Table of Contents
What is Information System?
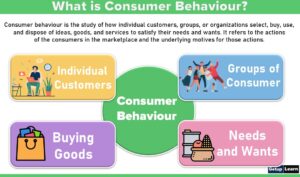
Information systems are “A combination of hardware, software, infrastructure, and trained personnel organized to facilitate an organization’s planning, control, coordination, and decision making.
Data is a raw material for information systems. Collecting data costs money and hence one must collect necessary and sufficient data.
Data is generally input to the information systems for processing. Data size is also growing but is useless unless it is processed to create information. Information is processed data, used by managers to initiate actions and to run the organization efficiently. The data processed by machines give information.
Types of Information
Following are the types of information:
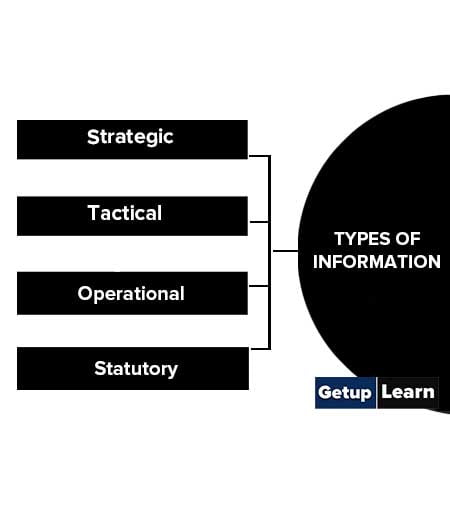
Strategic
It is needed for long-range planning and directions. This is less structured.
Tactical
It is needed to take short-range decisions to improve profitability and performance.
Operational
It is needed for day to day operations of the organization. Eg: Daily Sales, Billing.
Statutory
It is needed by law to send to government authorities. Eg: Sales tax return.
Need for Information Systems
Information systems are needed when timely processing for fast action is needed; the same data has to be processed in different ways and when organizations require innovative processing.
Functional areas of management are as follows:
- Production
- Marketing
- Materials, Purchase, Stores
- Finance Accounts
- Human Resource Development (HRD)
- Research and Development (R&D)
Quality of Information
Quality of information refers to its fitness for use or its reliability. Some of the attributes of information, which influence the quality of information are discussed as follows:
Timeliness
It means that information must reach the recipients within the prescribed timeframe. B.K.Chatterjee (1974) said “information delayed is information denied.
Accuracy
Accuracy is another key attribute of management information. As per Jhon G Burch
and Gary Grudnitski (1986), accuracy means more than just one plus equals two. It means that
information is free from mistakes and errors, is clear, and accurately reflects the meaning of the data
on which it is based.
Relevance
Relevance is yet another key attribute of management information: Information is said to be relevant if it answers specifically for the recipient what, why, where and when, who, and Why? In other words, the MIS should serve reports to managers which are useful and the information helps them make decisions.
Adequacy
Adequacy means information must be sufficient in quantity, i.e., MIS must provide reports containing information that is required in the deciding processes of decision-making. The report should not give inadequate or for that matter, more than adequate information, which may create a difficult situation for the decision-maker.
Completeness
The information which is provided to a manager must be complete and should meet all his needs. Incomplete information may result in wrong decisions and thus may prove costly to the organization.
Explicitness
A report is said to be of good quality if it does not require further analysis by the recipient for decision-making. On the other hand, a poor-quality report requires further analysis or processing of its contents.
Exception-based
Today, more and more organizations are being run on the principle of management by exception. Top managers need only exception reports regarding the performance of the organization. The exception reporting principle states that only those items of information which will be of particular interest to a manager are reported.
Dimensions of Information
Information may be understood to have various dimensions. However, for our purpose, the following three dimensions of information will be of interest:
Economic Dimension
This dimension of information refers to the cost of information and its benefits. The generation of information costs money. To decide about the money to be spent on information generation in an organization, a cost-benefit analysis should be undertaken.
Business Dimension
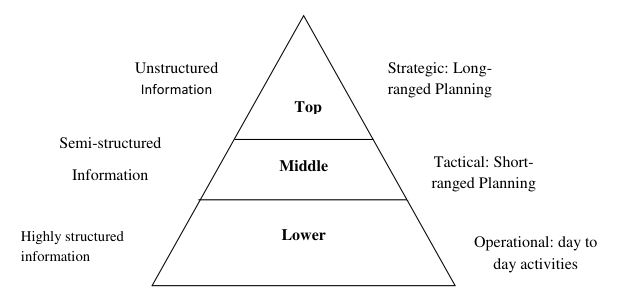
Information can also be understood from its business dimension. Different types of information are required by managers at different levels of the management hierarchy.
The information needs of managers at the strategic planning level are altogether different than those of operational control managers. It is because managers at different levels are required to perform different functions in an organization.
Technical Dimension
This dimension of information refers to the technical aspects of the database. Various aspects of the database, which are considered under this dimension, include the capacity of the database, response time, security, validity, data interrelationship, etc.
The technical dimension is covered under the design of information systems and under the topic of the database management system.
