Table of Contents
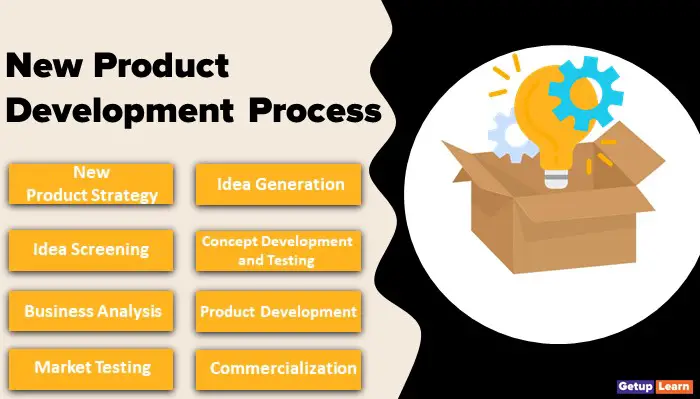
New Product Development Process
Developing a new product is key to organizations’ survival in the ever-changing marketing environment. Some organizations set a price limit while others focus on adding value and making the existing product better than before.
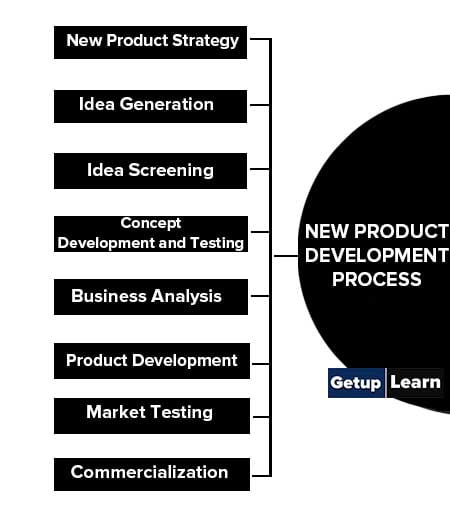
They do this with the price factor coming at a later stage. Depending on the organisation’s size and past experience, the new product development process may vary. Following are the steps of the new product development process:
- New Product Strategy
- Idea Generation
- Idea Screening
- Concept Development and Testing
- Business Analysis
- Product Development
- Market Testing
- Commercialization
New Product Strategy
The corporate strategy and objectives give guidelines for new product development by assessing organizational expertise and external opportunities. SWOT analysis gives inputs for emerging markets and emphasis is given to the threats and opportunities.
The same is aligned with the strengths and weaknesses of the organization. This gives direction as well as boundaries to the top management for new product development.
Idea Generation
Sources for idea generation include employees, customers, competitors, distributors, entrepreneurs, and suppliers. R & D team members too can be a source of ideas. The organization should encourage ideas by rewarding employees.
Customer surveys are important when developing a new product. By direct observation or conducting a brainstorming session with potential customers, organizations get an insight into the buying behavior, needs, and wants of the target market.
Besides this, inputs from the suppliers, sales representatives, distributors, and retailers who serve the competitor also contribute largely to idea generation. Entrepreneurs, University students, and Inventors are also sources of ideas for new inventions outside the organization. The organization should have a designated Manager or Idea Committee to compile ideas from different sources.
Idea Screening
The process relies mostly on the experience of the members of the top management and their judgment. Not all ideas are good ones, and this process is to ensure mistakes are avoided at the early stage.
Key factors to be considered are the new product’s value to the customer, expertise available within the organization, stipulated time for manufacturing the product, scope for promotion activities, financial feasibility (cost and profit margin), sustainability in the market, and customer service if needed (after-sales service).
The basis of the new product strategy or SWOT analysis is done and the best idea is selected. Most of organizations are more successful with products for which they have the expertise.
Concept Development and Testing
Some organizations conduct concept testing by discussing the concept of the new product with a few potential buyers through discussion in focus groups or individual interviews and their reaction is recorded.
For example, virtual reality programs use computers and systems by which customers can experience driving an automobile or wearing an attire via simulation. The inputs from consumers help organizations assess the customer appeal, target customers, customer expectations, etc.
Business Analysis
It refers to the detailed study of the economic feasibility of the new product ideas. The management prepares the sales, costs, and profit projections to assess if the new product should be introduced. It gives a clear picture of whether to continue with the development and evaluation process or drop the idea.
The costs include promotion activities, R & D, distribution, production, and associated services like consulting, accounting, legal, etc. The organization then arrives at the attractiveness of the new product in relation to the target market.
Product Development
The product is in the form of a concept word description, and the drawing takes the form of a prototype. Few physical versions of the product are made. This stage provides information on the costs of manufacturing, distribution, and packaging.
If the estimates are not feasible to the organization technically, or more modifications need to be done that are undesirable, the product idea may be dropped. If the firm wishes to go ahead with the production, supporting strategies are also developed at the same time like packaging, labeling, brand names, etc.
Market Testing
This stage thoroughly evaluates the market acceptance through market research before the complete product introduction in the market. The product is introduced in a small section of the market, which represents the whole market to test the product’s acceptability.
The test results from market testing help organizations estimate the projections. The most serious problem of conducting market testing is a competitor discovering the same and monitoring the results. If the product has not been patented, the competitor may launch an identical product much earlier.
