Table of Contents
Micro and Macro Environment in Marketing Management
In this article, we will be understanding briefly micro and macro environments in marketing management:
Micro Environment in Marketing
Consists of factors in the company’s immediate environment that affect the ability to serve its markets, e.g. company, supplies, market intermediaries, and customers.
To carry out a company’s primary goal i.e. profitably, the company links itself with a set of suppliers and a set of marketing intermediaries to reach its target customers. The suppliers/company/marketing intermediaries/ customers chain comprises the core marketing system of the company.
The company’s success will be affected by two additional groups, namely, a set of competitors and a set of the public.
Following are the factors of micro environment in marketing:
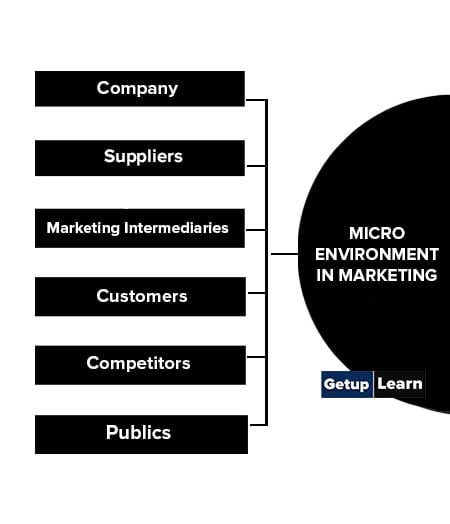
Company
The Company itself is a major component of the company’s microenvironment. The company’s mission and top management’s philosophy have a direct impact on the functioning of the company. Further, every company consists of several functional departments.
Marketing managers have to work closely with the functional departments. Financial management is concerned with the availability of funds to carry out the marketing planning, the efficient allocation of these funds to different products, brands, and marketing activities the likely rates of return that will be realized, and the level of risk in the sales forecast and marketing plans.
The research and development department focuses on researching and developing successful new products. Purchasing worries about obtaining sufficient supplies of raw materials as well as other productive inputs required to run this company. Manufacturing is responsible for acquiring sufficient production capacity and personnel to meet production targets.
Accounting has to measure revenues and costs to help marketers know how well it is achieving its profit objectives. All of the departments have an impact on the marketing department’s plans and actions. The various brand managers have to set their targets in consultation with the manufacturing and finance departments.
Suppliers
Suppliers are those who provide resources needed by the company and its competitors to produce goods and services. The “suppliers” environment can have a substantial impact on the company’s marketing operations. Marketing managers need to watch the price trends of their key inputs.
Marketing managers are equally concerned with supply accessibility. Supply shortages. Labour strikes and other events can prevent fulfilling delivery promises and lose sales in the short run and damage customer goodwill in the long run. Many companies prefer to buy from multiple sources to avoid depending on any one supplier who might raise prices arbitrarily or limit supply.
Company purchasing agents try to build long-term trusting relationships with key suppliers. In times of shortage, purchasing agents find that they have to “market” their company to suppliers in order to obtain preferential supplies. The marketing executive is a direct purchaser of certain services to support the marketing effort, such as advertising, marketing research, sales training, and marketing consulting.
In going outside, the marketing executive evaluates different advertising agencies, marketing research firms, sales, training consultants, and marketing consultants. The executive has to decide which services to purchase outside and which to produce inside by adding specialists to the staff.
Marketing Intermediaries
Marketing intermediaries as firms that aid the company in promoting, selling, and distributing its goods to final buyers. They include middlemen, physical distribution firms, marketing service agencies, and financial intermediaries.
Following are the marketing intermediaries in micro environment:
Middlemen
Middlemen are business firms that help the company find customers or close sales with them. They fall into two types, agent middlemen and merchant middlemen. Agent middlemen such as agents, brokers, and manufacturer’s representatives find customers or negotiate contracts but do not take title to the merchandise.
Merchant Middlemen such as wholesalers, retailers, and other resellers buy, take title to, and resell the merchandise. Market Intermediaries create place utility and time utility. They also create quantity utility and assortment utility.
Physical Distribution Firms
Physical distribution firms assist the company in stocking and moving goods from their original locations to their destinations. Warehousing firms store and protect goods before they move to the next destination.
Every company has to decide how much storage space to build for itself and how much to rent from warehousing firms. Transportation firms consist of railroads, truckers, airline barges, and other freight handling companies that move goods from one location to another. Every company has to decide on the most cost-effective modes of shipment, balancing such considerations as cost, delivery, speed, and safety.
