Table of Contents
- 1 What is Deposit Mobilization?
- 2 Deposit Mobilization Strategy
- 3 Principles of Deposit Mobilization of Schemes
-
4 Important Deposit Schemes
- 4.1 Current Account
- 4.2 Saving Account
- 4.3 Fixed Deposits
- 4.4 Cash Certificates
- 4.5 Daily Saving Scheme
- 4.6 Minor Saving Scheme
- 4.7 Monthly Interest Income Schemes
- 4.8 Retirement Scheme
- 4.9 Farmer Deposit Scheme
- 4.10 House Safe Saving Scheme
- 4.11 Housing Deposit Scheme
- 4.12 Educational Saving Scheme
- 4.13 Insurance Linked Scheme
- 5 Problems in Deposit Mobilization
- 6 FAQs Related to the Deposit Mobilization
What is Deposit Mobilization?
Commercial banks play an indispensable role in the development of the country. The main function of a commercial bank is the management of its liabilities and assets.
Liability management consists of the activities involved in getting funds from depositors and other creditors and determining the appropriate mix of funds for a particular bank, whereas asset management refers to the allocation of funds among investment alternatives. It is concerned with advances and loans.
Deposits are the most important source of funds for commercial banks. Commercial banks almost completely rely on deposits for funds. The survival of a bank is based on the quantum of deposits held by it and the manner in which deposits are managed.
Banks mobilize savings from people in urban and rural areas and make funds available for lending. Banks are always engaged in working out new plans, and policies to raise more and more funds from people.
Deposit Mobilization Strategy
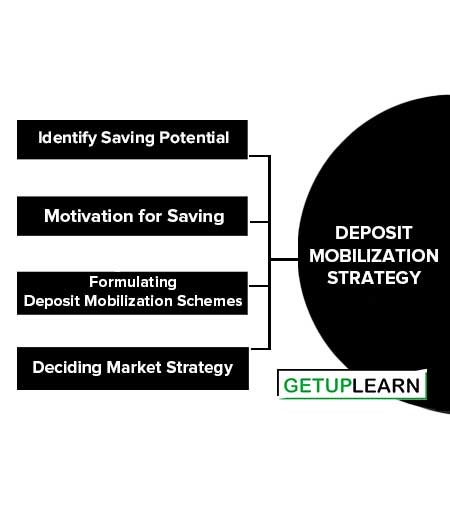
n the face of competition as a result of the liberalization of the economy, each and every bank has to formulate a suitable strategy for the mobilization of deposits by keeping the focus on the segment of the population from which deposits are intended to be mobilized. The formulation of a deposit mobilization strategy involves a number of steps such:
- Identify Saving Potential
- Motivation for Saving
- Formulating Deposit Mobilization Schemes
- Deciding Market Strategy
Identify Saving Potential
The bank must identify the saving potential of the people. For this purpose, the bank must know the strength of working people, their sources of income, their economic conditions, their habit of saving, family income, preference of investment, etc. high-income groups will provide more money for deposits in the bank than the lower income group of society.
Motivation for Saving
The bank should also take into account the motivation for savings to attract more deposits. As Banking Commission 1972 has said that some of the motivations for saving could be :
- To own a house
- To provide for children’s education and marriage
- To provide for old age
- To provide for medical expenditures and so on.
To make socially gainful use of such motivations, the banks should introduce deposit schemes that are able to exploit the motivation.
Formulating Deposit Mobilization Schemes
The bank should know the needs of people and tailor different schemes according to their needs, requirements, and preferences for deposits. For example, daily wage earners and small vendors or traders prefer to spare some money daily as their savings.
Neither it is convenient nor could they afford to go to the bank daily to deposit small money. In such cases, the bank should introduce schemes of daily collection and depute its own employees for the collection of the money. Different banks have floated different schemes to mobilize savings from the public taking into account the accessibility, convenience, feasibility, and capacity of depositors.