Commercialization
The new product after successfully passing the test marketing stage is launched in the entire market with all the related decisions like distribution, packaging, after-sales service, etc.
Contracts with suppliers are signed, channels of distribution are selected, and manufacturing facility and support services are set into operation on a full scale.
The timing of product introduction is critical to firms. If the organization learns that a competitor is on the verge of developing a similar product, the organization has to make a decision like Early entry (which enables a firm to have a strong distribution network and gain a reputation), Parallel entry, or Late entry (firm saves the cost of educating the consumer about the market – promotion activities).
Consumer Adoption Process
- Customers learn about new products, try them, and buy or reject them. Adoption is the decision of an individual to use the product; while, diffusion/distribution/circulation is the collective spread of individual adoption decisions throughout a market.
- Thus, the consumer adoption process is concerned with the individual whereas the diffusion process is concerned with the aggregate behavior.
- The fundamental reason for studying the diffusion and adoption processes is to increase the level of understanding of how? When? And why? New products are accepted or rejected.
There are five stages of consumer adoption process:
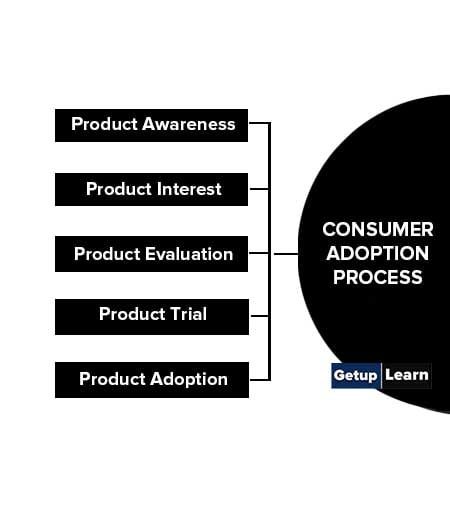
Product Awareness
This first stage is about creating awareness that your product is in the market. It is important that your company develops a successful avenue for your consumers to become aware of your product.
If consumers do not know your product exists then it might as well not exist! Create marketing material. These can be one-sheets, video teasers, images, and landing pages. Make these marketing materials easily accessible.
In the era of social media, many tools are available in the market that provides companies with the techniques and methods to increase product awareness through social channels – enabling them to reach a large number of customers at a low cost!
For example, Movie Teasers. Movie teasers are designed to inform the audience without providing them with in-depth information about the movie.
Product Interest
In this stage, consumers are ready to learn more about your company’s product and/or service. The organization must guide the consumer through the interest stage by providing easily accessible information on your product.
Among the methods used in today’s business landscape include a website describing the product, blog posts, tutorial or instructional videos, white papers, and other sources of info that the potential consumer can discover and review.
For example, Apple utilizes its product launch to provide information and insight into its latest product. With well-designed and organized speech, scripted presentation, and balanced use of technical and non-technical vocabulary, Apple delivers information eloquently and successfully to a broad range of customers.
Product Evaluation
Prior to purchasing, consumers examine, compare and evaluate the product. Such behavior increases in intensity and needs once the item in question is more expensive, sophisticated and complex, or critical.
Consumers go online and utilize social media channels to ask other individuals about your product or service. In addition, they find online reviews and recommendations.
It is advisable in creating information that outlines the difference between your product and competitive products, on features and services.
Another great system to utilize is the webinar. This platform allows you to communicate with potential customers in-depth information about your product and provides time for Q&A.
For example, PCMag is a world-renowned website for comparing gadgets and computers. They are notable for their reliable reporting, comprehensive evaluation editorials, and categorization of different gadgets based on their qualities.
Product Trial
This is the stage where the consumer “kicks the tries”. Nothing helps a consumer make a decision about your product more than actually trying your product out! There are many ways this is accomplished.
A free trial or a proof of concept campaign. In this stage, it is very important to set the customer expectations correctly and deliver on said expectations.
For example, Lux shampoo. HLL often gives free samples with the morning newspapers in small sachets.
Product Adoption
When the consumer enters the product adoption phase, he/she is ready to purchase your company’s product. This is the critical stage that businesses need to get their consumers to.
When the customer is here, you need to make the payment process simple, intuitive, and pain-free. In addition, you need to ensure that the consumer can easily obtain the product. If you make it to and through this last phase successfully, then you can take money to the bank.
Whether you have a new business or an existing business, a product built for the enterprise, or a product built for a consumer; the consumer adoption process is the same.
Some customers buy products more quickly than others and vice versa. An individual can be categorized into different groups depending on how quickly they adopt a new product.
What is a new product development process?
Following are the steps of new product development process:
1. New Product Strategy
2. Idea Generation
3. Idea Screening
4. Concept Development and Testing
5. Business Analysis
6. Product Development
7. Market Testing
8. Commercialization.
What is the consumer adoption process?
Customers learn about new products, try them, and buy or reject them. Adoption is the decision of an individual to use the product; while, diffusion/distribution/circulation is the collective spread of individual adoption decisions throughout a market. Thus, the consumer adoption process is concerned with the individual whereas the diffusion process is concerned with the aggregate behavior.
What are the stages of consumer adoption process?
Following are five stages of the consumer adoption process:
1. Product Awareness
2. Product Interest
3. Product Evaluation
4. Product Trial
5. Product Adoption.