Marketing Service Agencies
Marketing service agencies e.g. marketing research firms, advertising agencies, media firms, and marketing consulting firms- assist the company in targeting and promoting its products to the right markets.
Financial Intermediaries
Financial Intermediaries include banks, credit companies, insurance companies, and other companies that help finance and/or insure risk associated with the buying and selling of goods. The company’s marketing performance can be seriously affected by rising credit costs and/or limited credit.
Each time the company needs major capital, it must develop a business plan and convince financial intermediaries of the plan’s soundness. For these reasons, the company has to develop strong relationships with outside financial intermediaries.
Customers
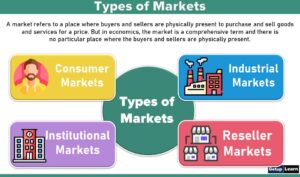
A company links itself with suppliers and middlemen so that it can efficiently supply appropriate products and services to its target market. Its target market can be one ( or more) or the following five types of customer markets:
-
Consumer Markets: Individuals and households that buy goods and services for personal consumption.
-
Industrial Markets: Organizations that buy goods and services for the purpose of making profits and/or achieving other objectives.
-
Reseller Market: Organizations that buy goods and services in order to resell them at a profit.
-
Government and Nonprofit Markets: Government and nonprofit agencies that buy goods and services in order to produce public services or transfer these goods and services to others who need them.
- International Market: Buyers found abroad, including foreign consumers, producers, resellers, and governments.
Competitors
A company rarely stands alone in its effort to serve a given customer market. Its efforts to build a marketing system to serve the market are marched by similar efforts on the part of others.
The company’s marketing system is surrounded and affected by competitors. These competitors have to be identified, monitored, and outmaneuvered to capture and maintain customer loyalty.
Publics
A public is any group that has an actual or potential interest in or impact on a company’s ability to achieve its objectives. A public can facilitate or impede a company’s ability to achieve its goals. The wise company takes concrete steps to manage successful relations with its key public.
Most companies operate public relations departments to plan constructive relations with various publics. These departments monitor the attitudes of the organization’s public and distribute information and communications to build goodwill.
Every company faces several important publics:
-
Financial Publics: Financial institutions – banks, investment houses, stock brokerage firms, insurance companies – affect the company’s ability to obtain funds.
-
Media Public: Companies must cultivate the goodwill of media organizations, specifically newspapers, magazines and radio, and television stations.
-
Government Public: Companies need to take government developments into account in formulating marketing plans.
-
Citizen-action Public: A company’s marketing practices may be questioned by consumer organizations, environmental groups, minority groups, and others.
-
Local Publics: Every company faces the local public such as neighborhood residents and community organizations. Large companies usually appoint a community relations officer to be with community issues, attend meetings, answer questions, and make contributions to worthy causes.
-
General Public: A company needs to be concerned with the general public’s attitude toward its products and practices.
- Internal Publics: A company’s internal publics include blue-collar workers, white-collar workers, managers, and the board of directors.
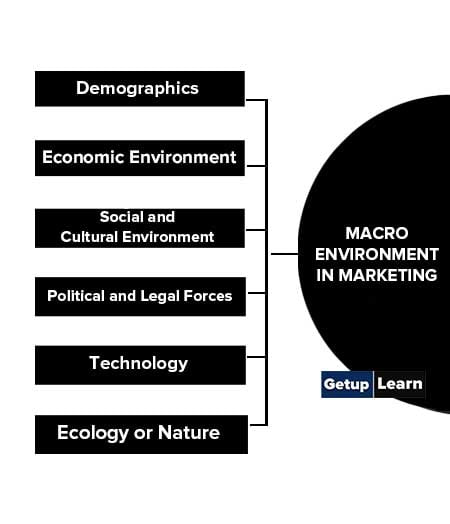
Macro Environment in Marketing
Consists of large society forces stated as uncontrollable factors, e.g. demographic, economic, physical, technological, political, legal, and socio-cultural forces.
The environmental factors must be duly considered in planning any marketing program. There are eight interrelated environmental forces considerably influencing the marketing management system of a business organization.