Deciding Market Strategy
After the formulation of mobilization schemes, the banks should decide on the market strategy. Different banks have different strategies due to competition among them. The marketing strategy should be formulated within the framework of corporate objectives and the overall strategy of the bank.
The success of the marketing strategy will depend upon the involvement and effort of the staff. Therefore, all those involved in the promotion of products of the bank should understand the strategy for its proper implementation.
Principles of Deposit Mobilization of Schemes
To attract more deposits, the banks have to formulate new schemes of different natures and suitability to the different classes of investors in both rural and urban centers. These schemes must satisfy the following fundamental principles:
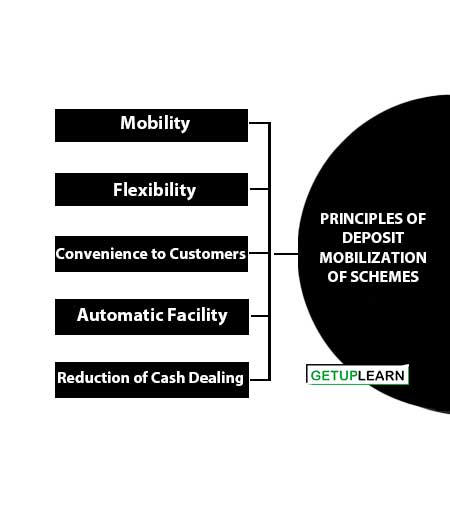
Mobility
It includes mobile bank schemes, small deposit schemes, cash collection agent schemes, etc.
Flexibility
It refers to providing morning services, evening services, and Sunday and holiday services.
Convenience to Customers
It includes those facilities which make banking services convenient to customers. These include the opening of branches in residential areas, shopping complexes, industrial complexes, and campuses of educational institutions.
Automatic Facility
It includes the use of technical devices and the computerization of services.
Reduction of Cash Dealing
It refers to traveler cheques and the use of credit cards, etc.
Important Deposit Schemes
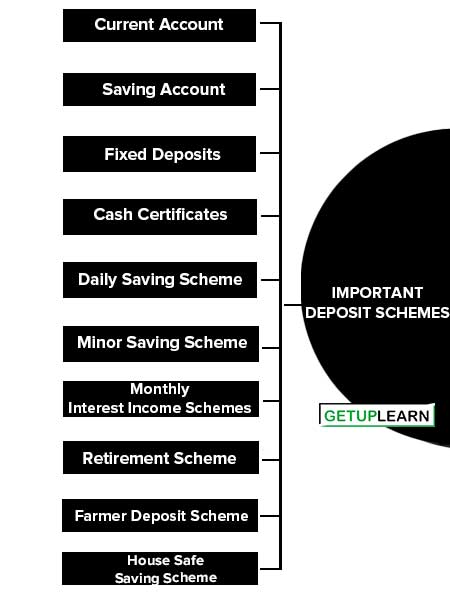
Following are some of the various deposit schemes offered by banks to attract deposits:
- Current Account
- Saving Account
- Fixed Deposits
- Cash Certificates
- Daily Saving Scheme
- Minor Saving Scheme
- Monthly Interest Income Schemes
- Retirement Scheme
- Farmer Deposit Scheme
- House Safe Saving Scheme
- Housing Deposit Scheme
- Educational Saving Scheme
- Insurance Linked Scheme
Current Account
The current account is meant for those customers who can withdraw their deposits at any time. There is no limit on the number of withdrawals. This scheme is most suitable for businessmen for their day-to-day business transactions. No interest is paid on these deposits.
Saving Account
The saving account is meant for the deposits of small depositors. The depositors can withdraw money from this account as per rules fixed by the bank. Interest is paid on these deposits.
Fixed Deposits
fixed deposits are those schemes on which a higher rate of interest can be earned. The funds are deposited with the bank for a specified period of time under this scheme. A higher rate of interest is paid on fixed deposits.
