Table of Contents
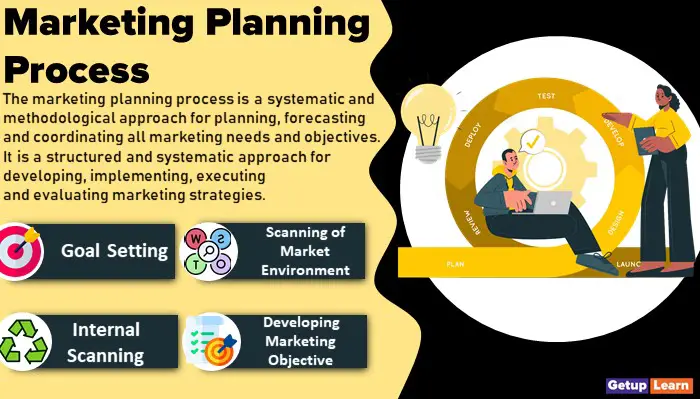
Marketing Planning Process
Following is the marketing planning process:
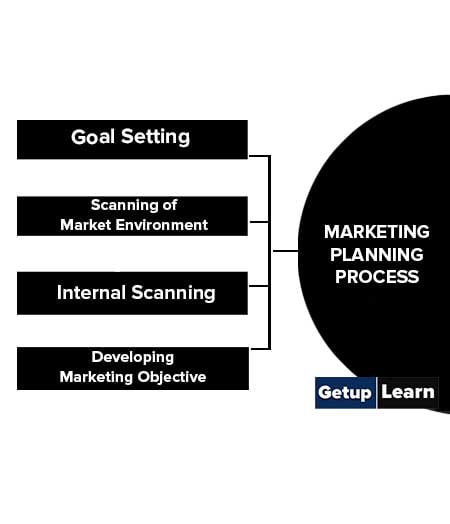
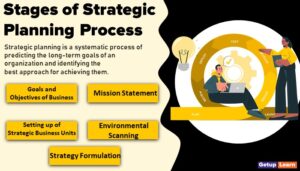
Goal Setting
As mentioned earlier, marketing strategy is derived from the business strategy as well as the corporate strategy. Marketing objectives would be set according to the goals that have been set at the higher hierarchies.
For example, If the corporate objective of the firm is to maximize the market share then the marketing objective would also focus on achieving the same objectives.
Scanning of Market Environment
Marketing planning scanning the market environment for finding opportunities and threats: The major reason market scan is done is to find the opportunities and threats that exist in the environment. The scanning done in strategic planning and marketing planning are almost similar.
The major difference is that marketing scanning involves scanning the environment of a specific business unit with a specific business purpose, whereas environmental scanning under strategic planning would entail the overall environment of the organization.
The business unit would analyze the environment and gather marketing information. It would also assess opportunities existing in the environment, and study consumer behavior and the product in question. A vital aspect of environmental scanning is to understand the competition and all factors in the competition.
Other than the competition itself, there are other important factors too that shape the competition. Porter in his article (1979) suggested five major forces that shape and decide the nature and intensity of competition.
- Existing competition
- The threat of new entrants
- The threat of substitute products
- Bargaining power of customers
- Bargaining power of suppliers
The intensity of competition depends on the size of the entrants, the bigger the new entrants, the more intense would be the competition. A threat of substitute products with an improvement in their performance or price differentiation can change the industry’s competitive scenario.
The collusion of customer groups can gain considerable bargaining power as to exert pressure on the organization regarding the quality, price, and output of the products. The same would hold true for suppliers where the sources of supply are limited and products supplied are specialized in nature.
Internal Scanning
Internal scanning is done to analyze the firm’s competencies and weaknesses. The firm needs to find where its competitive advantages lie, whether it’s product design, service, or distribution. This evaluation is required in order to ascertain how equipped a firm is to face market competition.
Developing Marketing Objective
The next step is the formulation of a marketing objective. The broad outline of marketing objectives would be derived from the corporate objectives of the related business. The corporate strategy would have already defined the direction for each business. Once the marketing planning is done, the next step would be developing the contents of a marketing plan.
What is Marketing Plan?
A Marketing Plan is a brief summary of objectives and recommendations. It may be part of an overall business plan. While a marketing plan contains a list of actions, a marketing plan without a sound strategic foundation is of no or little use.
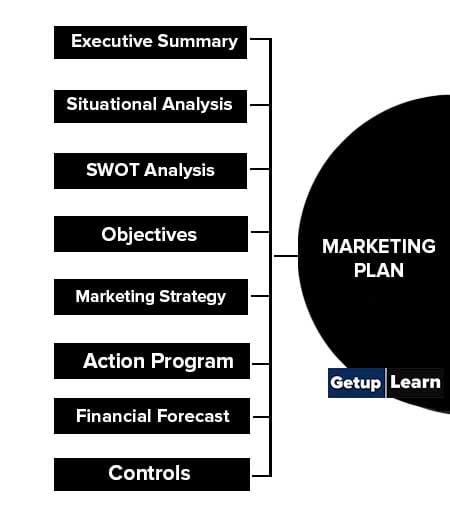
Following are the Contents of a marketing plan:
- Executive Summary
- Situational Analysis
- SWOT Analysis
- Objectives
- Marketing Strategy
- Action Program
- Financial Forecast
- Controls
Executive Summary
It is a brief summary of major objectives and recommendations, giving the management an overall view of the major purpose of the plan. (Table of content would follow the executive summary).
