Table of Contents
What is Unit Banking System?
Under a unit banking system, an individual bank operates through a single office. The size and area of operations of a Unit Bank are much smaller as compared to those of a bank under a branch banking system.
According to Shapiro, Solomon, and whit, “An independent unit bank is a corporation that operates one office and that is not related to each other banks through either ownership or control”. The unit banking system originated and grew in the U.S.A.
The operations of banks in the USA are not governed by one set of laws. Since states have also the power to enact banking laws, banks are governed by the legislative output of the federal government and state governments. Some states do not allow the opening of branches at all. Some states allow the opening of branches within the state or a town. National Bank established under Federal laws can open branches anywhere.
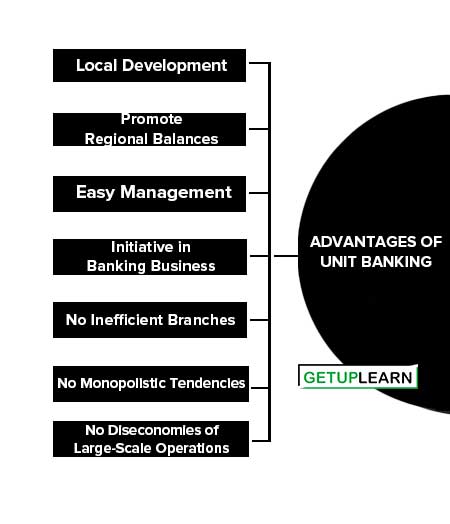
Advantages of Unit Banking
These are the following advantages of unit banking given below:
- Local Development
- Promote Regional Balances
- Easy Management
- Initiative in Banking Business
- No Inefficient Branches
- No Monopolistic Tendencies
- No Diseconomies of Large-Scale Operations
Local Development
Unit banking is localized banking. The Unit bank has the specialized knowledge of the local problems and serves the requirements of the local people in a better manner than branch banking. The funds of the locality are utilized for local development and are not transferred to other areas.
Promote Regional Balances
Under the Unit banking system, resources of rural and backward areas are not transferred to the big industrial commercial centers. This tends to reduce the regional imbalance.
Easy Management
The management and supervision of a unit bank are much easier and more effective. There are fewer chances of fraud and irregularities in the financial management of the Unit banks.
The manager of a local bank has greater chances of maintaining a friendly and personal relationship with the customers in the locality. He can easily acquire the personal knowledge of his customers, which is essential for his success.
Initiative in Banking Business
Unit banks have full knowledge of and greater involvement in the local problems. They have the initiative to tackle these problems through financial help.
No Inefficient Branches
Under a unit banking system, weak and inefficient branches are automatically eliminated. No protection is provided to such banks.
No Monopolistic Tendencies
Unit banks are generally small in size. Hence, there is no scope for monopolistic tendencies under a unit banking system.
No Diseconomies of Large-Scale Operations
Unit banking is free from the diseconomies and problems of large-scale operations which are generally by the branch banks.
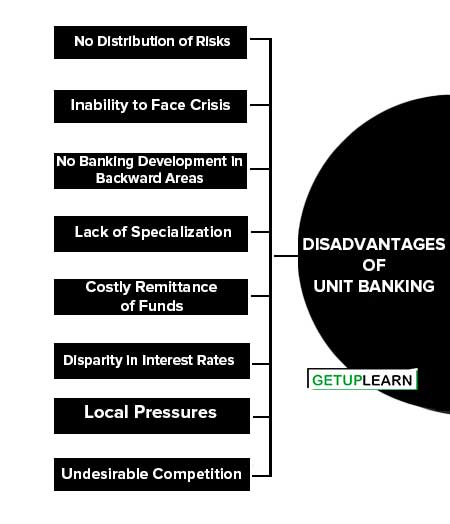
Disadvantages of Unit Banking
The following are the disadvantages of unit banking system:
- No Distribution of Risks
- Inability to Face Crisis
- No Banking Development in Backward Areas
- Lack of Specialization
- Costly Remittance of Funds
- Disparity in Interest Rates
- Local Pressures
- Undesirable Competition
No Distribution of Risks
Under unit banking, the bank operations are highly localized. Therefore, there is little possibility of distribution and diversification of risks in various areas and industries.
Inability to Face Crisis
Limited resources of the unit banks also restrict their ability to face financial crisis. These banks are not in a position to stand a sudden rush of withdrawals.
No Banking Development in Backward Areas
Because of their limited resources, unit banks cannot afford to open uneconomic banking businesses in smaller towns and rural areas. Hence, these areas remain unbanked.
Lack of Specialization
Because of their small size, unit banks are not able to introduce and get advantages of division of labor and specialization. Such banks cannot afford to appoint highly trained and specialized staff.
Costly Remittance of Funds
A Unit bank has no branches in other places. As a result, it has to depend upon the correspondent banks for the transfer of funds which is very expensive.
Disparity in Interest Rates
Since easy and cheap movement does not exist under the unit banking system, interest rates vary considerably at different places.
Local Pressures
Unit banks are highly localized in their business. Hence, the local pressures and interferences generally disrupt their normal functioning.
Undesirable Competition
Unit banks are independently run by different managements. This results in undesirable competition among the unit banks. Although both the branch banking system and unit banking system have their relative merits and demerits. But the merits of the former outweigh those of the latter.
There has grown a general tendency in favor of the branch banking system mainly because of large financial resources, economies of large operations, and effective control by the central bank. Experience has shown that the unit banking system is hampered by limited resources and does not work under economic depression.
Now-a-day, the branch banking system is especially suitable for underdeveloped countries. The entire banking system in India has developed on the lines of a branch banking system.
What are the advantages of unit banking?
The advantages of unit banking are:
1. Local Development
2. Promote Regional Balances
3. Easy Management
4. Initiative in Banking Business
5. No Inefficient Branches
6. No Monopolistic Tendencies
7. No Diseconomies of Large-Scale Operations.
What are the disadvantages of unit banking?
These are the disadvantages of unit banking:
1. No Distribution of Risks
2. Inability to Face Crisis
3. No Banking Development in Backward Areas
4. Lack of Specialization
5. Costly Remittance of Funds
6. Disparity in Interest Rates
7. Local Pressures
8. Undesirable Competition.