Types of Information Systems
Management Information Systems comprise many sub-systems and are influenced by the organization’s structure, activities, risk profile, and technological capabilities. Within an organization setup, depending on the level of management, the information systems perform various activities and play certain roles.
Information systems support top management in setting long-term goals, and policies and achieving strategic competitive advantage. Following are the types of information systems in the organization:
- Transaction Processing System (TPS)
- Decision Support System (DSS)
- Management Information System (MIS)
- Executive Support System (ESS)
Transaction Processing System (TPS)
Transaction processing systems were among the earliest computerized systems. Their primary purpose is to record, process, validate, and store transactions that take place in the various functional areas/of a business for future retrieval and use.
A Transaction Processing System (TPS) is an information system that records company transactions (a transaction is defined as an exchange between two or more business entities). Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) is cross-functional information systems that process data resulting from the occurrence of business transactions.
Transactions are events that occur as part of doing business, such as sales, purchases, deposits, withdrawals, refunds, and payments. Transaction processing activities are needed to capture and process data, or the operations of a business would grind to a halt.
Decision Support System (DSS)
A broad description of a decision support system is human and computer interaction used in decision-making. A Decision Support System (DSS) is an interactive computer-based system, which helps decision-makers utilize data and models to solve unstructured problems.
Decision support systems couple the intellectual resources of individuals with the capabilities of the computer to improve the quality of decisions. It is a computer-based support system for management decision-makers who deal with semi-structured and unstructured problems.
A decision support system is an information system whose primary purpose is to provide knowledge workers with information on which to base informed decisions. The decision support systems take the data and present it in various formats to aid the individual or group in reaching a decision.
The decision support systems are generally used by the highest level of management as an aid for the unstructured decisions they have to make. A decision support system provides facilities for verification of information integrity, and for the discovery of discrepancies in the received information.
Statistical methods and rule-based systems provide some tools for the analysis and pre-processing of data used for the generation and evaluation of alternative decisions.
Management Information System (MIS)
A Management Information System (MIS) is a subset of the overall internal controls of a business covering the application of people, documents, technologies, and procedures by management accountants to solve business problems such as costing a product, service, or a business-wide strategy.
Management information systems are distinct from regular information systems in that they are used to analyze other information systems applied in operational activities in the organization.
Academically, the term is commonly used to refer to the group of information management methods tied to the automation or support of human decision-making, e.g. Decision Support Systems, Expert systems, and Executive information systems.
Executive Support System (ESS)
Executive Support Systems (ESS) supply the necessary tools to senior management. The decisions at this level of the company are usually never structured and could be described as “educated guesses.” Executives rely as much, if not more so, on external data than they do on data internal to their organization.
Decisions must be made in the context of the world outside the organization. The problems and situations senior executives face are very fluid, and always changing, so the system must be flexible and easy to manipulate.
Functional Information System
The various types of systems in the organization have interdependencies. TPS is a major producer of information that is required by the other systems which, in turn, produce information for other systems. There are various types of functional information systems:
- Sales and Marketing Systems
- Manufacturing and Production Systems
- Finance and Accounting Systems
- Human Resources Systems
Sales and Marketing Systems
The sale and marketing function is responsible for selling the organization’s products or services. Marketing is concerned with identifying the customers for the firm’s products or services, determining what they need or want, planning and developing products and services to meet their needs, and advertising and promoting these products and services.
Manufacturing and Production Systems
The manufacturing and production function is responsible for actually producing the firm’s goods and services.
Manufacturing and production activities deal with the planning, development, and maintenance of production facilities; the establishment of production goals; the acquisition, storage, and availability of production materials; and the scheduling of equipment, facilities, materials, and labor required to fashion finished products.
Finance and Accounting Systems
The finance function is responsible for managing the firm’s financial assets, such as cash, stocks, bonds, and other investments, in order to maximize the return on these financial assets. The finance function is also in charge of managing the capitalization of the firm.
In order to determine whether the firm is getting the best return on its investments, the finance function must obtain a considerable amount of information from sources external to the firm.
Human Resources Systems
The human resource function is responsible for attracting, developing, and maintaining the firm’s workforce. Human resources information systems support activities such as identifying potential employees, maintaining complete records on existing employees, and creating programs to develop employees’ talents and skills.
Strategic-level human resources system identifies the employee requirements (skills, educational level, types of positions, number of positions, and cost) for meeting the firm’s long-term business plans.
What are the types of information?
Types of information are:
1. Strategic
2. Tactical
3. Operational
4. Statutory.
What is the quality of the information in MIS?
The quality of the information in MIS is given below:
1. Timeliness
2. Accuracy
3. Relevance
4. Adequacy
5. Completeness
6. Explicitness
7. Exception-based.
What are the dimensions of information?
These are the 3 dimensions of information:
1. Economic Dimension
2. Business Dimension
3. Technical Dimension.
What are the types of information systems?
Following are the types of information systems:
1. Transaction Processing System (TPS)
2. Decision Support System (DSS)
3. Management Information System (MIS)
4. Executive Support System (ESS).
What is a functional information system?
A functional information system is explained below:
1. Sales and Marketing Systems
2. Manufacturing and Production Systems
3. Finance and Accounting Systems
4. Human Resources Systems.