Table of Contents
What is Marketing and Customer Value?
Customer Value is the sum total of benefits that customers will accrue from a service or product in relation to its cost. The Customer Value Proposition (CVP) would be the total amount of benefits offered by the seller in return for payment for the goods or services.
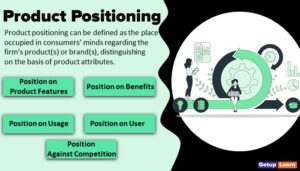
It is a defined statement that is formulated to convince customers that this particular product will add more value than a competitor’s product.
Conceiving and delivering excellent customer value is essential for all kinds of business organizations in today’s competitive business environment. Delivering value requires a deep insight into the art of value creation, by choosing the best value for its customers and delivering that value in an effective and efficient manner.
Find out more: Creating a good value proposition for its customers is also vital for an organization to differentiate its product from the competitor’s products and achieve sustainable competitiveness. A good understanding of customer needs and requirements are important aspects here.
Example of CVP: BMW’s value proposition is “the ultimate driving machine,” making luxury cars. When the direct competition came in this segment, BMW felt the need for differentiating its product. They added a customer value proposition ‘No cost maintenance,’ for the first four years / 100000 km.
Value Delivery Process
Previously, marketing was taking place during the selling process. As different individuals have specific wants, perceptions, preferences, and buying criteria, a smart company must design and deliver offerings for well–defined target markets.
This inspired a new view that marketing should take place at the beginning of planning. Companies instead of emphasizing making and selling should now see themselves as a value delivery process.
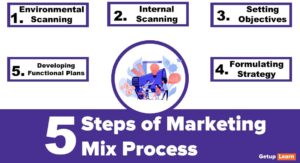
The value Creation and Delivery sequence should be divided into three phases:
First Phase
Before any product comes into the market, marketers must segment, target the market and develop the offering’s value positioning.
Second Phase
Marketers must identify the specific features of the product, price, and distribution.
Third Phase
In the third phase, marketers must communicate the value of the product through various means.
The value delivery process begins before the product exists, and continues through development, and after launch. Each phase has cost implications.
Core Competencies: “C. K. Prahlad and Gary Hamel” were the first to establish this business concept in 1990. According to them, it is a unique set of skills and resources that a company is able to utilize more effectively and efficiently than its market competitors. In a nutshell, core competencies are what make a company stands out from the crowd.