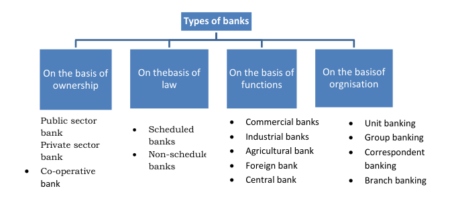
The Indian money market is not an integrated unit due to the existence of organized and unorganized sectors. The organized sector is fairly integrated. Both nationalized and private-sector commercial banks constitute the core of the organized sector.
Foreign banks, cooperative banks, the Reserve Bank of India (India’s central bank), finance companies, and mutual funds are some institutions that operate in the organized sector. The unorganized sector comprises indigenous bankers, moneylenders, and unregulated non-bank financial intermediaries such as chit funds, nidhis, etc.
Table of Contents
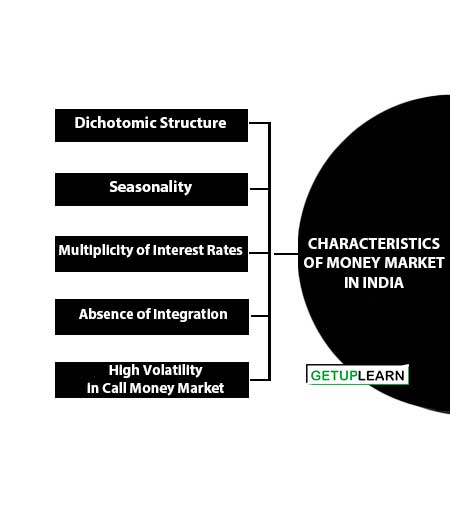
Characteristics of Money Market in India
Here are some of the characteristics of money market in India:
- Dichotomic Structure
- Seasonality
- Multiplicity of Interest Rates
- Lack of Organized Bill Market
- Absence of Integration
- High Volatility in Call Money Market
Dichotomic Structure
It is a significant aspect of the Indian money market. In both the organized money market as well as unorganized money markets, it has a simultaneous existence. The organized money market consists of all scheduled commercial banks, RBI, and other recognized financial institutions while the unorganized money market includes domestic money lenders, traders, indigenous bankers, etc.
The organized money market is in full control of the RBI but the unorganized money market remains outside the RBI’s control. Thus, both the organized and unorganized money market exists simultaneously.
Seasonality
The demand for money in the Indian money market is of a seasonal nature. The demand for money is generated from agricultural operations, as India is an agricultural predominant economy (though its dominance has reduced over the years).
More agricultural activities take place during the busy season i.e. between October and April, leading to a higher demand for money.
Multiplicity of Interest Rates
In the Indian money market, we have many levels of interest rates. They differ from period to period, from bank to bank, and even from borrower to borrower. Again in both organized and unorganized segments, the interest rates differ. Thus, there is an existence of a multiplicity of rates of interest in the Indian money market.
Lack of Organized Bill Market
The organized bill market is not prevalent in the Indian money market. Though the RBI tried to introduce the Bill Market Scheme (1952) and New Bill Market Scheme in 1970, yet it has a long way to go to reach at maturity stage. Hence, there is no properly organized bill market in India.
Absence of Integration
Integration is a very important feature of the Indian money market. The Indian money market is divided among several segments or sections which are hardly connected with each other. There is a lack of coordination among these different components of the money market.
High Volatility in Call Money Market
The call money market is a market for very short-term money. Here money is demanded at the call rate. Basically, the demand for call money comes from commercial banks and institutions such as the LIC, GIC, etc which suffer huge fluctuations and make this market highly volatile.
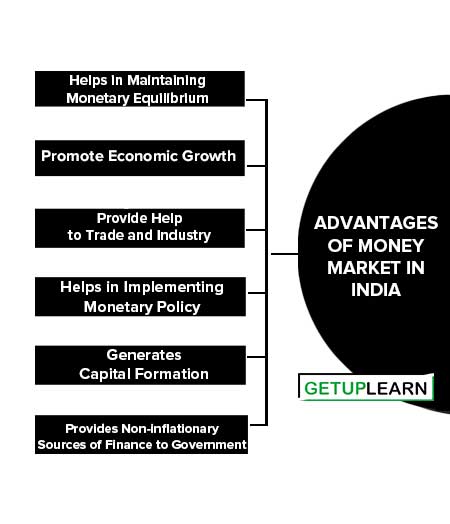
Advantages of Money Market in India
The major strength or advantages of money market in India are given below:
- Helps in Maintaining Monetary Equilibrium
- Promote Economic Growth
- Provide Help to Trade and Industry
- Helps in Implementing Monetary Policy
- Generates Capital Formation
- Provides Non-inflationary Sources of Finance to Government
Helps in Maintaining Monetary Equilibrium
Monetary equilibrium means maintaining the balance between the demand and supply of money for short-term monetary transactions. Money market instruments provide short-term finance as and when required. This helps in maintaining monetary equilibrium.