Cash Certificates
The cash certificate scheme is also a kind of fixed deposit scheme. Interest is included in the final payment. In fact, the maturity value payable is discounted at the interest rates payable on long-term deposits. The discounted amount is the value that a customer is asked to pay to get a cash certificate.
Daily Saving Scheme
this scheme is meant to attract the deposits of very small depositors. Daily collections are made by the agents of the bank at the doors of the depositors. The accumulated amount together with the interest is repaid after five years.
Minor Saving Scheme
This scheme was introduced as an attempt to encourage children to develop the habit of savings. The withdrawal facility is available in the scheme, e.g., the Kiddy Bank scheme of Andhra Bank.
Monthly Interest Income Schemes
These schemes are fixed deposits on which interest is paid monthly instead of yearly or half-yearly. Interest is paid either by way of cash or is credited to the current account or saving deposit account also.
Retirement Scheme
In this scheme, monthly deposits are collected for a number of years. After a certain period, the interest amount is doubled and paid annually in monthly installments.
Farmer Deposit Scheme
This scheme is introduced to attract the deposits of the farmers. Under this scheme, the farmers can deposit their income once or twice a year. They can also spend one-tenth of their deposits every month.
House Safe Saving Scheme
This scheme is introduced recently by the banks. A small portable safe is provided to the depositor at the residence. The key to the safe is kept by the bank. The depositor puts his small savings in it as convenient to him and after some time hands the same over to the bank and gets it entered into his account.
Housing Deposit Scheme
This scheme is suitable for those who want to acquire or construct their own houses. Account holders have to deposit monthly installments for a fixed period and at maturity the depositor can obtain the loan in a predetermined multiple of the amount of the deposit at concessional rates.
Educational Saving Scheme
This scheme is planned to enable the account holder to meet a liability, in the future, by saving regularly over a given period of time, e.g. children’s education, marriage, etc.
Insurance Linked Scheme
This scheme provides life insurance protection on the life of an account holder covered under a special Insurance Linked Saving Bank Account.
Men not below 18 years of age and not above 49 years of age and women in the same age group, if they have an independent regular income by way of salary, professional income, and rent dividend on shares are eligible for opening an account under this scheme.
Problems in Deposit Mobilization
The main problems in deposit mobilization are discussed below:
- Lack of Innovative Deposit Schemes
- Schemes only for Urban Depositors
- Lack of Publicity Techniques
- Lack of Trained Staff
- Lack of Services Facilities
Lack of Innovative Deposit Schemes
The strategy for deposit mobilization depends upon the formulation and implementation of various deposit schemes of the banks. All the deposit schemes are identical in their content and differ only in name. There is a need for the formulation of new schemes of a different nature according to different classes of depositors.
Schemes only for Urban Depositors
Most of the current deposit mobilization schemes are meant for urban depositors. They neglect the potential rural depositors. The banks should formulate the schemes according to the needs and requirements of rural depositors and also mobilize rural savings.
Lack of Publicity Techniques
Most of the banks have used the same publicity techniques related to deposit mobilization both for rural and urban areas. But the rural areas require a different type of publicity.
Lack of Trained Staff
The bank staffs at various levels are not adequately aware of different deposit mobilization schemes. As a result, the customers do not get adequate guidance regarding the profitability of these schemes.
Lack of Services Facilities
Banking is a service-oriented industry. The customers are not able to receive satisfactory services from the staff. Customer service is an important problem in the mobilization of deposits. It should be handled properly.
What is the deposit mobilization strategy?
The following is the deposit mobilization strategy:
1. Identify Saving Potential
2. Motivation for Saving
3. Formulating Deposit Mobilization Schemes
4. Deciding Market Strategy.
What are the important deposit schemes?
The main important deposit schemes:
1. Current Account
2. Saving Account
3. Fixed Deposits
4. Cash Certificates
5. Daily Saving Scheme
6. Minor Saving Scheme
7. Monthly Interest Income Schemes
8. Retirement Scheme
9. Farmer Deposit Scheme
10. House Safe Saving Scheme.