They are dynamic as well as uncontrollable forces included in the environment of the marketing system of a business enterprise. Following are the factors macro environment in marketing:
- Demographics
- Economic Environment
- Social and Cultural Environment
- Political and Legal Forces
- Technology
- Ecology or Nature
Demographics
Demography is the study of the size, composition, and distribution of the human population in relation to social factors such as geographic boundaries.
The terms demography and demographics come from the Greek word demos, meaning “people” (as does the word democracy). Demography may be defined as the study of the size, composition (for example, by age or racial group), and distribution of the human population in relation to social factors such as geographic boundaries.
The size, composition, and distribution of the population in any geographic market will clearly influence marketing. Demographic factors are of great concern to marketing managers.
Economic Environment
Socio-cultural factors of a market need to be understood to accommodate the diversity of values, beliefs, customers, rituals, faiths, etc. of diverse cultures with the increased areas of operation of business wherein companies are becoming global, a critical understanding of culture is a must for planning the marketing mix.
High economic growth assures a higher level of employment and income, and this leads to a marketing boon in many industries. Marketing plans and programs are also influenced by many other economic items such as interest rates, money supply, price level, consumer credit, etc.
Higher interest rates adversely influence the real estate market and markets for consumer durable sold on an installment basis. Exchange fluctuations, currency devaluation, and changes in political and legal set-up influence international marketing.
The level of take-home pay determines disposable personal income and it influences marketing programs directly. Economic conditions leading to recession can influence the product planning, price fixing, and promotion policies of a business enterprise. The marketing mix must be formulated on the basis of important economic indices.
We have an ever-changing society. New demands are created and old ones are lost in due course. Marketing management is called upon to make necessary adjustments in marketing plans in order to fulfill new social demands.
There are three aspects of the social environment:
- Changes in our lifestyles and social values, e.g. changing role of women, emphasis on quality of goods instead of quantity of goods, greater reliance on governments, greater preference for recreational activities, etc.
- Major social problems, e.g., concerns for pollution of our environment, socially responsible marketing policies, need for safety in occupations and products, etc.
- Growing consumerism indicates consumer dissatisfaction since1960. Consumerism is becoming increasingly important to the marketing decision process. The social environment in many countries is responsible for emphasizing the social responsibility of business and a customer-oriented marketing approach.
Societal marketing concept demanding not only consumer welfare but also citizen welfare is due to the prevalent social environment and social or cultural values in many countries. Marketers are now called upon not only to deliver a higher material standard of living but also to assure the quality of life, i.e. environment free from pollution.
Political and Legal Forces
Political and legal forces are gaining considerable importance in marketing activities and operations of business enterprises. Marketing systems are affected by government monetary and fiscal policies, import-export policies, and customs duties.
Legislation controlling the physical environment, e.g., antipollution laws also influence marketing plans and policies. Then in many countries, we have specific legislation to control marketing e.g., forward markets of commodities and securities. Consumer legislation tries to protect consumer interests.
Marketing policy-making is influenced by government policies and controls throughout the world. Marketers need to understand the government machinery, policies, and laws that are likely to affect their businessmen. They must be in a position to anticipate the likely changes in the political situation so as to take corrective action in time.
Technology
Phenomenal development in science and technology since 1950 has created a tremendous impact on lifestyles, our consumption as well as in the economic welfare of society. In most cases, the market was the mother of invention.
The evolution of the global market by 2001 has been due to the wonders of science and technology. Technology is the way things are done, materials, and techniques used to achieve business objectives. It is the driving force being many new product innovations and the development of many markets.
The time between idea, invention, and commercialization is now considerably shortened and a technological breakthrough can take place within a few years now. For instance, ideas for frozen foods need 70 years for their commercialization.
The strides in information technology and computers have revolutionized our entire lifestyles and products are changing forms and marketers have to understand and appreciate them.
Ecology or Nature
Ecology is the science of dealing with living things and their environment. All living things are related to other living things and they likewise are related to their physical environment. “Green marketing is a concept” that is increasingly becoming popular and marketers who take care of ecology are more acceptable to society. Ecology has assumed unique importance under the societal marketing concept since 1970.
What is the micro environment in marketing?
Micro environments in marketing are:
1. Company
2. Suppliers
3. Marketing Intermediaries
4. Customers
5. Competitors
6. Publics.
What is the macro environment in marketing?
Macro environments in marketing are:
1. Demographics
2. Economic Environment
3. Social and Cultural Environment
4. Political and Legal Forces
5. Technology
6. Ecology or Nature.