Table of Contents
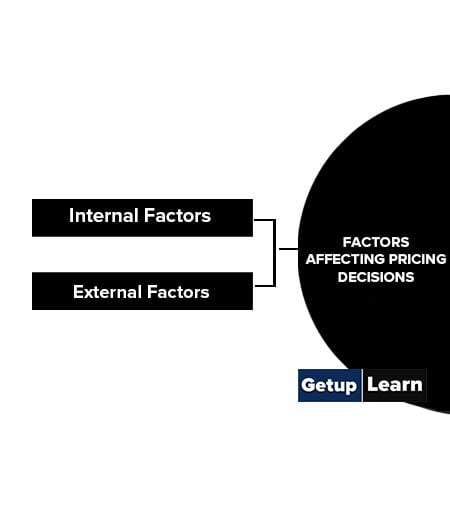
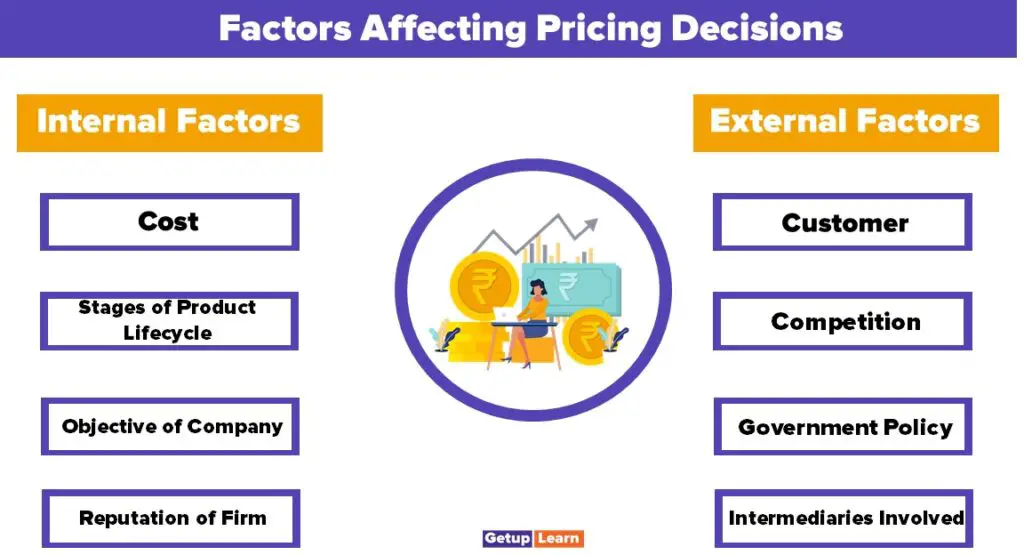
Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions
Setting the price for any product is not very easy, various internal, as well as external factor, has to be taken into consideration before finalizing the price for any goods or services. The following are the different factors affecting pricing decisions:
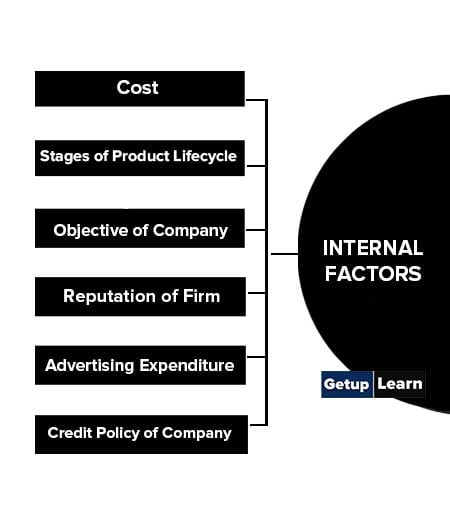
Internal Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions
Following are the internal factors affecting pricing decisions:
- Cost
- Stages of Product Lifecycle
- Objective of Company
- Reputation of Firm
- Advertising Expenditure
- Credit Policy of Company
Cost
Cost means all kinds of expenditures incurred by the company to manufacture products. There are various variables as well as the fixed costs incurred by the company to manufacture the product. Before fixing a price for any commodity it is necessary for the company to cover its variable as well as a fixed cost.
