Table of Contents
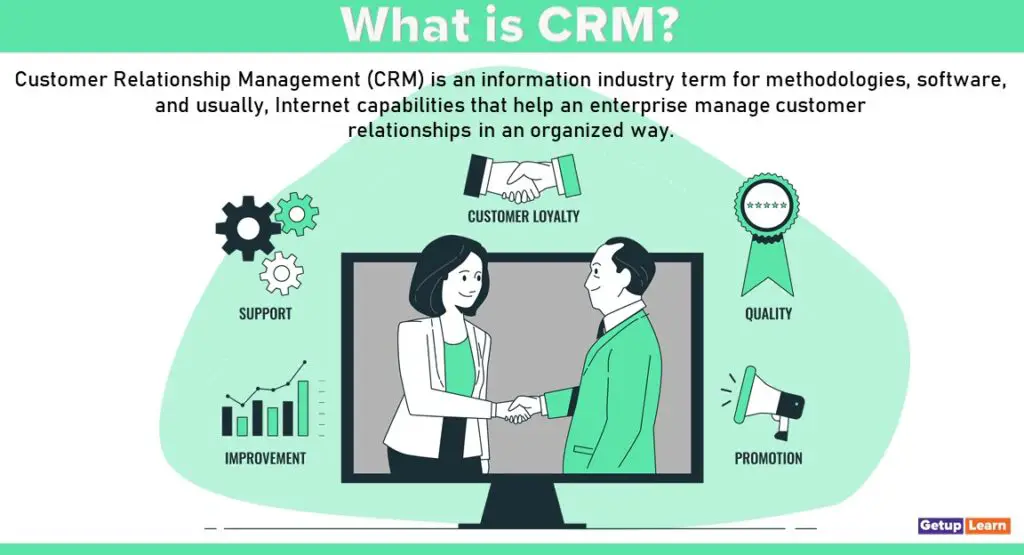
What is CRM?
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is an information industry term for methodologies, software, and usually, Internet capabilities that help an enterprise manage customer relationships in an organized way.
Every organization emphasizes building a long-term relationship with customers to nurture its stability in today’s market. Customers want to receive exactly what they demand and in a quick time.
CRM is the strategy to build strong relations with customers and at the same time reduce cost and enhance productivity and profitability in business. A system is vast and significant, but it be can implement for small businesses, as well as large enterprises also as the main goal is to assist the customers efficiently.
Usually, an organization consists of various departments which predominantly have access to customers’ information either directly or indirectly. A CRM system loads this information centrally, examines it, and then makes it addressable within all departments.
CRM is a platform for all business units to interact with their clients. It is very difficult to manage relationships with customers. It majorly depends on how systematically and flexibly a CRM system is implemented or integrated.
But once it’s accomplished it serves the best way of dealing with customers. In turn, customers feel the gratitude of self–satisfaction, and loyalty which results in better bonding with the supplier and hence increasing the business.
A CRM system is not only used to deal with existing customers but is also useful in acquiring new customers. CRM strategies have given a new outlook to all the suppliers and customers to keep the business going under an estimable relationship by fulfilling mutual needs of buying and selling.
Definition of CRM
These are some of the simple definitions of CRM:
[su_quote cite=””]Customer relationship management is the process of managing all aspects of interaction a company has with its customers, including prospecting, sales, and service. CRM applications attempt to provide insight into and improve the company/customer relationship by combining all these views of customer interaction into one picture.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=””]Customer relationship management is an integrated approach to identifying, acquiring, and retaining customers. By enabling organizations to manage and coordinate customer interactions across multiple channels, departments, lines of business, and geographies, CRM helps organizations maximize the value of every customer interaction and drive superior corporate performance.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=””]Customer relationship management is a business strategy that maximizes profitability, revenue, and customer satisfaction by organizing around customer segments, fostering behavior that satisfies customers, and implementing customer-centric processes.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=””]
Customer relationship management is an integrated information system that is used to plan, schedule, and control the
pre-sales and post-sales activities in an organization. CRM embraces all aspects of
dealing with prospects and customers, including the call center, sales force, marketing,
technical support, and field service.
