Table of Contents
What is Strategic Planning Process?
Strategic planning is a systematic process of predicting the long-term goals of an organization and identifying the best approach for achieving them.

Preparing effective marketing strategies requires an understanding of the strategic planning process corporate policies, objectives, and business plans. A strategic plan defines the organization’s strategy.
The existing situation and possible opportunities need to be analyzed to determine the right direction for the organization. This has to be done along with the firm’s competencies, its competitive advantage, its weaknesses, and the business that they want to be in.
The uncertainty and risk in business environments make it necessary for firms to focus on competitive strategic plans. The well-studied guide-map on directions that it should take, is definitely preferred over treading on an ambiguous path.
This enables the firm to respond to entirely unexpected developments in its internal and external environments. A strategic plan, where the most significant decisions are taken, helps keep firms well ahead of the competition and to realize their mission in the long run as well as the firm’s well–being and growth.
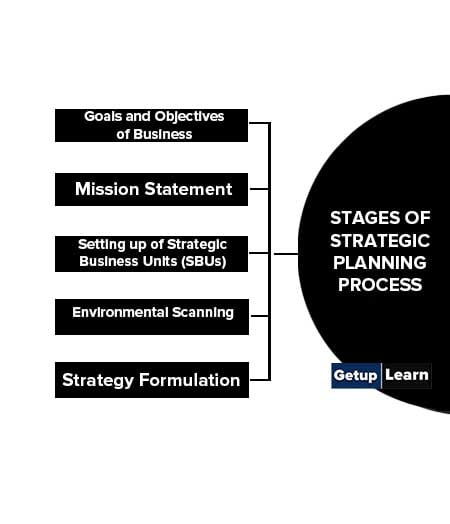
Stages of Strategic Planning Process
There are five stages of strategic planning process:
- Goals and Objectives of Business
- Mission Statement
- Setting up of Strategic Business Units (SBUs)
- Environmental Scanning
- Strategy Formulation
Goals and Objectives of Business
Defining the firm’s business is the focal point of strategic planning. It is a crucial factor that enables the firms in selecting appropriate opportunities for leading the firm in the right direction. Management experts Peter Drucker and Theodore Levitt stressed the basic questions which every firm needs to find answers to.
That has to be done on a continuous basis. What business are we in? Whom do we intend to serve? Do we accurately define our business? Do we know our customers? What brings us to this particular business? What would be the nature of this business in the future?
What business would we like to be in the future? What are our basic strengths and competencies to pursue the current business or enter into a desired business?
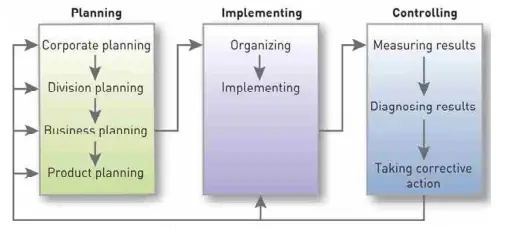
The Strategic Planning, Implementing, and Controlling Process
Mission Statement
A mission statement defines the purpose of the company’s existence. The mission statement should be able to guide the actions of the organization, set its overall objectives, provide a route map, and guide decision–making.
The mission provides a framework, on the basis of which the company’s strategies are formulated. Every organization develops its unique mission statement which it communicates to its stakeholders so that they can understand the purpose of the firm’s existence.
A common mission statement provides a sense of integration within the organization and emphasizes focus on realizing the organizational goal. Mission statements are again guided by the vision of the organization. Vision is what the organization wishes to achieve over a period of time, say in two decades.
Examples of Mission Statements:
- “McDonald’s vision is to be the world’s best quick service restaurant experience. Being the best means providing outstanding quality, service, cleanliness, and value so that we make every customer in every restaurant smile.”
- “Amazon’s vision is to be earth’s most customer-centric company; to build a place where people can come to find and discover anything they might want to buy online.”
Setting up of Strategic Business Units (SBUs)
SBUs are essentially for multi-product organizations. SBU can be defined as an independent organizational unit, small enough to be flexible and large enough to have control over most of its activities and decisions.
An SBU can also be called a profit center or responsibility center that concentrates on a particular product offering for a particular market segment. They typically have an independent marketing plan, competition analysis, and marketing campaign, though they may be a part of a larger business organization.
Characteristics of strategic business unit:
- It could be a set of businesses that can operate separately from the rest of the organization.
- It has its own competition.
- It has a separate manager who is responsible for the overall functioning, decision-making, strategic planning, performance, and profit management of the firm.
Once the strategic business units are set, the organization would go in for environmental scanning to find out the opportunities and threats that exist, as well as to uncover the strengths and weaknesses that lie within the organization.
Environmental Scanning
No firm can function in isolation; it operates in an environment known as the business environment, consisting of various factors that influence business policies and decisions.
The business environment can be divided into Internal environment and external environment.
- The internal environment is internal to the firm and would consist of the factors such as the internal policies of the firm, the management, its employees, etc.
- An external environment would be external to the firm and would consist of factors such as the competitors of the firm, market, consumers, technology, government policies, etc. The external environment can be further divided into micro and macro environments.
The overall environment has a significant impact on the strategies of an organization, many times the changes in the environment determine or lead to changes in its strategic plans.
The external and internal environment when scanned thoroughly reveals available opportunities, hidden threats, its own weaknesses, and competitiveness/ strengths. Once the environmental scan is carried out, the firm is in a position to formulate its strategies.
Strategy Formulation
Organizations have a hierarchy of interrelated strategies, with different strategies formulated for different levels of the organization:
Corporate Strategy
Corporate Strategy: This is concerned with meeting the stakeholder expectations and delivering value to the stakeholders, mainly influenced by investors in the organization, and acts as a guideline for strategic planning throughout the organization. Corporate strategy is often incorporated in a “mission statement”.
Business Strategy
Business Strategy: This is more concerned with the functioning and competitiveness of a business for a particular market. It would usually be concerned with strategic decisions regarding the choice of products, delivering customer value, gaining competence, finding and exploring or generating new opportunities.
Functional Strategy
Functional strategy is concerned with how each functional area is organized to deliver the corporate and business-unit level strategic direction. Under the functional strategy, we would concentrate on marketing strategy.
What are the stages of strategic planning process?
Following are the stages of strategic planning process:
1. Goals and Objectives of Business
2. Mission Statement
3. Setting up of Strategic Business Units (SBUs)
4. Environmental Scanning
5. Strategy Formulation.