Stages of Product Lifecycle
Every product has to pass on through various stages of the product lifecycle. The price of the product is also influenced by the stage at which the product is in.
At the introduction of the Product Company generally charge a lower price, during growth company charges a higher price whereas decline stage of the product Lifecycle Company again charges a lower price for its product.
Objective of Company
The pricing policy of the company is also depending upon the objective of the company. If the company’s objective is to capture market share then it will charge a lower price and if the objective of the company is to earn more ROI then it will charge a higher price for its products.
Reputation of Firm
The goodwill of the company also affects its pricing policy of the company. If the company carries a good reputation in the market then it will help the company to higher prices for its products. Eg. Amul company charges a high price for its dairy products as it carries a good reputation in the market.
Advertising Expenditure
Advertising and promotional expenditure incurred by the company also affect the pricing policy. If the expenditure of the company on these activities is more than the price charged by the company for products; will be higher and vice-versa.
Credit Policy of Company
Every company gives a credit period to wholesalers or retailers for making repayment of the price charged by the company. If the company has a policy of giving more credit periods then the price charged by the company will be higher. If the credit period is given less credit period then the price charged will be lower.
External Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions
Following are the external factors affecting pricing decisions:
Customer
Customer tests and preferences change over a period of time. Therefore the company needs to take into consideration various customer factors before determining the price for its products. Customer factors such as purchasing capacity, income level, etc. need to be considered.
Competition
The study of the pricing policy of the competitors is very important before setting prices for products. If competition is tough in the market then the company should restore lower pricing for its products to get competitive advantages in the market. If there is a monopoly or less completion then the company charges a higher price for its product.
Government Policy
Government rules and regulations are very important before finalizing the price of the product. For a certain category of goods and services government may announce a predetermined price and all companies dealing in such kind of goods and services has to follow the norms of the government.
Intermediaries Involved
To travel goods from a company to a consumer many intermediaries are involved. The larger the number of intermediaries in the supply chain higher will be the price of the product and if the number of intermediaries is less then the price of the product will be less.
Methods of Pricing
Determining the price of a product is not an easy task. The price of the company should be set in such a way as it is able to recover the cost of the company in the long run. Price should be determined in such a way that it not only attracts the customer to buy the product but also generates a reasonable return to the company on their investment.
In order to earn more profit in the short run company may charge a higher price for its products but if the customer fees the price charged by the company is higher than any other alternative available in the market then customer may not prefer to buy the product and company will find it difficult to generate revenue on their products.
There is various method of pricing which help the company to recover its cost and get some profit margin for its products. Before selecting any method of pricing company has to take into consideration various factors that affect pricing.
We can classify the types of pricing methods:
Cost Oriented Pricing
Recovery of cost is the prime motto of every company as no company wants to make a loss. Following are types of cost-oriented pricing methods:
- Cost Plus Pricing
- Mark Up Pricing
- Break Even Pricing
- Target Return Pricing
- Early Cash Recovery Pricing
Cost Plus Pricing
This is the easiest method to determine the price of the product. Under this method, the company finalized its full cost i.e. total cost, and then adds a specific percentage to the total cost to determine the selling price for its products.
This difference between the selling price and the total cost is the profit of the company. For Example: if the total cost of the company’s product is INR 1000 and the company decided to get a 10% profit on the total cost then the selling price of the company will be INR 1100 (1000+ 100).
Mark Up Pricing
This method is somewhat similar to cost plus pricing only difference is that in cost plus pricing specific percentage is charged on the total cost of the company but in markup pricing, the specific percentage is charged on the selling price of the company.
In this method, the company is aware of the cost and expected profit margin, and by using the company calculates the selling price of this product. For example; if the total cost of the company is INR 900 and the expected profit the company wants to earn on its selling price is 10% then the selling price of the company will be INR 1000. (900×100)/90.
