Table of Contents
What are Currency Options?
With the opening and integration of capital markets worldwide, the free flow of foreign currency from one country to another has increased at a faster pace. Foreign currency options are used by different market participants e.g. exporters, importers, speculators, arbitrageurs, bankers, traders, and financial institutions.
Currency options are devised to protect investors against unfavorable movements/fluctuations in foreign exchange rates. Like other option instruments, currency options are also financial instruments that give the option holder the right, not the obligation to buy or sell a particular currency at a specific exchange rate (price) on or before an expiration date. Here the underlying asset is the foreign currency.
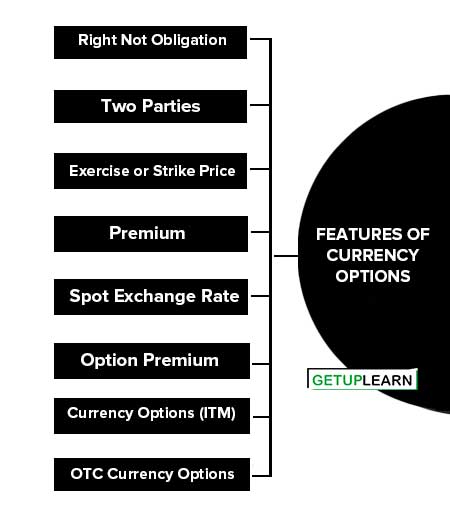
Features of Currency Options
These features of currency options which explained below:
- Right Not Obligation
- Two Parties
- Exercise or Strike Price
- Premium
- Spot Exchange Rate
- Option Premium
- Currency Options (ITM)
- OTC Currency Options
Right Not Obligation
The currency options give the holder to buy or sell a currency right (not obligation at a fixed price (exchange rate) for a specified time period.
A call currency option gives the holder to buy a currency at a fixed rate (price at a specified time and a put currency option gives the owner the right to sell a currency at a fixed price (exchange rate) at a specified time. the buyer is known as the holder and the seller is called the writer of the currency option. The writer gets the premium from the holder for the obligation undertaken in the contract.
Two Parties
There are two parties in the contract. The buyer (holder) and the seller (writer). In other words, a yen call option gives the holder the right to buy yen against the rupee, which is also a rupee put option.
Exercise or Strike Price
The exercise/strike price is the rate at which the currency is exchanged for another.
The premium is the cost or price or value of the option itself.
Spot Exchange Rate
The spot exchange rate is the current rate of exchange.
The option premium is paid in advance by the buyer to the seller which lapses irrespective of whether the option is exercised or not. In the OTC market, the premium is quoted as a percentage of the transaction amount, whereas in domestic currency amount per unit of foreign currency is in the exchange-traded options.
Currency Options (ITM)
The currency options can be in the money (ITM), out of the money (OTM) or at the money (ATM) as explained in the earlier lessons.
OTC Currency Options
Currency options can be traded on the counter (OTC) market as well as exchange-traded. OTC currency options are custom-tailored and have two categories: retailer and wholesale markets. The retail segment of currency options markets is influenced by participants such as traders, financial institutions, and portfolio managers who trade (purchase) from banks.
The wholesale currency options market is participated by big commercial banks, financial institutions, and investment banking firms for speculation or arbitrage purposes.
This market has so many limitations like- relatively lower liquidity due to its customer-tailored nature; non-standardized, risk of non-performance by the writer (counterparty risk); mispricing due to non-competitiveness; differing exercise prices, expiration date, amount, and premium.
On the other hand, the currency option can also be traded through recognized exchanges worldwide. The first such exchange to introduce currency options trading is Philadelphia Stock Exchange (PHLX) in 1982.
Since then a lot of exchanges have been involved in currency option trading. The exchange-traded options are cleared through the clearing house, which is the counterparty to every option contract and guarantees the fulfillment of the contracts.
