and Survival
5. Functions in All Business Entities
6. Subsystem of Business Operations
7. Impact of External Factors
8. Interdisciplinary Nature
9. Role of Procedural Finance Functions
10. Characteristics and Industry Needs.