Break Even Pricing
Break-even pricing is a no profit no loss pricing method. Break-even pricing is the price at which the selling price is equal to the total cost of the company. In this method, the company determines the volume of sales required to recover both variables as well as the fixed cost of the company.
For example: if the variable cost per unit is Rs 20 and Selling price per unit is Rs 30 and the fixed cost incurred by the company is Rs 4,00,000 then in order to cover both variables, as well as the fixed cost company, should sell at least 40,000 units in order to break even. If the company is not able to sell 40,000 units then it has to increase the selling price in order to break even.
Target Return Pricing
Under this method of pricing, the company decided to sell price in order to achieve a particular level of return on their investment (ROI). The target selling price is determined by using the following formula.
Target sales price per unit = total cost + (expected % of ROI) / total sales in units
For Example:
The total investment of the company is INR 1, 00,000
Expected return on investment 20%
The total cost of the company is INR 50,000
Expected sales in units 5,000
50,000 + (20% on 1, 00,000)/5 000
Target sales price per unit = INR 14 per unit.
Early Cash Recovery Pricing
The company uses this pricing method when the product life cycle is very short and the company has to recover its investment at the earliest. This pricing method is followed when a company introduces some innovative product in the market and they think that competitors will also introduce a similar kind of product at a lower price and the company may have to exit from the market.
The company tries to recover its cost in the short run by maximizing its profit of the company. This pricing policy is generally followed in the case of fashion brands and technology-related products.
Market Oriented Method of Pricing
Following are the market-oriented method of pricing:
Perceived Value Pricing
The customer has some perceived value at which he would like to buy the product. Every company should take into consideration the perceived value of customers before setting prices for its products. The company conducts a primary market survey to know customers perceived value.
Customer choice about the product is influenced by various factors such as after-sale service provided by company staff, advertising, etc. If the customer perceived a lower value then the company will charge a lower price for its product and vice versa.
Going Rate Pricing
In this pricing method price charges by major competitors will be taken as standards for setting prices for their own products. Companies determine the price for their product on the basis of market price of similar commodities in the market This method of pricing is further subdivided into three categories:
Competitors Parity Method
Under this method, the company charges the same price as charged by the competitor in the market. If the competitor increases the price company will also increase the price and if the competitor decreases the price then the company will also decrease the price for its products irrespective of its demand in the market or cost structure the company.
Premium Pricing
In this pricing, method company charges some additional price for its products for having additional features than that of competitors. A company that provides some additional features in its products than competitors is only in the position to charge premium prices for its products.
Discount Pricing
This method of pricing is exactly the opposite of premium pricing. In discount, pricing companies charge a lower price for their products due to the lack of additional features as provided by their competitors.
Seal-Bid Pricing
In order to win the bid, the company submits a tender with as lowest price possible. This pricing policy is adopted in case of big contracts or orders where big companies or government departments invite tenders from various companies to give the assignment.
In this method of pricing buyer expectation is lower pricing tender and the seller wants to full fill buyer expectation by giving tender or quotation at a lower rate taking into consideration the expected pricing policy of the competitor.
Following are the faq’s factors affecting pricing decisions:
What are the factors affecting pricing decisions?
Following are the two bases of factors affecting pricing decisions:
Internal Factor: Cost, Stages of Product Lifecycle, Objective of Company, Reputation of Firm, Advertising Expenditure, Credit Policy of Company.
External Factor: Customer, Competition, Government Policy, Intermediaries Involved.
What are the methods of pricing?
Following are the two bases methods of pricing:
Cost-Oriented Pricing: Cost Plus Pricing, Mark Up Pricing, Break Even Pricing, Target Return Pricing, Early Cash Recovery Pricing.
Market Oriented Method of Pricing: Perceived Value Pricing, Going Rate Pricing, Seal-Bid Pricing.