Promote Economic Growth
Through the instruments of the Money market, one can get funds available for various business activities pushing toward surplus capital formation. Indian money market efficiently provides money to needy business entrepreneurs as well as other players in the industry which promotes economic growth.
Provide Help to Trade and Industry
The money market provides adequate funds to trade and industry. Besides this, it also gives the facility of discounting bills of exchange for trade and industry. With the availability of finance, it becomes easier for trade and industry to attain more profit.
Helps in Implementing Monetary Policy
Monetary policy can be effectively implemented only through the instruments of the Money market. As the money market is governed by RBI, thus according to the changes in the economy, RBI brings changes in the Monetary Policy through money market instruments.
Generates Capital Formation
The money market provides investment avenues for short-term periods. Thus it inoculates the person to invest more in the money market instruments. As the money market is highly liquid, a person can get his/ her instrument converted easily. This helps in generating more capital formation in the economy.
Provides Non-inflationary Sources of Finance to Government
Government can also raise finance through investment in the money market. It is possible by issuing treasury bills in order to raise short-term loans. Raising finance through Treasury bills is non-inflationary as this does not lead to increases in prices. Thus money market provides a non-inflationary source of finance to the government.
Disadvantages of Money Market in India
Among the developing countries, the Indian money market is considered the advanced money market, but still it suffers from many weaknesses. These weaknesses affect the efficiency of the Indian Money market. Some of the important disadvantages of money market in India are:
- Absence of Integration
- Multiple Rate of Interest
- Insufficient Funds
- Shortage of Investment Instruments
- Shortage of Commercial Bill
- Lack of Organized Banking System
- Less Number of Players
Absence of Integration
The Indian money market is broadly classified into Organized and Unorganized Sectors. The former includes the legal financial institutions backed by the RBI. The unorganized sector is comprised of various institutions which are not backed by RBI such as indigenous bankers, money lenders, traders, etc. There is a lack of proper integration between these two sectors.
Multiple Rate of Interest
In the Indian money market, there exist too many rates of interest, especially in the banks. These rates are different for lending, borrowing, government activities, etc. Thus so many rates of interest create confusion among investors.
Insufficient Funds
With the seasonal changes, the Indian economy faces the problem of frequent shortages of financial resources. Lower income means lower savings by people and hence a lack of banking habits among people. It implies that the demand for money is more than the supply of money and hence the shortage of funds arises.
Shortage of Investment Instruments
In the Indian money market, there are various investment instruments such as Treasury Bills, Commercial Bills, Certificates of Deposits, Commercial Papers, etc. are used. But the size of the population and market of these instruments are inadequate.
Shortage of Commercial Bill
In India, the use of commercial bills is very limited as many banks keep large funds for liquidity purposes. Similarly, people preferred to do transactions in the form of cash and hence the scope for commercial bills is limited.
Lack of Organized Banking System
In India, the banking system suffers from major weaknesses such as the NPA, huge losses, and poor efficiency even though we have a big network of commercial banks. The absence of an organized banking system is again another major problem for the Indian money market.
Less Number of Players
In India, the players in the money market are very less in number. Players are those entities who can act as mediators.
FAQs About the Money Market in India
What are the characteristics of money market in India?
The characteristics of money market in India are:
1. Dichotomic Structure
2. Seasonality
3. The Multiplicity of Interest Rates
4. Lack of Organized Bill Market
5. Absence of Integration
6. High Volatility in Call Money Market.
What are the advantages of money market in India?
The advantages of money market in India are:
1. Helps in Maintaining Monetary Equilibrium
2. Promote Economic Growth
3. Provide Help to Trade and Industry
4. Helps in Implementing Monetary Policy
5. Generates Capital Formation
6. Provides Non-inflationary Sources of Finance to Government.
What are the disadvantages of money market in India?
The disadvantages of money market in India are:
1. Absence of Integration
2. Multiple Rate of Interest
3. Insufficient Funds
4. Shortage of Investment Instruments
5. Shortage of Commercial Bill
6. Lack of Organized Banking System
7. Less Number of Players.