Table of Contents
What is Sales Planning?
The military saying, “If you fail to plan, you plan to fail,” is very true. Without a plan, managers are set up to encounter errors, waste, and delays. A plan, on the other hand, helps a manager organize resources and activities efficiently and effectively to achieve goals.
Out of the five management functions planning, organizing, staffing, leading, and controlling planning is the most fundamental. All other functions stem from planning. It is the foundation of management.
However, most of the time, planning doesn’t always get the attention that it deserves; this is often noticed when the root cause of most management failures is traced to a lack of proper planning. A plan is a blueprint for goal achievement that specifies the necessary resource allocations, schedules, tasks, and other actions.
Sales Planning Conceptual Framework
Planning not only provides direction and a unity of purpose for organizations, but it also answers six basic questions in regard to any activity (including sales):
- What needs to be accomplished?
- When is the deadline?
- Where will this be done?
- Who will be responsible for it?
- How will it get done?
- How much time, energy, and resources are required to accomplish this goal?
Need for Sales Planning
Need for sales planning because these reasons:
- Without a plan to provide directions, decision-making is aimless and disconnected.
- Sales managers must make their decisions within an environment where change is continuous Planning helps minimize environmental shocks.
- It is important to improve the morale of the employees.
- Through planning, there is an improvement in cooperation and coordination.
- It helps in developing individual and collective standards.
- Increases the sales organization’s flexibility toward the dynamic business environment.
- Planning improves the quality of decision-making.
- Focuses attention on organizational objectives and results.
- Establishes a basis for teamwork.
- Helps anticipate problems and cope with changes.
- Provides guidelines for decision-making.
- Serves as a foundation and a prerequisite to employing all other management functions.
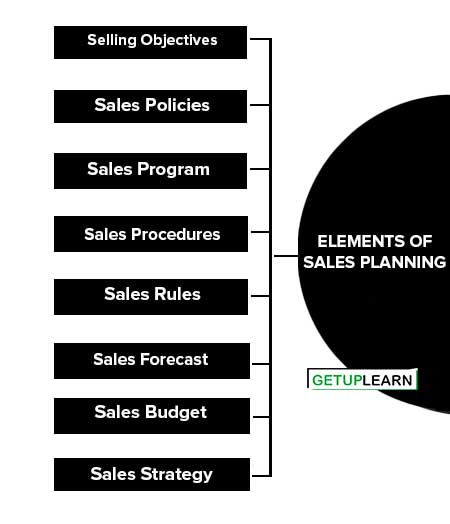
Elements of Sales Planning
The main elements of sales planning include the following:
- Selling Objectives
- Sales Policies
- Sales Program
- Sales Procedures
- Sales Rules
- Sales Forecast
- Sales Budget
- Sales Strategy
Selling Objectives
This includes the list of objectives that need to be attained after the completion of the sales planning process. The objectives should be realistic and attainable. For example, if the sales representative is selling financial products to the customer, a target of 20 to 30 products per month is mostly an achievable target.
If the sales planning document sets the objective as 100 financial products, then it might not be achievable most of the time. Hence the objectives must be achievable and be completed on time. The objectives may be short-term (to be achieved in about one year) or long-term (to be achieved in a 2-3 years time period) in nature.
Sales Policies
They provide guidelines to the sales staff to help them in performing the sales activities. Policies help sales representatives in achieving their targets. For example, when a sale gets returned by the customer, the refund policy will guide the sales representatives on how to deal with the situation effectively, so that the customer will be handled with care rather than getting into an uncomfortable situation.
The sales policies also help in clearly identifying the right pricing for the customer depending upon the relationship the customer shares with the company.
Sales Program
Sales programs help to develop the necessary skill set in achieving sales objectives effectively and in a given time period. They are essential to ensure the sales representative can handle any sales situation that they are entitled to perform.
Sales planning should clearly mention the required skill set needed in handling the sales and the program appropriate to instill those skills in the sales representative.
A sales program may be necessary whenever a new product/ service is introduced by the company or when the sales representatives handle sales from new territories. Cross-cultural training would be given most of the time when the sales include customers other than the native country.
Sales Procedures
The sales procedure is the sequence of various activities that need to be performed for different sales functions. They vary from sale to sale and from market to market. Sales procedure for a business to consumer sales varies greatly from business to business sales.
