Table of Contents
- 1 What is Demand Measurement?
- 2 What is Sales Forecast?
- 3 4 Measures of Market Demand
-
4 Concept of Demand Measurement
- 4.1 Market Demand
- 4.2 Market Forecast
- 4.3 Market Potential
- 4.4 Company Demand
- 4.5 Company Sales Forecast
- 4.6 Company Sales Potential
- 4.7 Opinion of Executives
- 4.8 Sales Force Composite Method
- 4.9 Customer’s Expectations
- 4.10 Statistical Sampling
- 4.11 Time Series Analysis
- 4.12 Correlation Analysis
- 4.13 Delphi Method
- 5 FAQ Related to Demand Measurement
What is Demand Measurement?
Every company is curious to know the existing status of its product, its prospects, the specific time period who is their customer, and whether there are chances to increase the sales and market share in the market.
What is Sales Forecast?
A sales forecast can be defined as an estimate for sales in terms of monetary and volume, for a specific period, with a selected marketing plan, under an envisaged economic and marketing environment. Sales forecasting serves as the starting point for all business activities of a company.
These are decisions taken by the sales forecasting:
- Number of Salesmen required in achieving sales quotas or objectives.
- Allocation of sales quota to each salesman.
- Determinations of sales force compensation plan.
- Determination of sales territories based on market potential.
-
Advertising and sales promotion programs.
-
Physical distribution and channel selection.
-
Pricing decisions and strategy.
- Production plan.
- Inventory control and purchasing.
- Estimating standard costs.
-
Budgeting and controlling expenses.
- Planning Requirements.
The marketing mix revolves around the sales forecasts made by the company for its product.
4 Measures of Market Demand
A sales forecast can be based on market demand. According to Kotler, Kevin, and Keller, 90 different types of demand estimates could be prepared by a company for its products.
A company can measure demand for six different product levels, five different space levels, and three different time levels. Each serves a specific purpose. A company might forecast short-run demand, plan production, borrow cash, and also forecast regional demand.
The market is dynamic and forecasts depend on the type of market. Following are 4 ways of measures of market demand:
- The potential market is the set of consumers who have an interest in a market offer, but their interest is not enough to define the market unless they acquire sufficient income and access to the product.
- The available market is the set of consumers who have interest, income, and access to a particular offer.
- The qualified available market is the set of consumers who have interest, income, access, and qualification for the market offer.
- The target market is part of the qualified available market the company decides to pursue.
- The penetrated market is the set of consumers who are buying the company’s product.
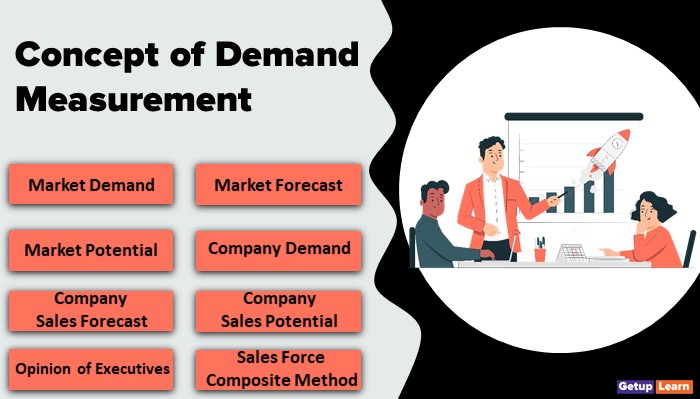
Concept of Demand Measurement
Following are the concepts of demand measurement for better understanding:
- Market Demand
- Market Forecast
- Market Potential
- Company Demand
- Company Sales Forecast
- Company Sales Potential
- Opinion of Executives
- Sales Force Composite Method
- Customer’s Expectations
- Statistical Sampling
- Time Series Analysis
- Correlation Analysis
- Delphi Method
Market Demand
In order to find the Total market demand, the Marketer needs to evaluate the opportunities available in the market. Market demand for the product is the volume that would be bought by a target group of customers in a target geographical area in a specific time period in a specified marketing environment under a specific marketing program.
Market Forecast
Only a small amount of marketing expenditure and efforts will actually occur. The market demand corresponding to this level is called the market forecast.
Market Potential
The market potential is the highest limit approached by market demand as industry marketing expenditures approach infinity for a given marketing environment.
Company Demand
Company demand is the company’s estimated share of market demand at alternative levels of company marketing efforts in a given time period. This share will depend on how its products, services, prices, communications, etc. are perceived by consumers relative to the competitors.
Company Sales Forecast
This is the expected level of company sales based on a chosen marketing plan and an assumed marketing environment. Related to the company sales forecasts, there are two additional concepts involved. First is a “sales quota, ” which is the sales goals set for a product line, company division, or sales officer.
Generally, sales quotas are set slightly higher than estimated sales to stretch the sales forces’ effort. The second is a “sales budget”, which is a conservative estimate of the expected volume of sales and is used for making current purchasing, production, and cash flow decisions.
The Sales budget is based on the sales forecast and the need to avoid excessive risk. Sales budgets are generally set slightly lower than the sales forecast.
Company Sales Potential
This is the sales limit approached by company demand as the company’s marketing efforts increase relative to that of competitors. The absolute limit of company demand is, of course, the market potential. For estimating current demand, companies estimate total market potential, then analyze and determine the area market potential (territory–wise), industry sales, and market shares.
Opinion of Executives
This is one of the oldest methods where the executive in charge of the business makes assumptions for future sales based on personal knowledge based on market information, through customer contacts, or by reading published data. The weakness of this method is that it lacks of scientific validity and subjectivity.
Sales Force Composite Method
Many organizations make their sales forecast on the basis of the estimate given by salesmen. The sales manager prepares the consolidated sheet territory or region-wise according to the estimate given by each salesperson. As salespersons are in direct contact with the customers they can provide first–hand information.
Customer’s Expectations
Customers can be requested to communicate their buying intentions in the coming period. This is suitable for businesses selling products to a few key customers (like in industrial marketing). If the customers’ expectations are accurate, sales forecasts will also be accurate.
Statistical Sampling
Sampling can be used to get total sales estimates. Based on a sample survey done in representative subgroups of territories, data can be extended or generalized to get the total sales forecast.
Time Series Analysis
This is the mathematical projection of future sales. It involves the projection of past sales trends into the future (trend extrapolation). To predict future sales, an analysis of four kinds of historical sales variations is done:
- Seasonal Variations
- Business Cyclical variations (depression, boom, slump, etc.)
- Long-term trends in sales
- Irregular or unexplained variations
By isolating variations in sales, an analyst can estimate with accuracy the sales forecast.
Correlation Analysis
When there is a close relationship between sales volume and a well–known economic indicator or index, a correlation study can be done. A high correlation means that the extrapolated index values will indicate future sales volume. E. g. : Sales of petrol are related to automobile sales.
Delphi Method
This is also a form of expert opinion method used especially for working out broad-based, futuristic estimates rather than sales forecasts. In this method, a panel of experts in the field is interviewed with the help of a questionnaire and their reactions and opinions are recorded.
An analysis of the result gives the final estimates. Since no single sales forecasting method is perfect, companies and marketers generally use a combination of forecasting methods to ensure that they get reliable estimates.
what are the concept of demand measurement?
Concept of demand measurement are given below:
1. Market Demand
2. Market Forecast
3. Market Potential
4. Company Demand
5. Company Sales Forecast
6. Company Sales Potential
7. Opinion of Executives
8. Sales Force Composite Method
9 Customer’s Expectations
10. Statistical Sampling.