Table of Contents
- 1 What is Recruitment?
- 2 Definition of Recruitment
- 3 Factors Affecting Recruitment
- 4 Process of Recruitment
- 5 Sources of Recruitment
- 6 Alternatives to Recruitment
-
7 FAQ Related to Recruitment
- 7.1 What is meant by HR recruitment?
- 7.2 What is the definition of recruitment?
- 7.3 What are the factors affecting recruitment?
- 7.4 Which is the step by step process of recruitment?
- 7.5 What are the sources of recruitment internal and external?
- 7.6 What is an advantage of internal recruitment?
- 7.7 What are the disadvantages of internal recruitment?
What is Recruitment?
Recruitment is the process of hiring the right number of people of the right type at the right place. It is the process of generating a pool of qualified applicants for a job. It includes identifying and encouraging the candidates to apply for a job, receiving applications and screening the applicants.

Recruitment forms a step in the process that continues with selection and ceases with the placement of the candidate. It is the next step in the procurement function, the first being manpower planning.
Recruiting makes it possible to acquire the number and types of people necessary to ensure the continued operation of the organisation. Recruiting is the discovery of potential applicants for actual or anticipated organisational vacancies.
Definition of Recruitment
These are some simple definitions of recruitment which easy to understand:
[su_quote cite=”Michael Armstrong”]Recruitment means attracting candidates, which is primarily a matter of identifying, evaluating and using the most appropriate source of applicants.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”Kempner”]Recruitment forms the first stage in the process which continues with selection and ceases with the placement of the candidate.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”Edwin Flippo”]Recruitment is the process of searching for prospective employees and stimulating and encouraging them to apply for jobs in an organisation.[/su_quote]
[su_quote cite=”Dale Yoder”]Recruitment is a process to discover the sources of manpower to meet the requirements of the staffing schedule and employing effective measures for attracting that manpower in adequate numbers to facilitate the selection of an efficient workforce.[/su_quote]
Factors Affecting Recruitment
The recruitment policy of an organisation is the guiding tool that governs the Human Resources practices relating to recruitment. A good recruitment policy has to factor in many aspects to make it effective. The following are factors affecting the recruitment policy of an organisation:
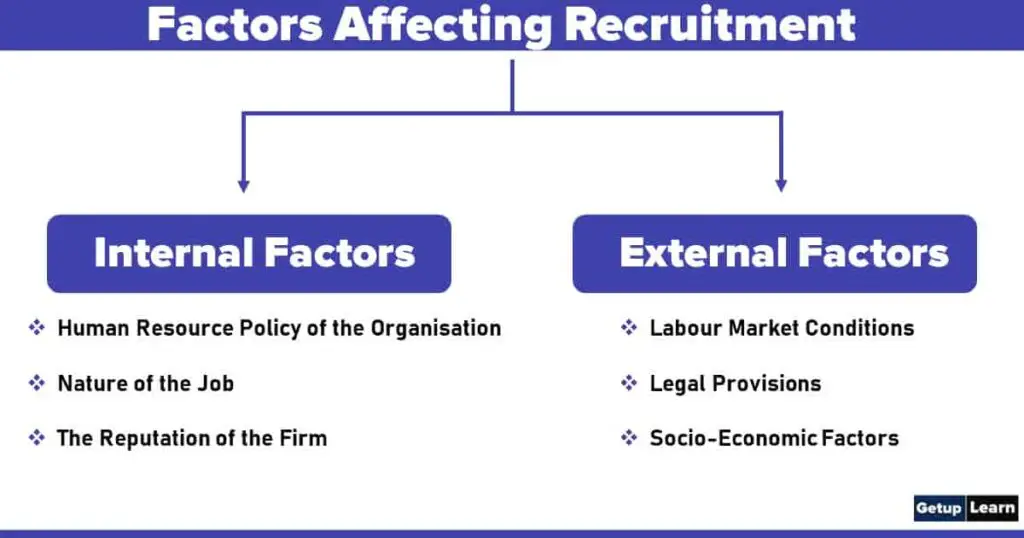
Internal Factors
Internal factors are those that are in control of the organisation. The following are the internal factors that influence the recruitment policy of the organisation:
Human Resource Policy of the Organisation
The overall Human Resource Policy of the organisation has an influence on the recruitment policy. It gives specific guidelines to the Human Resources managers on various matters of employment as it states the organisation’s intent regarding recruitment, selection, training, promotion, compensation and other aspects of Human Resource Management. According to the Human Resources policy, the recruitment policy would be framed.