The sales procedure may include meeting the customer, explaining the product /service through slides, using closing techniques, taking the order, and following up. The procedure for B2B sales may indicate taking a complete team from various departments who are the stakeholders in the project to carry out the explanation of the product/ service. The procedure for B2C sales may indicate that a single representative is enough to handle the task.
Sales Rules
Sales rules indicate the set of actions that need to be performed or otherwise depending upon the situation. For example, in credit card payments, if the customer is asking for a refund of the late payment fee, then the rule says clearly not to refund if the amount is received after the due date.
Hence, the sales staff is not permitted to refund the amount no matter how loyal the customer is to the company. In some cases, a refund could be done.
Sales Forecast
Sales forecast lays the foundation of the sales planning and objective setting. Based on the sales forecast the sales manager would know the sales that could be attainable for the coming period (next quarter or year). Various time series analysis tools such as trend estimation, moving average, weighted moving average, exponential smoothing, etc. may be used to forecast.
Forecasts can be also done based on the predictions done by industry experts. Methods can be many but the aim of forecasting is to clearly identify the demand and plan the sales activities to generate more leads to the business. Sales forecast also help in identifying the strategies to gain or maintain the market share.
Sales Budget
The sales budget identifies the necessary expenditure that is occurred in making the sales. The sales budget estimates the revenue based on sales that would be generated and identifies the profit for the organization after subtracting the operational costs of the sales staff. The sales budget sets the standards for the sales team in terms of the expenditure that is permitted to incur upon the sale.
Hence the sales manager has to see that the operational costs are under control and provide some mechanisms like video conferencing to reduce the traveling costs. To attain a desired profitable level in sales, it is very important to curtail and control operational costs.
Sales Strategy
Sales strategy involves how the company is going to act in the marketplace with the proposed products/ services. The market is dynamic and competitive in nature which makes the companies alert all the times with their strategies regarding all the marketing mix elements. The company, which can handle the sales strategies in the marketplace, is likely to be the winner.
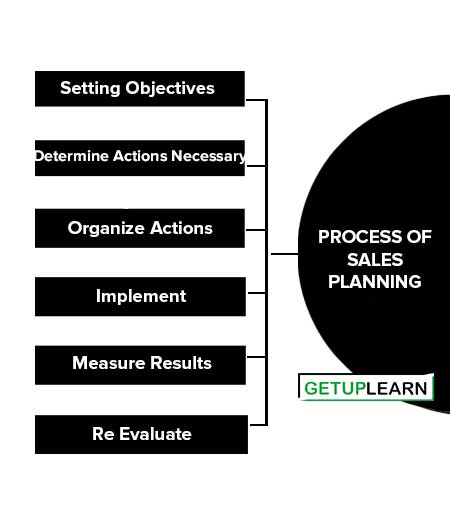
Process of Sales Planning
The sales planning process is very important for an organization. It can be carried out only when the company has a strategic marketing plan in place. The first thing that an organization does is make a strategic marketing plan.
Once the strategic marketing plan is made, the organization knows the segment that has to be targeted, and also, the consumer buying behavior for that segment. These are the of process of sales planning:
- Setting Objectives
- Determine Actions Necessary
- Organize Actions
- Implement
- Measure Results
- Re Evaluate
Setting Objectives
The sales planning is going to start only when the objectives for the sales team have been defined. For example, The objective of an air conditioning company might be to increase the market share of the company. For this, it may decide to penetrate a new geographic market.
Determine Actions Necessary
Once the objectives of the sales plan are known, the actions and operations needed in effect before implementing the sales plan have to be determined. This is a crucial step in the sales planning process because if the correct operations strategy is not made, then in future the company will face a lot of operational difficulties resulting in failure to meet sales objectives.
For example, The air conditioning company needs to penetrate a new geographic territory to increase market share. Thus it needs Sales as well as service operations backup in this territory. The marketing department should also know the new territory so that they can come up with aggressive marketing tactics to target that territory.
Organize Actions
Once the necessary operations have been charted out, there is a need to organize the sales planning. For example, the first priority of the air conditioning company in the new territory will be to have a sale and service setup and the necessary channel in place.
This shall be followed by using aggressive marketing tactics in the new sales territory. Thus an organized action plan needs to be made during the sales planning process.