The primary goal of CRM is to improve long-term
growth and profitability through a better understanding of customer behavior. CRM
aims to provide more effective feedback and improved integration to better gauge the
return on investment (ROI) in these areas
[/su_quote]
Stages of Customer Relationship
We talk about the relationship between supplier and buyer as not a personal relationship or one–time relationship. For example, A customer buying a product from the outlet is not called a relationship. A relationship is when two parties are involved in an interaction and transactions happen many times.
This relationship only exists when the two parties diverge from a state of autonomy to mutual or interdependent. If the customer returns to a café and orders the same tea again because he likes the environment and taste or the method of making tea, it more looks like a relationship.
We can say that there is a change in the relationship with the customers from time to time as the environment is very dynamic. Following are the 5 stages of customer relationship:
Exploration
In this stage, a customer tries to investigate the supplier’s competency and they cross verify the product or brand usefulness for them. If the test results fail to satisfy customers’ demands, the relationship can end.
Awareness
Awareness is the process when the customer understands the motivational values of the supplier or the products he sells.
Expansion
Here supplier wins the customer’s faith and the customer falls under the interdependence of the supplier. Supplier’s business gets expanded and does business with the particular customer.
Commitment
Commitment is a powerful stage when suppliers learn to adapt business rules and goals to excel.
Dissolution
Dissolution is a stage when customer requirement suddenly changes and he looks for better perspectives. This sudden change is the end of the relationship.
Different Types of Customers
The customer is the king. Customer use products and services and then judges their quality. Customers are responsible for the profit of the organization. Hence, it’s important for an organization to retain customers or make new customers and flourish the business. Following are the different types of customers:
Loyal Customers
They are less in numbers, promote sales and profit, are completely satisfied with the product and service of the organization, and frequently visit the organization. They want individual attention and demand politeness and respect from the supplier.
Hence it is crucial to interact and keep in touch with them on a regular basis and invest time and effort with them.
Discount Customers
They are frequent visitors but they visit only when discounts are provided on regular products and brands. If more discounts are provided, they purchase more. Focus on these types of customers is important as they also promote a distinguished part of profit into the business.
Impulsive Customers
This type of customer does not have any specific item in their product list but they urge to buy what they find good and productive at that point in time. Handling these customers is a challenge as they are not particularly looking for a product and want the supplier to display all the useful products, in front of them to choose from.
If impulsive customers have treated accordingly then there is a high probability that they could be responsible for a high percentage of sales.
Need-Based Customers
This means that customer purchase that product or service which they are in need of and only tend to buy items to which they are habitual. These are frequent customers but do not become a part of buying most of the time so it is difficult to satisfy them.
These customers should be handled positively by showing them ways and reasons to switch to other similar products and brands and initiating them to buy. These customers could possibly be lost if not tackled efficiently with positive interaction.
Wandering Customers
These are the least profitable customers as sometimes they themselves are not sure what to buy. These customers are normally new in the industry and most of the time visit suppliers only for confirming their needs on products.
They investigate features of the most prominent products in the market but do not buy any of those or show the least interest in buying. To grab such customers, they should be properly informed about the various positive features of the products so that they develop a sense of interest.
Features of CRM
Following are the features of customer relationship management:
- Customer’s Needs
- Customers Response
- Customer Satisfaction
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Retention
- Customer Complaints
- Customer Service
Customer’s Needs
It is very important for the organization to identify the customer needs by knowing the customers (likes and dislikes), and interviewing them, thereby enabling the organization to satisfy their needs. Without identifying the needs, it is an arduous task to serve the customer effectively and maintain a long–term deal.
Customers Response
This means Organisation reactions towards the queries and activities of the customer. It is very important for the organization to deal with these queries in a competent way in order to minimize misunderstanding.
The success of the organization depends on how tactfully they deal with these queries and provide the best solution. If the supplier solves customers’ queries proficiently, he can able to succeed in developing professional and emotional relationships with them.
Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is defined as a measurement that determines how happy customers are with a company’s products, services, and capabilities.
In today’s competitive business marketplace, customer satisfaction is an important performance exponent and basic differentiator of business strategies. Hence, the more customer satisfaction; the more the business and the bonding with the customer.
Customer Loyalty
This type of customer is loyal to the supplier and buys products on the regular basis. If the customers are satisfied with the service of the supplier, then they visit the organization more frequently or he rebuys a particular product or brand many times by that supplier.
To continue customer loyalty the most important aspect an organization should focus on is customer satisfaction. Hence, customer loyalty is an influencing aspect of CRM and is crucial for business success.
Customer Retention
Customer retention is a strategic process to retain existing customers and not let them diverge or defect to other suppliers or organizations.
Usually, a loyal customer is tended towards sticking to a particular brand or product as far as his basic needs continue to be properly fulfilled. He does not opt for taking a risk in going for a new product. The more the possibility to retain customers, the more the probability of net growth of the business.
Customer Complaints
Always there exists a challenge for suppliers to deal with complaints raised by customers. Normally raising a complaint indicates the act of dissatisfaction with the customer. There can be several reasons for a customer to lodge a complaint.
A genuine reason can also exist due to which the customer is dissatisfied but sometimes complaints are lodged due to some misunderstanding in analyzing and interpreting the conditions of the deal with the supplier.
Handling these complaints to the ultimate satisfaction of the customer is important for any organization. Hence it is essential to have a predefined set of processes in CRM to deal with the complaints and efficiently resolve them quickly.
Customer Service
It is the process of delivering information and services regarding all the products and brands. Customer satisfaction depends on the quality of the service delivery. If the quality and trend of service go beyond customers’ expectations, the organization is supposed to have good business with customers.
Importance of CRM
CRM is the final goal of a new trend in marketing that focuses on understanding customers as individuals instead of as part of a group. The marketer makes their communication more customer-specific.
Importance of CRM: CRM plays an important role in maintaining and creating relationships with customers. Developing good Customer relationships is a business nonetheless it also ideates strong personal bonding among people.
CRM drives business to new levels of success. Once the bonding is established it is easy for any organization to identify the actual needs of customers and help them to serve them in a better way.
It is a belief that the more sophisticated strategies involved in implementing the CRM, the more strong and more fruitful is the business. Most organizations have dedicated world-class tools for maintaining CRM systems in their workplace.
These are the importance of CRM in business:
- A CRM system consists of a historical view and analysis of all the acquired or to-be acquired customers. This helps in reducing searching and correlating customers and to foresee customers’ needs effectively to increase business.
- CRM contains every bit of details of a customer, hence it is very easy to track a customer accordingly and can be used to determine which customer can be profitable and which may not be.
- In a CRM system, customers are grouped according to different aspects, the type of business they do, or the physical location. They are allocated to different customer managers often called Account Managers. This helps in focusing on each customer separately.
- A CRM system is not only used to deal with existing customers but is also useful in acquiring new customers. The process starts with identifying a customer and maintaining all the corresponding details in the CRM system which is also called an ‘Opportunity of Business.
The Sales and Field representatives then try getting business out of these customers by rigorously following up and converting them into a winning deal. This is very easily and efficiently done by an integrated CRM system.
- The strongest aspect of CRM is that it is cost-effective. The advantages of implementing a CRM system are that there is less need for paper and manual work which means lesser staff to manage and lesser resources to deal with. The technologies used in implementing a CRM system are also not costly.
- All the details in the CRM system are kept centralized which is at any time at the fingertips. This reduces the processing time and increases productivity.
- Efficiently dealing with all the customers and providing them with what they actually need increases customer satisfaction. This increases the chance of getting more business which ultimately enhances turnover and profit.
- If the customer is satisfied, they will be loyal and will remain in business forever resulting in an increased customer base and ultimately enhancing the net growth of the business.
