Table of Contents
- 1 What are Export Documents?
- 2 Types of Export Documents
-
3 Documents Required for Export
- 3.1 Commercial Invoice
- 3.2 Customs Invoice
- 3.3 Consular Invoice
- 3.4 Certificate of Origin
- 3.5 Certificate of Value
- 3.6 Certificate of Health
- 3.7 Certificate of Inspection
- 3.8 Packing List
- 3.9 GR-I Form
- 3.10 GR-3 Form
- 3.11 Bill of Lading
- 3.12 Letter of Credit
- 3.13 Airway Bill
- 3.14 Marine Insurance Policy
- 4 Types of Foreign Exchange Exposure
- 5 Managing Foreign Exchange Risk
- 6 FAQs Related to the Export Documents
What are Export Documents?
Export Documents: Exporting goods from one country to another typically involves several types of documentation to ensure that the process complies with the regulations of both the exporting and importing countries.
Here are some of the most common export documents you may need to prepare.
Types of Export Documents
Here are some of the most common types of export documents you should know:
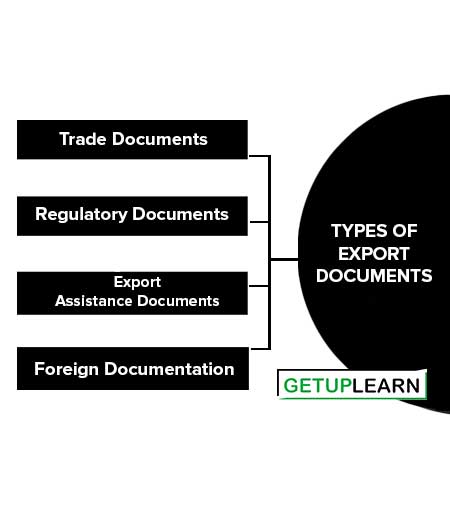
Trade Documents
Trade documents facilitate the export and import trade. These documents include commercial invoices, bills of exchange, bills of lading, letters of credit, marine insurance policies, and certificates.
Regulatory Documents
The government of exporting country uses regulatory documents to regulate the export transactions and to see whether the provisions have complied which include the GR-I form, export policy, inspection certificate, and shipping bill.
Export Assistance Documents
Export assistance documents are required to claim various assistance under the various export assistance schemes. Such documents include statements of exports, copies of shipping bills, shipment invoices, and bank certificates.
Foreign documentation
These documents are required by the importers to satisfy the requirements of the government. These are obtained by the exporter in his country and submitted to the importer for the purpose. These include a certificate of origin, a consular invoice, and a quality control certificate.
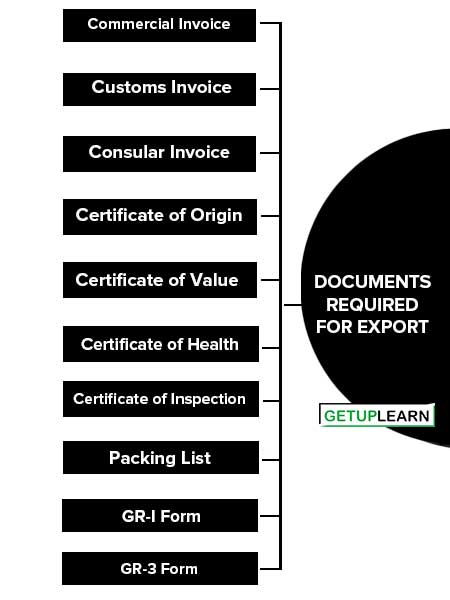
Documents Required for Export
The following are the most frequently required documents for an export shipment. These are the documents required for export:
- Commercial Invoice
- Customs Invoice
- Consular Invoice
- Certificate of Origin
- Certificate of Value
- Certificate of Health
- Certificate of Inspection
- Packing List
- GR-I Form
- GR-3 Form
- Bill of Lading
- Letter of Credit
- Airway Bill
- Marine Insurance Policy
Commercial Invoice
Commercial Invoice is the seller‘s bill for the merchandise. This is the basic document in an export transaction. It contains information on the basis of which duty will be assessed and all other documents are prepared.
It contains a description of the goods, the price per unit at a particular location, the total value of the goods, packing specifications, terms of sales, letter of credit, identification marks, and a number of the packages, names, and addresses of both buyers and seller, name of shipping vessel and the port of destination.
There is no standard form for a commercial invoice. The exporter can design his form, but the contents must comply with the regulations of the importing country. The commercial invoice is prepared and signed by the seller. It is submitted in triplicate. The main purpose of the commercial invoice is to check the appropriateness of goods shipped to be consistent with those mentioned in other documents.