Implement
After the actions have been planned and organized, implementing them is the next step. Many problems may have to be faced while implementing a sales plan.
For example, the customers of the new territory might not respond to the new air conditioners entering the market. On the other hand, the product might be picked up readily by the customers and the company might not be able to adapt with the unexpected demand.
Measure Results
As in any planning process, the fifth and very important step in the sales planning process is to measure the results. Unlike advertising, sales results are very easy to measure because everything is documented and recorded.
For example, the air conditioning company will measure the total sales of the geographic territory in the study, along with the competitors’ sales as well for record keeping.
Re Evaluate
When there are sales records in hand, it has to be ensured that they are properly analyzed to know whether or not the sales planning process has succeeded. This critical analysis is important to know as to which strategy worked and which strategy failed. This stage helps to set objectives for the next year.
Sales Strategy
Discussed below are different sales strategies useful in B2B and B2C situations:
Components of Sales Strategy
| Classifying market segments and individual customers within a target segment | 1. Each firm should first decide on target market segments and if possible, to classify customers into high, medium, low sales & profit potentials. 2. Sales strategy is developed accordingly |
| Relationship Strategy | 1. Whether a selling firm should use transactional, value-added, or collaborative relationship depends on both the seller and the customer. 2. Each selling firm to decide which segments and individual customers respond profitably to collaborative relationship |
| Selling Methods | 1. These are: .Stimulus Response, .Formula Based, .Need-Satisfaction, .Team Selling, .Consultative Selling. 2. Selection of appropriate selling method depends on relationship strategy |
| Channel Strategy | 1. There are many sales/ marketing channels. For example: company sales force, distributors, franchisees, agents, the internet, brokers, discount stores. 2. Selection of a suitable channel depends on both the buyer and the seller, products / services, and markets |
Sales planning and strategies would be different for B2B (Business to Business) and B2C (Business to Consumer) markets most of the time. The following are the main considerations in B2B markets:
- It deals with the business to business deals where time management is a critical factor for customer satisfaction.
- Since the sales process takes place for months, maintaining the progress in sales is very important.
- The sales staff has to stick with the timings given by the customer and ensure that all the team members are present at the right time.
- The sales team has to deal with customers and plan the activities.
- There is no standardization of activities that can be applied to several customers. Since the requirements differ from customer to customer, the B2B sale plan has to deal with a flexible plan and plan the resources accordingly.
- Customer health in financial terms is very important and hence the customer business trend is observed from time to time. Most of the time the sales are on a credit basis with timely payments in regular intervals.
- Forecasting plays a very important role in preparing a sales plan for B2B customers. Monitoring the forecast of the customer business will give a clear picture of the company’s future sales. For example, if the company is selling product ‘A’ to the customer who in turn sells it to its customers after some value addition, and if the customer business in the future sees a downtrend for the product ‘A’ then it clearly indicates that the leads in future will take a downturn. In such cases, the company has to use appropriate sales strategies to sustain itself in the marketplace.
The following are the main considerations in B2C markets:
- Handling Warehouse Effectively
- Handling Distribution Channels
- Handling Retail Stores
- Handling Price Changes
Handling Warehouse Effectively
The sales plan has to take care that the stock of goods is ensured at all times to handle the demand. Thus, the right forecasting of the demand and coordination with the manufacturing department at regular intervals is very important.
Problems may occur when the goods are produced in more or less than the required quantities by the market. In case of overproduction, goods lie in inventories thereby adding up the inventory costs. In case of low production, companies may lose the customer to their competitors if the goods are not available.
Knowledge of the tax structure is very important to avoid double taxation for selling idle stocks in other states. Due to this, the profit on the product may go down to such a level that a loss is incurred to the company. Having knowledge about the no-tax zones also helps in decreasing the costs.
Handling Distribution Channels
The sales plan has to ensure that the products may not end up lying with the distributors due to less demand. The sales plan has to take care that the goods are distributed in necessary quantities only and are not pushed excessively into the market when the demand is less.
Excessive distribution of goods may damage the relationship between the distributors and the company. This process is very critical in the case of perishable goods like fruits, vegetables, etc.
