Table of Contents
Why is CRM Important in Banking?
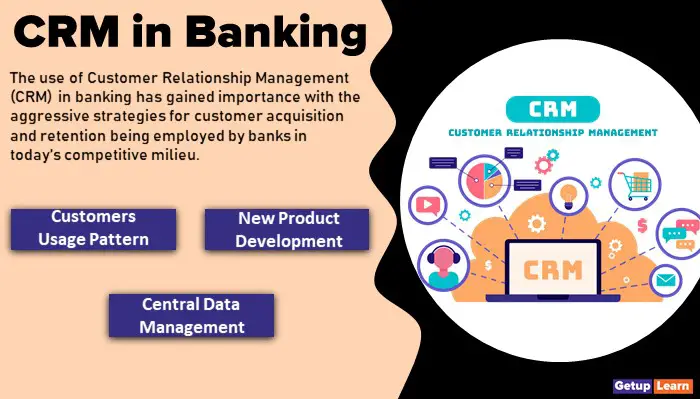
The use of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) in banking has gained importance with the aggressive strategies for customer acquisition and retention being employed by banks in today’s competitive milieu.
This has resulted in the adoption of various CRM initiatives by these banks to enable them to achieve their objectives.
The steps that banks follow in implementing Customer Relationship Management (CRM) are:
- Identifying CRM initiatives with reference to the objectives to be attained (such as increased number of customers, enhanced per– customer profitability, etc.).
- Setting measurable targets for each initiative in terms of growth in profits, number of customers, etc.
- Evaluating and choosing the appropriate Customer Relationship Management (CRM) package that will help the company achieve its CRM goals (a comparison of pay–offs against investments could be carried out during the evaluation exercise).
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) has been deployed in retail banking. The challenges in managing customer relations in retail banking are due to the multiple products being offered and the diverse channels being used for the distribution of the products. Customer expectation from banks can be summed up as:
“Any time anywhere service, personalized offers, and lower payouts”.
Aggressive marketing and promotions on the part of the banks have resulted in most customers happily switching loyalties to enjoy better privileges, thereby making the task of retaining them more difficult for the banks.
Objectives of CRM in Banking Sector
These are the following objectives of crm in banking sector:
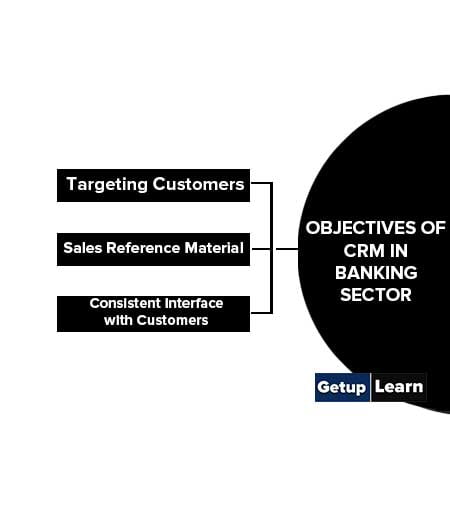
Targeting Customers
It is necessary for banks to identify potential customers for approaching them with suitable offers. The transactional data that is generated through customer interactions and also by taking into account the profile of the customer (such as the lifecycle stage, economic background, family commitments, etc.) needs to be collated into one database to facilitate its proper analysis.
For example, a customer interacts with the banks for savings accounts, credit cards, home loans, car loans, demat accounts, etc. the data generated through all these services needs to be integrated to enable effective targeting.
After the integration is done, a profitability analysis of the customer needs to be undertaken to acquire an understanding of the profit–worthiness of the customer before targeting him with new offers.
Sales Reference Material
A consolidated information database on all products, pricing, competitor information, sales presentations, proposal templates, and marketing collateral should be accessible to all the people concerned.
These prove to be very helpful in Sales Force Automation (SFA) wherein the salesperson gets instantaneous access to all relevant material as and when it is required (especially when he/she is in a meeting with a client).
Consistent Interface with Customers
The communication to customers from various departments like sales, finance, customer support, etc. should be consistent and not contradictory. Therefore, all departments should be privy to a unified view of the customer to enable a consistent approach.
Removal of inconsistencies is necessary to ensure that customers are not harassed and frustrated owing to poor internal co–ordination. This is bound to enhance customer satisfaction. The contact centers used to interface with customers should ensure consistency in customer interaction, irrespective of the medium used for the interaction such as telephone, Internet, e–mail, fax, etc.
Banks can use the data on customers to effectively segment the customers before targeting them. Proper analysis of all available data will enable banks to understand the needs of various customer segments and the issues that determine “value” for that segment.
Accordingly, suitable campaigns can be designed to address the issues relevant to that segment and to ensure higher loyalty from these customers. When data analysis is done in the right manner, it helps in generating opportunities for cross-selling and up-selling.
Benefits of CRM in Banking Sector
Following are the benefits of CRM in banking sector with example of ICICI’s:
Customers Usage Pattern
ICICI’s CRM data warehouse integrates data from multiple sources and enables users to find out about the customer’s various transactions pertaining to savings accounts, credit cards, fixed deposits, etc. The warehouse also gives indications regarding the customer’s channel usage.
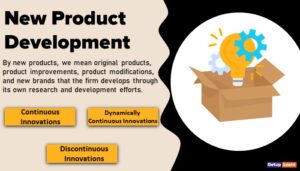
New Product Development
Analysis at ICICI guide product development and marketing campaigns through Behaviour Explorer, whereby customer profiling can be undertaken by using ad hoc queries. The products thus created take into account the customer’s needs and desires, enabling the bank to satisfy customers through better personalization and customization of services.
Central Data Management
The initial implementation of CRM allowed ICICI to analyse its customer database, which includes information from eight separate operations systems including retail banking, bonds, fixed deposits, retail consumer loans, credit cards, custodial services, online share trading and ATM.
What are the benefits of CRM in banking sector?
Benefits of crm in banking sector are:
1. Customers Usage Pattern
2. New Product Development
3. Central Data Management.
What are the objectives of crm in banking sector?
Objectives of crm in banking sector are:
1. Targeting Customers
2. Sales Reference Material
3. Consistent Interface with Customers.