Situational Analysis
It portrays the significant data on sales, costs, profits, markets, competitors, etc. This data is further used for doing the SWOT analysis (strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats).
SWOT Analysis
The management needs to evaluate the opportunities in SWOT analysis and any factors affecting the achievement of objectives.
Objectives
This stage outlines the financial and marketing objectives like sales volume, market share, profitability, etc.
Marketing Strategy
Here the target segments are defined for whom the market offering is focused on. The product positioning is planned with the help of input received from related functional areas such as purchase, finance, and sales departments.
Action Program
Action Program: (The operational marketing plan itself, for the period under review) the marketing program is specified which would be used to achieve the set objectives.
Financial Forecast
It would generally be the overall budgeting – on the revenue side the sales forecast and average price would be depicted, and on the expense side, it would show the estimated expenses. The difference between revenue and expenses would be the estimated profit.
Controls
This final stage of the marketing plan would outline controls for monitoring the implementation of the plan. There would be a periodic review of the results and corrective measures would be recommended as required.
Formulating Marketing Strategy
The marketing strategy would be a proper outline of the game plan of the organization. The main elements involved in formulating marketing strategy are:
The essence of the marketing strategy of a firm is felt by its target market and marketing mix. The target market would be to whom the firm intends to cater and the marketing mix would determine how the products will be offered to the target market.
Selecting Target Market
Selecting Target Market Target market is the market that one would want to cater to. Selecting the target market is a significant part of developing a marketing strategy.
Marketing Mix
Marketing Mix can be defined as the effective combination of the Ps of marketing to formulate a unique selling proposition for the product. Every firm would have a different combination of the marketing mix as per its individual requirements.
Marketing Mix is also known as the 4 Ps of Marketing – Product mix (eg, frozen foods along with a variety of fresh fruits), Place mix (eg, chain of the whole–sellers, retailers, along with events), Price mix (eg, extra filled packs, say 20% extra, along with the special promotional price for trials) and Promotion mix (eg, above–the–line, say TV, along with below–the–line promotions, say direct mail or events).
Additional 3 Ps of marketing applicable to services – Physical evidence, People, and Process Every business due to the difference in its nature and situation uses different marketing strategy styles, whichever best suits them.
Types of Marketing Strategies
These are the types of marketing strategies:
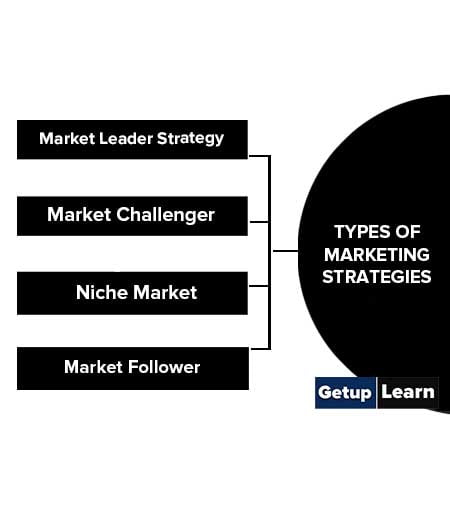
Market Leader Strategy
Market leader strategy is also known as offensive or confrontation strategy. Generally employed by firms who are currently not the leaders in the market but aspire to be the market leader. The firm tries to expand its market share by using all the marketing mix elements, the target of attack would be the market leader.
The firm tries to expand its market and increase its consumer base by offering competitive prices, and superior service, improving the quality of products, enhancing features of its existing products, finding new uses for existing products, or entering newer market segments.
Market Challenger
This strategy would focus on gap analysis. The gap analysis can be done by comparing the performance of competitors’ existing products in the market with the actual expectation of the consumers regarding the product.
The firm can then strive to bridge the gap by providing products as per customers’ expectations leading to higher customer satisfaction levels. In this strategy, competitors’ weaknesses are taken as opportunities for the firm.
Niche Market
Niche markets are small differentiated markets that no other firms have thought of entering into. Generally, these markets are too small to attract a large number of competition.
Niche may serve some specific customer or some specific area. Eg., companies focused on adventure sports, trekking; or travel companies concentrating on a specific segment of pilgrims.
Market Follower
The market follower depends on its competitors to identify markets. As a follower, the firm needs to be keen on its competitor’s weaknesses and try to improve on them.
This marketing strategy saves the firm on costs arising from having to carry out research because it only has to work on its competitor’s weaknesses to better its products.
What are the types of marketing strategies?
Types of marketing strategies are given below:
1. Market Leader Strategy
2. Market Challenger
3. Niche Market
4. Market Follower.
What are the 7 steps of a marketing plan?
Following are the Contents of a marketing plan:
1. Executive Summary
2. Situational Analysis
3. SWOT Analysis
4. Objectives
5. Marketing Strategy
6. Action Program
7. Financial Forecast
8. Controls.
What are steps of marketing planning process?
Following are the stages of marketing planning process:
1. Goal Setting
2. Scanning of Market Environment
3. Internal Scanning
4. Developing Marketing Objective