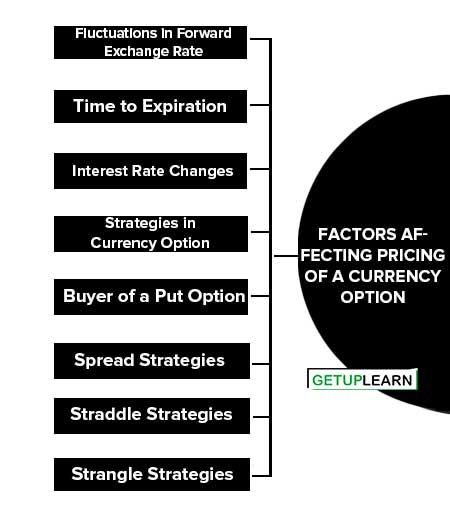
Factors Affecting Pricing of a Currency Option
There are so many determinants of the valuation of a currency call option. These are factors affecting the pricing of a currency option discussed below:
- Fluctuations in Forward Exchange Rate
- Time to Expiration
- Interest Rate Changes
- Strategies in Currency Option
- Buyer of a Put Option
- Spread Strategies
- Straddle Strategies
- Strangle Strategies
Fluctuations in Forward Exchange Rate
Change in the spot exchange rate has a direct impact on the time value of the currency option. Past and expected changes in the spot exchange rates should be taken care of by the traders of currency options. This sensitivity is known as Delta (Δ) the value of which is given by:
| Δ Premium Change Premium Δ (Delta) = ———————— = ———————————– Δ Spot Exchange Rate Change in Stock Exchange Rate |
Time to Expiration
The longer the time to maturity, the higher will be the value of the currency option. This sensitivity is known as theta and is measured by the ratio of relative change in premium w.r.t. time.
| Δ Premium Theta = ———————— Δ Time |
The longer maturity currency options have better value because with the time period expiring to maturity the time value of currency option deteriorates.
Interest Rate Changes
The differential in the interest rates has also an impact on the valuation of currency options. The change may be in the interest rate of domestic currency or in the foreign currency. There are two measures to quantify this sensitivity i.e. Rho and Ph. Rho is the ratio of change in premium paid in foreign currency option w.r.t. change in the interest rate in domestic currency.
| Δ Premium in US Doller Rho (ρ) = ———————— Δ Rs. Interest Rate |
On the other hand φ (Phi) is the ratio of changes in premium in domestic currency w.r.t. change in the interest rates.
| Δ Premium φ (phi) = ———————— ΔForeign Interest Rate |
When interest rates on foreign currency are higher than the interest rate on the domestic currency, the foreign currency sells forward at a discount and vice-versa. When the domestic interest rate rises, the trader should buy a call option on a foreign currency option to avoid loss due to an increase in the value of the option.
Strategies in Currency Option
The strategies for options trading have been discussed in lesson 8. To give a small view of the strategies in currency options, the following strategies can be used: The currency options trader definitely looks for the maximum trade-off (payoff) from exercising the option.
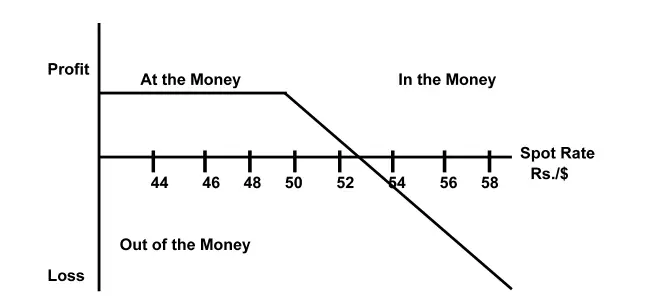
If an investor buys a call, then he will buy in anticipation of a rise in the exchange rate of that currency in the future. Suppose an Indian foreign exchange dealer anticipates a rise in the exchange rate from Rs. 52/$ then he will get a profit as shown in Figure.