Nature of the job
The nature of the job has an influence on the recruitment policy of the organisation as the procedure adopted for managerial as well as non-managerial positions might be different. Further, the recruitment policy also differs according to the level of education as well as technical skills required. Moreover, the number of vacancies also determines the re-recruitment policy.
The Reputation of the Firm
The position of the organisation in the labour market influences the recruitment policy. An organisation with a positive image is also able to attract prospective candidates with little effort. So, the recruitment policy is framed according to it.
External Factors
These are the external factors that are not in control of the organisation. These factors include:
Labour Market Conditions
The demand and supply of employees with the required skills influence the recruitment policy of the organisation. In the case where there is a shortage of employees with the required skills, aggressive recruitment programs and policies may be adopted. Generally, it is very difficult to predict the demand and supply of labourers in real life in an exact manner as the clear cut boundaries of the labour market cannot be defined.
Legal Provisions
Many times, to protect the interest of certain sections of society, the government enacts certain rules. These rules, regulations and legal provisions have an influence on the recruitment policy of the organisation. While framing their recruitment policy, government rules and provisions regarding the same should be kept in mind.
Socio-Economic Factors
Characteristics of society like education, age of people, the economic situation of people, licensing provisions, attitudes towards certain sections of society such as women, have an influence over the recruitment policy of the organisation as these conditions have to be considered by the organisation before the Human Resource Policy is framed.
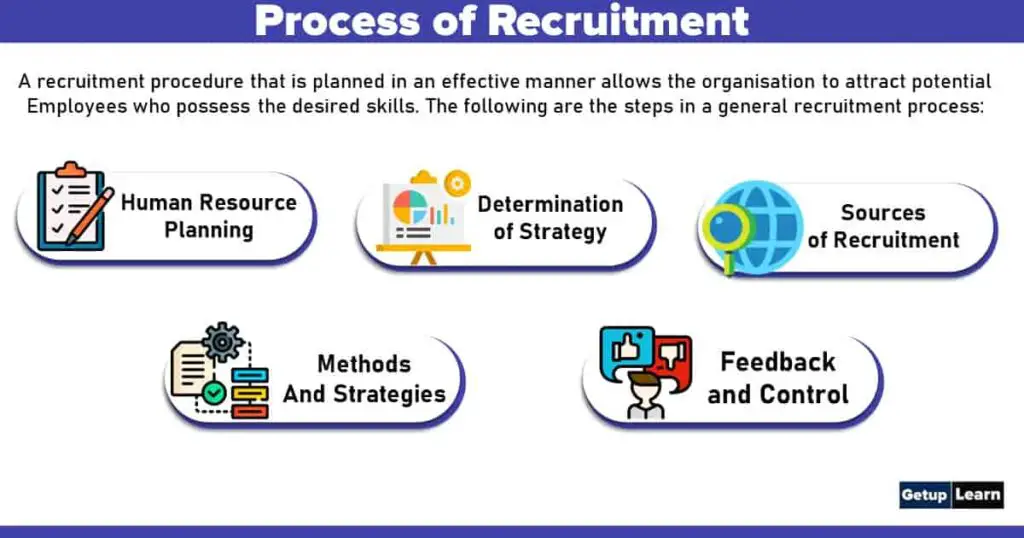
Process of Recruitment
In order to undertake the recruitment process in an effective manner, generally, there are a few steps which are followed. A recruitment procedure that is planned in an effective manner allows the organisation to attract potential employees who possess the desired skills. The following are the steps in a general recruitment process:
- Human Resource Planning
- Determination of Strategy
- Evaluation of Sources of Recruitment
- Implementation of Recruitment Methods and Strategies
- Feedback and Control
Human Resource Planning
This is the first step of the recruitment process wherein the human resource plans are framed according to the objectives of the organisation. Through Human Resource Planning, the organisation can determine the level and type of human resources which are required.
Human Resource Planning also involves preparing a detailed profile of all jobs in an organisation. Through these profiles, it is easier for the management to estimate the skills which would be required in an employee and from where they can be procured.
With the help of Human Resource Planning, the human resource requirements of the organisation are estimated and on the basis of that, the recruitment policy of the organisation can be framed.
Determination of Strategy
For the determination of strategy for choosing the candidates, the sources of recruitment, the method of recruitment and the activities to be undertaken are decided. For this, job specification reports which specify the quality and quantity of personnel required may be used. after that, a strategy should be designed in such a manner that a maximum number of applicants are attracted.
Evaluation of Sources of Recruitment
In order to proceed further, the internal and external sources of recruitment should be evaluated. Through an evaluation of the sources of recruitment, the organisation would be able to determine from which source the prospective employee would be available.