If they lie for more time in the distribution channels then the chances of them being sold to the end customer decreases due to getting spoiled. It is the task of the sales plan to ensure that proper checks are done to remove excessive stock of perishable goods from the distribution channel and store them appropriately in inventories and sell them when the demand rises.
Handling Retail Stores
It has to be ensured that the sales staff visits retail outlet on monthly basis and check for the stock of goods. Products that are lying for more time mean that more costs have to be incurred for the shelf space.
In organized retail, the shelf space comes at a cost, and in the case of unorganized retail; excessive stock means the company might enter into a credit situation with the retailer as he/she will not be able to pay. More credit in retail may lead to untimely payments and bad relationships.
Hence the sales plan has to deal with such situations and ensure that the stock is sold properly and any excessive stock has to be removed from the retailer’s place. The sales plan also has to ensure that the stocks are made available all the time in case of a hiked demand.
Handling Price Changes
The interest rates or tax rates may go up intermittently, and there is also the factor of inflation, due to which the cost of the product shoots up due to a rise in the operating costs. As a result, the profit margins shrink.
Hence the sales plan has to handle any such situations where the price needs to be increased and necessary sales activities have to be performed to deal with the price changes in the marketplace.
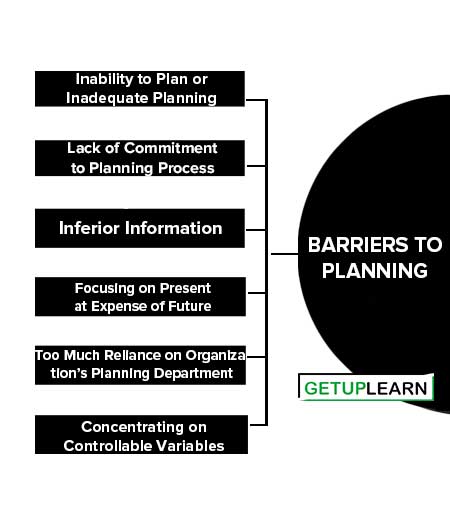
Barriers to Planning
Various barriers can inhibit successful planning. In order for plans to be effective and to yield the desired results, managers must identify any potential barriers and work to overcome them. The common barriers that inhibit successful planning are as follows:
- Inability to Plan or Inadequate Planning
- Lack of Commitment to Planning Process
- Inferior Information
- Focusing on Present at Expense of Future
- Too Much Reliance on Organization’s Planning Department
- Concentrating on Controllable Variables
Inability to Plan or Inadequate Planning
Managers who are not successful planners due to lack of experience, education, and/or ability may not know how to conduct planning as a process. It is very critical to have a responsible person or persons as planners.
Lack of Commitment to Planning Process
The development of a plan requires hard work and proper time management. Another possible reason for lack of commitment can be fear of failure. As a result, non-committed managers may do little or nothing to help in the planning process.
Inferior Information
Facts that are out‐of‐date, of poor quality, or of insufficient quantity can be major barriers to planning. No matter how well managers plan, if they are basing their planning on inferior information, their plans will probably fail.
Focusing on Present at Expense of Future
Failure to consider the long‐term effects of a plan because of emphasis on short‐term problems may lead to trouble in preparing for the future. Managers should try to keep the big picture i.e. their long‐term goals, in mind when developing their plans.
Too Much Reliance on Organization’s Planning Department
Many companies have a planning department or a planning and development team. These departments conduct studies, do research, build models, and project probable results, but they do not implement plans.
Planning department results are aids in planning and should be used only as such. Formulating the plan is still the manager’s responsibility since he or she has a thorough knowledge of the actual working conditions.
Concentrating on Controllable Variables
Managers often concentrate more on the things and events that are controllable and not paying much attention to the various uncontrollable factors like economy, politico-legal or technological factors etc. this may be due to the reason that managers tend to demonstrate a decided preference for the known and an aversion to the unknown.
FAQs About the Sales Planning
What are the elements of sales planning?
The following are the elements of sales planning: 1. Selling Objectives 2. Sales Policies 3. Sales Program 4. Sales Procedures 5. Sales Rules 6. Sales Forecast 7. Sales Budget 8. Sales Strategy.
What is the process of sales planning?
These are the steps of process of sales planning: 1. Setting Objectives 2. Determine Actions Necessary 3. Organize Actions 4. Implement 5. Measure Results 6. Re Evaluate.