In today’s commercial world, the practice of dealing with existing customers and thriving in business by getting more customers into the loop is predominant. Installing a CRM system can definitely improve the situation and help in challenging the new ways of marketing and business in an efficient manner.
Hence every organization should be recommended to have a full-fledged CRM system to cope with all the business needs.
Challenges of CRM
Many companies have misconceptions about CRM in regard to assessing customer satisfaction in order to enhance business. There are several misunderstandings in CRM to be checked otherwise these may cost the organization revenue and profits. These are some challenges of CRM that we faced:
- Identifying CRM With a Software System
- CRM is a Complicated System Difficult to Understand
- CRM is Expensive and Unaffordable
- Wrong assessment for Return on Investment in CRM
- Who is Responsible for CRM Implementation?
Identifying CRM With a Software System
Three important aspects plays important role in the success of CRM business strategy – people, business process, and technology. It is not possible to implement the CRM successfully without these three. So, CRM is not an IT issue only to be simply equated to software.
It would be improper to have a successful business purely ‘technology–centric’ ignoring the importance of people and processes. Software is only an enabling or a facilitating device. The process is implemented and enabled by the software only when it is properly designed and developed by people.
Only then it can deliver customer and company value. Therefore, the right implementation sequence has to be followed and it must include proper competencies and people’s attitudes, the right business strategies, and then the right IT implementation.
CRM is a Complicated System Difficult to Understand
The meaning of CRM is simple to fetch customers, retain them and maximize profitability. Because of the fast–developing technology, there is pressure on IT professionals to cope with the new developments. So, the ‘how’ part of implementing CRM may be felt difficult.
But the ‘why’ part of the CRM concept is also not difficult to understand. If we look back to when there was no IT implementation, customer relationships were being managed then by keeping in mind a customer database.
Presently, with advanced technology, the quality of customer management has entirely changed. But the core of CRM and the target remain the same to maximize business profits. Keeping this perspective in mind, proper techniques must be employed to access its utility.
CRM is Expensive and Unaffordable
CRM is expensive and unaffordable for small enterprises. It is a myth that IT maintenance cost is unaffordable for small and medium-class entrepreneurs. Nowadays Application Service Providers with simple and limited functions provide CRM at affordable prices.
Its operation is easy without involving expensive IT professionals. Therefore, to target good results emphasis should be on people and procedure strategies and in the end utilize the software.
Wrong assessment for Return on Investment in CRM
In CRM implementation, Return on Investment means the evaluation of returns with the costs incurred. CRM is sometimes regarded as giving a poor ROI. In fact, the probability of poor ROI is more if CRM is not deployed and the opportunity is lost.
The main causes of poor ROI are ignoring people and procedure strategies, absence of quantified benchmarking to measure the results, lack of vision in a strategic gain of opportunities, etc. These are the points to ponder before implementing a CRM.
Who is Responsible for CRM Implementation?
The Marketing, Sales, Customer Service, or IT officials? – It is not advisable to lay the responsibility on all. The result will be that none of them will feel responsible. The ultimate responsible person should be the CEO as he formulates and manages the business strategies.
In order to have a better success index, the CEO and his immediate deputy should be educated and trained in the implementation of CRM. A better understanding of different dimensions of CRM, therefore, is a must to potentially enhance the benefits of CRM implementation.
What are the stages of Customer Relationship?
Stages of customer relationship are:
1. Exploration
2. Awareness
3 Expansion
4. Commitment
5. Dissolution.
What are the different types of customers?
Following are the 5 different types of customers:
1. Loyal Customers
2. Discount Customers
3. Impulsive Customers
4. Need-Based Customers
5. Wandering Customers.
What are the features of CRM?
These are the 7 features of CRM:
1. Customer’s Needs
2. Customers Response
3. Customer Satisfaction
4. Customer Loyalty
5. Customer Retention
6. Customer Complaints
7. Customer Service.
What is meaning of CRM?
CRM is the final goal of a new trend in marketing that focuses on understanding customers as individuals instead of as part of a group.