Methods of human resource planning ensure the best fit between employees and jobs while avoiding manpower shortages or surpluses. There are four key steps to the HRP process. They include analyzing present labour supply, forecasting labour demand, balancing projected labour demand with supply, and supporting organizational goals.
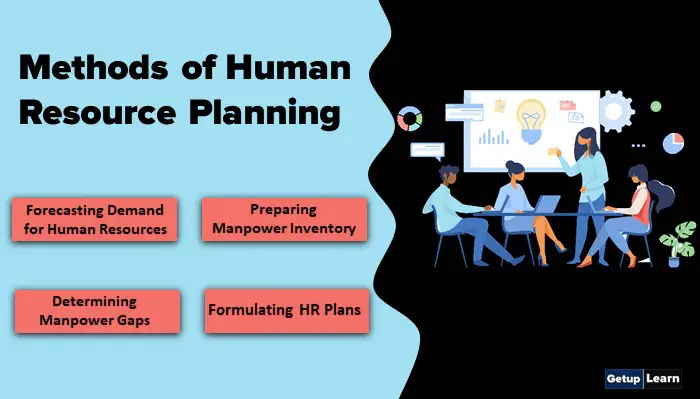
Table of Contents
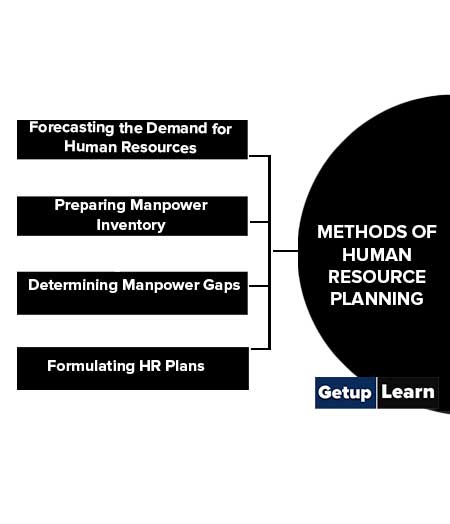
Methods of Human Resource Planning
The methods of human resource planning are usually followed in a large organization. These are the methods of human resource planning steps:
- Forecasting the Demand for Human Resources
- Preparing Manpower Inventory
- Determining Manpower Gaps
- Formulating HR Plans
Forecasting the Demand for Human Resources
Most firms estimate how many employees they require in the future. The demand for skilled humans at various levels is primarily due to the following factors:
External Challenges
These challenges arise from three important sources:
-
Economic developments: Liberalisation, opening up of the banking sector, capital market reforms, and online trading systems have created a huge demand for finance professionals during 1990-1995 in India. The late 90s saw the rise of manufacturing, FMCG, Pharmaceuticals, Auto-components, Healthcare, and Chemical Industries in a steady manner. Consequently, the demand for Engineering and Management graduates, Scientists, and Healthcare .professionals has picked up in recent times.
-
Political, legal, social, and technical changes: The demand for certain categories of employees and skills is also influenced by changes in the political, legal, and social structure of an economy. Likewise, firms employing the latest technology in construction, power, automobiles, software, etc., have greatly enhanced the worth of technicians and engineers during the last couple of years.
Technology, however, is a double-edged weapon and hence, its impact on HR plans is difficult to predict. For example, computerization programs in Banks, Railways, posts, and Telegraph Departments may reduce demand in one department (bookkeeping, for example) while increasing it in another (such as computer operations). High technology with all its attendant benefits may compel organizations to go lean and downsize their workforce suddenly. Employment planning in such situations becomes complicated.
- Competition: Companies operating in fields where a large number of players are bent on cutting each other’s throats (with a view to enhancing their market shares) often reduce their workforce. Competition is beneficial to customers but suicidal for companies operating on thin margins. Such companies have to necessarily go ‘lean’ by reducing their workforce. On the other hand, companies that are doing well and progressing smoothly will always look for people with critical skills.
Organizational Decisions
The organization’s strategic plan, sales, and production forecasts, and new ventures must all be taken into account in employment planning. If Britannia Industries Ltd expects higher demand for biscuits and bread, the long-term HR plan must take this into consideration.
Likewise, if it tries to venture into other lucrative fields such as milk-based products and confectionery items, the demand for people possessing requisite skills in those areas in the next couple of years should be looked into carefully.