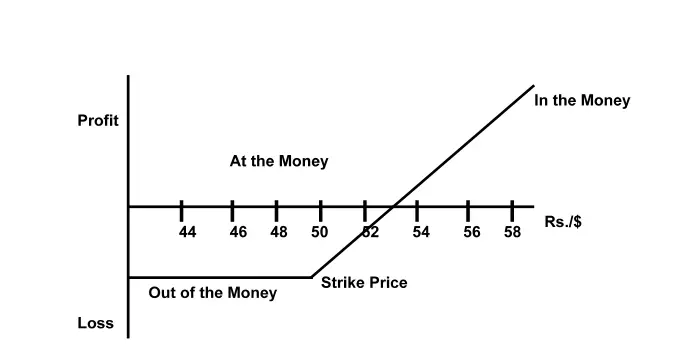
Profit = Spot exchange rate – (Strike price + Premium)
If there is an expected fall in the spot rate of the currency option than the strike rate for a seller (writer) he will not exercise the option.
The profit = Premium – (spot rate – Strike rate).
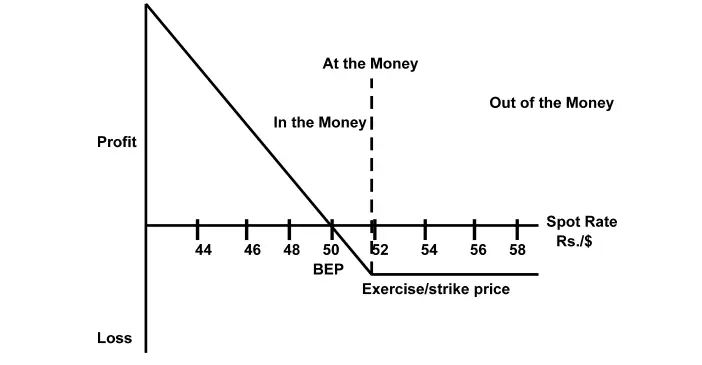
Buyer of a Put Option
In a currency put option, the investor will exercise the option if the current spot rate is lower than the strike price. The profit in this case will be:
Profit = Strike Price – (Sports Rate + Premium)
The buyer of the currency put option has enormous potential to earn and the loss is limited to the amount of premium paid to the writer.
The profit and payoff of a writer (seller) of a put option are given by the following Fig. 6.9. The writer will not exercise the option if the spot price is less than the strike price.
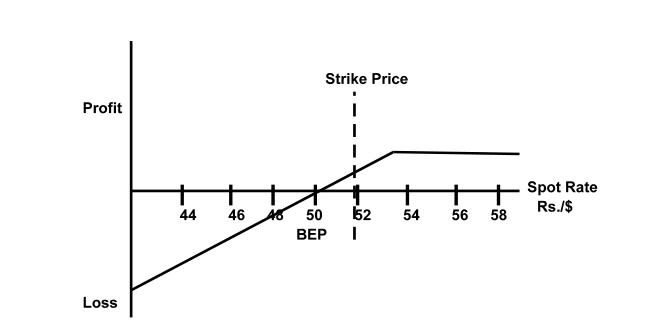
The profit will be given by: Profit = Premium – (Strike Rate – Spot Price)
Spread Strategies
In these strategies, both calls or puts are purchased or sold simultaneously. There may be bull spread, bear spread, butterfly spreads, calendar spread and diagonal spreads, etc.
Straddle Strategies
A straddle of currency options is created by buying or selling a call and put with a similar strike rate and expiration date.
Strangle Strategies
Like in straddle, strangle has the same strategy but for the difference in strike prices of the call and the put.
FAQs About the Currency Options
What are the features of currency options?
The following are the features of currency options:
1. Right Not Obligation
2. Two Parties
3. Exercise or Strike Price
4. Premium
5. Spot Exchange Rate
6. Option Premium
7. Currency Options (ITM)
8. OTC Currency Options.
What are the factors affecting pricing of a currency option?
The factors affecting pricing of a currency option are:
1. Fluctuations in Forward Exchange Rate
2. Time to Expiration
3. Interest Rate Changes
4. Strategies in Currency Option
5. Buyer of a Put Option
6. Spread Strategies
7. Straddle Strategies
8. Strangle Strategies.