Customs Invoice
The commercial invoice prepared on a special form as per the specifications of the customs authorities is known as a customs invoice. The prescribed forms are bought from commercial stationery stores.
Consular Invoice
This document is required in some importing countries. This is a special type of invoice signed by the importer’s consul located in the exporter’s country. There are prescribed forms which have to be bought from the consul of the importing country and as copies 6 have to be completed.
The invoice is in the language of the importing country stipulated that this invoice should not contain errors of any kind and erasures and strikeovers in typing or changes or additions in pen and ink are not allowed. Countries like USA, Canada, Philippines, Mexico, Taiwan, Turkey, and Liberia require consular invoices.
Certificate of Origin
This certificate has to be obtained by the buyer without which permission to import may be refused in some countries. The main aim of this document is to certify that a particular good was originally produced or manufactured in a particular country.
This certificate also establishes the right of the product to preferential duties to which it may be entitled. This document is required in countries where the preferential system of tariff is provided to goods from certain countries. A certificate of origin can also be useful to control the implementation of export quotas that have been established by international agreements such as coffee.
Certificate of Value
This certificate is intended to confirm the invoice value shown in the commercial invoice. The exporter has to sign this certificate of value stating that the invoice contains a true and full statement of the price paid for the goods. A certificate of value is one of the forms of invoice prescribed for shipments to most Commonwealth countries.
Certificate of Health
A certificate of health is required by many countries when animals, animal products, plants, plant products, and the like are exported. These certificates confirm that the goods are free from diseases, They do not contain insects or pests and the food products have been prepared according to the prescribed standards.
It is issued by the Department of Agriculture or the Department of Health of the exporting company.
Certificate of Inspection
This certificate is issued by one of the authorized inspection agencies in the exporter’s country.
Packing List
This list is prepared when the quantity, weight, or contents of the individual units in a shipment vary. It enables the receiver to check the shipment and sort out the packages and in weighing the goods. There is no specific form prescribed for this purpose.
GR-I Form
It is a declaration form prescribed by the R.B.I. This document is Filled in and submitted by the exporter declaring that the foreign exchange to be realized in lieu of goods exported will be deposited with the RBI. The form is prepared in duplicate.
The original copy has to be submitted to the customs authorities at the port of shipment. The duplicate copy of the form is submitted to the negotiating bank along with other documents after the shipment of the goods. These forms are sent back to the RBI by the customs authorities and by the bank.
GR-3 Form
GR-3 form is used to get the permission of RBI when the exporter wants to retain the proceeds in the exporting country with agents or branches abroad.
Bill of Lading
A Bill of Lading is the most important document in export trade. It is prepared by the exporter in a prescribed form. The form is to be obtained from the shipping company and filled in with the necessary information relating to the goods shipped and the same is to be signed by the shipping company.
The original copies signed by the shipping company become a negotiable title to the goods covered by the bill. It is necessary that the importer must have the original bills of lading before he can obtain the goods. Therefore, the exporter has to send them on the same ship or in advance by airmail.
Letter of Credit
Letter of credit, popularly known as LOC, is the most important form in the export trade. It is a promise by the overseas importer through his banker where the letter of credit is opened by him, to the exporter through his banker to pay the proceeds on the receipt of documents certifying the shipment of goods. The exporter should carefully examine the terms and conditions of the LOC.
Airway Bill
An Airway Bill is a receipt issued by an airline for the carriage of goods. It is also known as an air consignment note. It is not in a negotiable form and the same is indicated in the bill itself. The consignee’s name is mentioned in the bill and the goods are delivered to him. The consignor can retain control over the goods until payment is made.
The airway bill is issued in three parts. The first part is marked “for the carrier”. It is signed by the consignor or his agent. The second part is marked “for the consignee” and it is signed by the consignor and the carrier or his agent. The third part is marked “for the consignor” and it is signed by the carrier or his agent and handed over to the consignor when the goods are accepted by the carrier as air freight.
Marine Insurance Policy
Marine Insurance policy is also an important document in case of export trade. The policy is generally taken at the time when the goods are ready for shipment. The policy can be used as collateral security by the exporter when he wants an advance against credit.
