Table of Contents
Meaning of Capital Budgeting
Capital budgeting means planning the capital expenditure in the acquisition of fixed (capital) assets such as land, building, plant, or new projects as a whole. It includes replacing and modernizing a process. Introduction of a new product and expansion of the business.
It involves the preparation of a Detailed Project Report (DPR) and cost and revenue statements indicating the profitability. The project which gives the highest return on investment is to be selected and then investment is to be made in such a project as to maximize the profitability of the firm.
Features of Capital Budgeting
The following basic features of capital budgeting may be deduced from the preceding discussion:
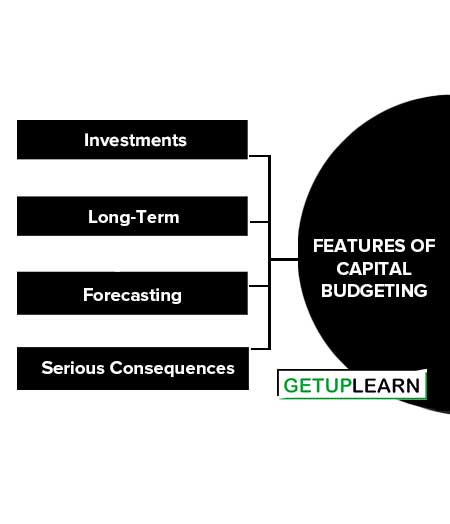
Investments
Capital expenditure plans involve a huge investment in fixed assets.
Long-Term
Capital expenditure, once approved, represents a long-term investment that cannot be reversed or withdrawn without sustaining a loss.
Forecasting
Preparation of capital budget plans involves forecasting several years’ profits in advance in order to judge the profitability of projects.
Serious Consequences
In view of the investment of a large amount for a fairly long period of time, any error in the evaluation of investment projects may lead to serious consequences, financially and otherwise, and may adversely affect the other future plans of the organization.
Need for Capital Budgeting
A capital buffeting decision is of paramount importance in financial decision-making. These are the need for capital budgeting given below:
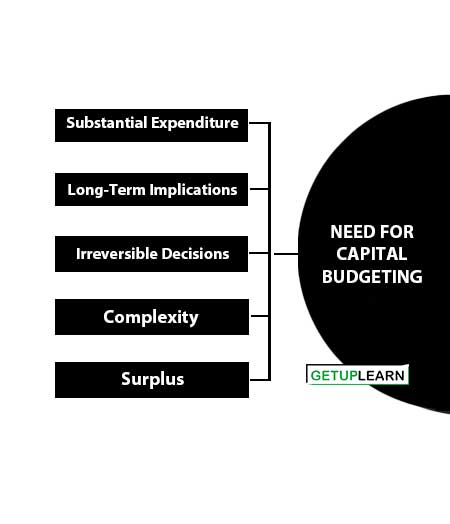
Substantial Expenditure
Capital budgeting decisions involve the investment of a substantial amount of funds. It is therefore necessary for a firm to make such decisions after thoughtful consideration so as to result in the profitable use of its scarce resources.
The hasty and incorrect decision would not only result in huge losses but may also account for the failure of the firm.
Long-Term Implications
Capital budgeting decisions have an effect over a long period of time. These decisions not only affect the future benefits and costs of the firm but also influence the rate and direction of growth of the firm.
Irreversible Decisions
The capital budgeting decisions are irreversible and the heavy amount invested cannot be taken back without causing a substantial loss because it is very difficult to find a market for second-hand capital goods and their conversion into other uses may not be financially feasible.
Complexity
Capital budgeting decisions are based on forecasting future events and inflows. Quantification of future events involves applications of statistical and probabilistic techniques, careful judgment, and application of mind is necessary.
Risk
The longer the time period of returns, the greater the risk/uncertainty associated with cash flows. Hence capital budgeting decisions should be taken after a careful review of all available information.
Surplus
Funds are raised by the firm at a certain cost (i.e., WACC). Even internally generated funds have an implicit cost. Hence, there is a need to obtain a surplus over and above the cost of funds. Only then, the investment is justified.
Advantages of Capital Budgeting
The main advantages of capital budgeting are as under:
- At any given time, numerous investment proposals may be available. Capital budgeting evaluates them and ranks them as per merit. This enables management to decide on implementing appropriate proposals.
- The limited funds available can be most effectively utilized.
- The timing and actual execution of each project can be adjusted to changes in the capital market.
- Different sources of finance can be considered and a judicious selection of sources can reduce the overall cost of capital.
- Capital budgeting can take care of the proportion of debt and equity in the capital structure and the resulting capital gearing.
- In tight money situations, capital rationing can be followed not to waste scarce funds available.
Significance of Capital Budgeting
The following are the main significance of capital budgeting:
- Long-Term Implications
- Large Investment
- Irreversible Decisions
- Most Difficult to Make
- Long–Term Effect on Profitability
- Maximisation of Shareholders Wealth
Long-Term Implications
The effect of capital budgeting decisions will be felt by the firm over a long period and therefore they have a decisive influence on the rate and direction of the growth of the firm.
Large Investment
Capital budgeting decisions involve large investment of funds. Therefore, it is absolutely necessary that the firm should carefully plan its investment programme so that it may get the finances at the finances at the right time and they are put to most profitable use.
Irreversible Decisions
In most cases, the capital budgeting decisions are irreversible. The amount invested cannot be taken back without causing a substantial loss because it is very difficult to find a market for the second-hand capital goods.
Most Difficult to Make
The capital budgeting decisions require an assessment of future events which are uncertain. It is really a difficult task to estimate the probable future events because of the various uncontrollable factors.
Long–Term Effect on Profitability
Capital budgeting decisions have a long-term and significant effect on the profitability of a concern. Not only the present earnings but also the future growth and profitability of the firm depend upon the investment decisions taken today.
With the help of capital budgeting the management protects the interest of the shareholders and of the enterprise by selecting the most profitable projects.
FAQs About the Need for Capital Budgeting
What are the features of capital budgeting?
The features of capital budgeting are:
1. Investments
2. Long-Term
3. Forecasting
4. Serious Consequences.
What is need for capital budgeting?
The following are points of need for capital budgeting:
1. Substantial Expenditure
2. Long-Term Implications
3. Irreversible Decisions
4. Complexity
5. Risk
6. Surplus.
What are the significance of capital budgeting?
The significance of capital budgeting is:
1. Long-Term Implications
2. Large Investment
3. Irreversible Decisions
4. Most Difficult to Make
5. Long–Term Effect on Profitability
6. Maximisation of Shareholders Wealth.