Table of Contents
Meaning of Insurance
The term “insurance” can be defined in both financial and legal terms. The financial definition focuses on an arrangement that redistributes the cost of unexpected losses. That is the collection of a small premium payment from all exposed and distributed to those suffering loss.
The legal definition focuses on a contractual arrangement whereby one party agrees to compensate another party for losses. The financial definition provides for the funding of the losses whereas the legal definition provides for the legally enforceable contract that spells out the legal rights, duties, and obligations of all the parties to the contract. Let us have a look at these definitions.
Functions of Insurance
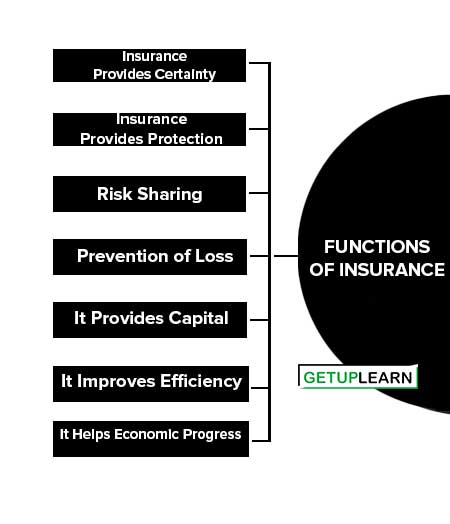
The functions of insurance are of two types. They are primary functions and secondary functions:
- Insurance Provides Certainty
- Insurance Provides Protection
- Risk Sharing
- Prevention of Loss
- It Provides Capital
- It Improves Efficiency
- It Helps Economic Progress
Primary Functions
The primary functions of insurance include the following:
Insurance Provides Certainty
Insurance provides certainty of payment at the uncertainty of loss. The uncertainty of loss can be reduced by better planning. But, the insurance relies upon the insured for such difficult tasks.
There are different types of uncertainty in a risk. In other words, there are uncertainties of happening of time and amount of loss, insurance removes all these uncertainties and the assured is given the certainty of payment of loss.
Insurance Provides Protection
The main function of insurance is to provide protection against the probable chances of loss. In other words, insurance guarantees the payment of loss to the insured in order to protect him from his sufferings. Insurance cannot present the happening of risk but can provide for losses at the happening of the risk.
Risk Sharing
The risk is uncertain, and hence the loss arising from risk is also uncertain. When risk takes place, the risk is shared by all persons who are exposed to the risk. In ancient days, risk-sharing is done only at the time of damage or death. But, today, risk sharing is done by each and every insured on the basis of the probability of risk.
Secondary Functions
The secondary functions of insurance include the following:
Prevention of Loss
The insurance forms hand with institutions that are engaged in preventing losses to society. It is because the reduction in loss causes the lesser payment to the assured. Lesser payment results in more savings for the insurer.
More savings to the insurer results in lesser premiums to the insured. Lesser premium results in more business for the insurer. Finally, more business results in lesser shares to the insured.
It Provides Capital
It provides capital to society. The surplus and accumulated funds are invested in productive channels. The shortage of capital in society is minimized with the help of investment in insurance. The industry, the business, and individuals are benefited from the investments of the insurers.
It Improves Efficiency
Insurance eliminates worries and miseries of losses at death and destruction of property. A protected person from risks can devote his body and mind to better achievement. It improves not only his efficiency but also the efficiency of the masses.
It Helps Economic Progress
Insurance by protecting society from losses of damage, destruction, and death, provides an initiative to work hard for the betterment of society. Capital is a factor of economic progress provided by the masses.
What are the functions of insurance?
The functions of insurance are 1. Insurance Provides Certainty 2. Insurance Provides Protection 3. Risk Sharing 4. Prevention of Loss 5. It Provides Capital 6. It Improves Efficiency 7. It Helps Economic Progress.