Types of Foreign Exchange Exposure
Types of foreign exchange exposure may be classified into three broad types such as:
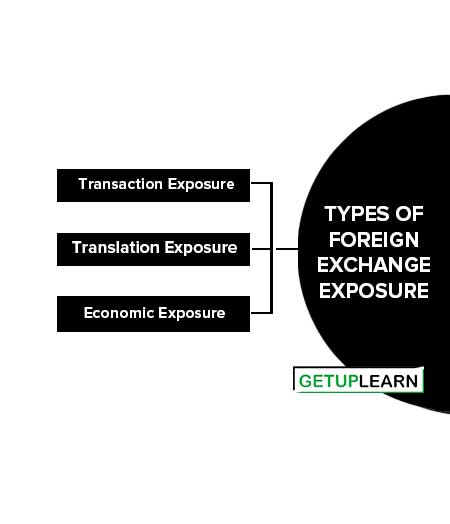
Transaction Exposure
When a firm has a payable or receivable denominated in a foreign currency, a change in the exchange rate will alter the amount of local currency received or paid. Such a risk or exposure is referred to as transaction exposure.
Translation Exposure
Translation exposure relates to the change in accounting income and balance sheet statements caused by the changes in exchange rates. That is the translation exposure results from the need to translate foreign currency assets or liabilities into the local currency at the time of finalizing accounts.
Economic Exposure
According to Van Horne, James C, economic exposure is defined as the “Change in the value of a company that accompanies an unanticipated change in exchange rates”. Economic exposure is considered the most important as it has an impact on the valuation of a firm.
Since economic exposure emanates from unanticipated changes, its measurement is not as precise and accurate as those of transaction and translation exposure; it involves subjectivity. According to Shapiro “It is based on the extent to which the value of the firm as measured by the present value of the expected future cash flows will change when exchange rates change”
Managing Foreign Exchange Risk
Foreign exchange risk management is the process through which finance managers try to eliminate or reduce the adverse impact of unfavorable changes in the foreign exchange rates to a tolerable level. These are the techniques used in managing foreign exchange risk:
Spot Exchange Transaction
Spot exchange transactions occur when currencies are traded for immediate delivery.
Forward Contracts
Forward contracts are widely used by business firms to hedge against adverse exchange rates. Business firms enter into a forward contract to buy or sell foreign currency in exchange for home currency, normally at a specific future date, at a predetermined exchange conversion rate.
The forward rate is agreed upon by the parties at the time of the making of the contract and remains fixed irrespective of future exchange rate fluctuations.
Currency Futures
These are more popularly known as “Futures Contracts” and are traded at the future markets. A futures contract is a standardized agreement to buy or sell a pre-specified amount of foreign currency in the futures market at some specified future date between the parties to the contract Interest rate futures.
Apart from currency futures, interest rate futures represent another major technique available to business firms. Interest rate futures can be used to hedge or reduce the risk of a rise in interest rates in the future.
Currency Options
A currency option is a financial instrument that provides its holder the right but no obligation to buy or sell a pre-specified amount of a foreign currency at a pre-determined rate in the future. While the buyer of an option wants to avoid the risk of adverse changes in the exchange rate, the seller of the option is prepared to assume the risk.
Options are of two types, namely call option and put option.
Call Option
In a call option, the holder has the right to buy a specific currency at a specific price on a specific maturity date or within a specified period of time. However, the holder of the option is under no obligation to buy the currency.
Such an option is to be exercised only when the actual price in the forex market, at the time of the exercising option, is more than the price specified in the call option contract.
Put Option
A put option confers the right but no obligation to sell a specified amount of currency at a pre-fixed price on or up to a specified date. Obviously, put options will be exercised when the actual exchange rate on the date of maturity is lower than the rate specified in the put option contract.
Swaps
Swaps are exchanges or swaps of debt obligations between two parties. In general, currency swaps are arranged between two firms or parties through a bank. Swaps are of two types namely, interest rate swaps and currency swaps.
Interest Rate Swaps
An interest rate swap is a transaction involving an exchange of one stream of interest obligations for another. Typically, it results in an exchange of fixed-rate interest payments for floating-rate interest payments. Occasionally, it involves an exchange of one stream of floating-rate interest payments for another.
Currency Swap
In a currency swap, both the principal and interest in one currency are swapped for principal and interest in another currency. On maturity, the principal amounts are swapped back.
What are the types of export documents?
The types of export documents are:
1. Trade Documents
2. Regulatory Documents
3. Export Assistance Documents
4. Foreign documentation.
What are the documents required for export?
The documents required for export are:
1. Commercial Invoice
2. Customs Invoice
3. Consular Invoice
4. Certificate of Origin
5. Certificate of Value
6. Certificate of Health
7. Certificate of Inspection
8. Packing List
9. GR-I Form
10. GR-3 Form.
What are the types of foreign exchange exposure?
The following are the types of foreign exchange exposure:
1. Transaction Exposure
2. Translation Exposure
3. Economic Exposure.
What is foreign exchange risk?
These are the techniques used in managing foreign exchange risk:
1. Spot Exchange Transaction
2. Forward Contracts
3. Currency Futures
4. Currency Options
5. Swaps.