Workforce Factors
Demand is modified by retirements, terminations, resignations, deaths, and leaves of absence. Past experience, however, makes the rate of occurrence of these actions by employees fairly predictable.
Forecasting Techniques
The manpower forecasting techniques commonly employed by modern organizations are given below:
-
Expert forecasts: In this method, managers estimate future human resource requirements, using their experiences and judgments to good effect.
- Trend analysis: HR needs, can be estimated by examining past trends. Past rates of change can be projected into the future or employment growth can be estimated by its relationship with a particular index.
Preparing Manpower Inventory
The basic purpose of preparing manpower inventory is to find out the size and quality of personnel available within the organization to man various positions. Every organization will have two major sources of supply of manpower:
Internal Labor Supply
A profile of employees in terms of age, sex, education, training, experience, job level, past performance, and future potential should be kept ready for use whenever required. Requirements in terms of growth/diversification, and internal movement of employees (transfer, promotions, retirement, etc.) must also be assessed in advance.
External Labor Supply
When the organization grows rapidly and diversifies into newer areas of operations (merchant banking, capital market operations, mutual funds, etc. In the case of a bank) or when it is not able to find the people internally to fill the vacancies, it has to look into outside sources.
To the extent an organization is able to anticipate its outside recruitment needs and looks into the possible sources of supply keeping the market trends in mind, its problem in finding the right personnel with appropriate skills at the required time would become easier.
Determining Manpower Gaps
The existing number of personnel and their skills (from human resource inventory) are compared with the forecasted manpower needs (demand forecasting) to determine the quantitative and qualitative gaps in the workforce. A reconciliation of demand and supply forecasts will give us the number of people to be recruited or made redundant as the case may be.
This forms the basis for preparing the HR plan. The Box below shows how demand and. supply forecasts can be related over a period of three years.
Formulating HR Plans
Organizations operate in a changing environment. Consequently, human resource requirements also change continually. Changes in product mix, union agreements, and competitive actions are some of the important things that need special attention.
The human resource requirements identified along the procedure outlined in the above box need to be translated into a concrete HR plan, backed up by detailed policies, programs, and strategies (for recruitment, selection, training, promotion, retirement, replacement, etc.
- Recruitment Plan
- Redeployment Plan
- Redundancy Plan
- Training Plan
- Productivity Plan
- Retention Plan
- Control Points
Recruitment Plan
Will indicate the number and type of people required and when they are needed; special plans to recruit the right people and how they are to be dealt with via the recruitment program.
Redeployment Plan
Will indicate the programs for transferring or retraining existing employees for new jobs.
Redundancy Plan
Will indicate who is redundant, when, and where; the plans for retraining, where this is possible; and plans for a golden handshake, retrenchment, lay-off, etc.
Training Plan
Will indicate the number of trainees or apprentices required and the program for recruiting or training them; existing staff requiring training or retraining; new courses to be developed or changes to be effected in existing courses.
Productivity Plan
Will indicate reasons for employee productivity or reducing employee costs through work simplification studies, mechanization, productivity bargaining; incentives and profit sharing schemes, job redesign, etc.
Retention Plan
Will indicate reasons for employee turnover and show strategies to avoid wastage through compensation policies; changes in work requirements and improvement in working conditions.
Control Points
The entire manpower plan is subjected to close monitoring from time to time. Control points are set up to find out deficiencies, and periodic updating of manpower inventory, in the light of changing circumstances, be undertaken to remove inefficiencies and develop future plans.
In methods of human resource planning, organizations can ensure that they have the right mix of employees with the right skills and abilities to meet the organization’s future needs.
How many methods are there for manpower planning?
The following are the methods for the manpower planning process:
1. Forecasting the Demand for Human Resources
2. Preparing Manpower Inventory
3. Determining Manpower Gaps
4. Formulating HR Plans.
How to formulate HR plans?
The following are steps for formulating HR plans:
1. Recruitment Plan
2. Redeployment Plan
3. Redundancy Plan
4. Training Plan
5. Productivity Plan
6. Retention Plan
7. Control Points.
What are the demand forecasting methods of human resource planning?
The following are the demand forecasting methods of human resource planning:
1. External Challenges
2. Organizational Decisions
3. Workforce Factors
4. Forecasting Techniques.
What are the methods of human resource planning?
The following are the methods of human resource planning:
1. Workforce Analysis
2. Job analysis
3. Succession Planning
4. Forecasting
5. Recruitment and Selection
6. Training and Development.