Implementation of Recruitment Methods and Strategies
Once the source of recruitment is finalised, then the method of recruitment has to be finalised. While doing so, it is important that the method and strategy adopted is according to the laws and regulation.
Feedback and Control
Once the entire recruitment process is completed, it is essential to ensure that the process which was followed was able to generate an applicant pool that possessed the desired qualifications. For this, the effectiveness of the recruitment process should be assessed.
In case it is found that the strategy and the method adopted limits the applicant pool or the quality of the applicants is inferior to what was desired, then the recruitment process should be changed to help the organisation achieve the desired result.
Sources of Recruitment
Having different sources of recruitment plays an important role for the organisation as it allows the organisation to successfully gather a large pool of applicants without compromising their quality. But no single source of recruitment combines the benefits of all sources.
So, in order to build a diverse applicant pool, many times, organisations use multiple sources of recruitment. The sources of recruitment can be majorly divided into two types:

Internal Sources of Recruitment
Internal sources of recruitment refer to filling open jobs with the current employees of the organisation. In order to use the internal sources of recruitment, many times promotions, transfers or demotions are resorted to. Normally, the internal sources of recruitment include existing employees, former employees and employee referrals which are discussed as under:
Existing Employees
The most common source of internal recruitment is through existing employees. Generally, organisations maintain an inventory of the qualifications of the employees to choose suitable candidates in case a vacancy arises. In order to fill the vacancy through this method, a job posting is done to create an applicant pool of internal candidates.
Job posting refers to the process of advertising available positions to the employees. On receiving the applications, the skills, experience, interests and career goals of the employees are evaluated by the Human Resources department in consultation with the supervisor of the employee.
Once the suitability of the employee is established, promotions or transfers from among the existing employees are initiated. But there is a strong possibility that this method may create bitterness among the employees who are not selected.
Former Employees
Former employees may be considered as an internal source of recruitment as they are familiar with the policies and practices of the organisation as well as employees of the organisation. This source is relied on as the performance of the ex-employee as well as attitude is well known and the risk involved in choosing them is relatively less.
Employee Referrals
Under this method, the present employees provide information about the candidates who are willing to be considered. This source is relied on by the organisation as it is a cost-effective source of recruitment. One assumption is made that the present employees will recommend only suitable candidates for the vacant jobs.
The advantage of this method is that when friends work together, they are less likely to leave the company soon. But the major drawback of this method is that if any referrals are rejected, then it might be a cause of friction in the employee-employer relations.
External Sources of Recruitment
Those sources that have to be searched from outside the organization are external sources of recruitment. External sources are external to a concern. It involves a lot of time and money. The external sources of recruitment include Employment at the factory gate, advertisements, employment agencies, employment exchanges, labour contractors educational institutes, recommendations etc.
The external source of recruitment is a way to reach out to the external labour market to meet the workforce requirements. The following are the important external sources of recruitment:
- Employment Exchanges
- Outsources to Recruitment Agencies
- Advertisement
- Campus Recruiting
- Walk-in Interviews
- E- Recruiting
Employment Exchanges
They are established by the Government to act as a liaison between job providers and job seekers. The employment exchanges help the employees to locate suitable candidates for the vacancies arising in their organisation and the job seekers get information about such job opportunities.
They would find a match for these vacancies with the names of the job aspirants who have registered their names with them. But this method of recruitment is not so effective in India as they are more helpful to the Government in finding appropriate candidates.
Outsources to Recruitment Agencies
When an external Human Resources consultant is called for rendering services, then it is called Outsourcing Recruitment. These agencies specialize in recruitment activities. They charge fees from either the applicant or from the organisation or from both.
When these agencies are hired, a source of qualified applicants is readily available. The subsequent selection process is simplified and unqualified candidates need not be evaluated by the organisation.
Advertisement
One of the most preferred modes of external recruitment is Print Advertisement. They reach many people in a short period of time and vacancies can be communicated to potential candidates quickly. They enjoy a wider coverage and better reach. They are a cost-effective way to fill in vacancies which are in large numbers.
In case jobs require special skills, qualifications, knowledge and experience, the advertisements may be placed in professional or trade journals to reach the target group effectively.
Campus Recruiting
When an applicant pool from graduating classes is created, then it is called campus recruiting. It is adopted in Knowledge-based companies. It is ideal for entry-level managerial and professional jobs like management trainees and technical personnel.
The main aim is to attract good candidates. As college graduates have no firsthand knowledge of the company, they generally go by the reputation of the company and the career growth prospects. This source of recruitment is preferred mostly in the case of entry-level jobs and is not suitable where experience plays a vital role in performing the job.
Walk-in Interviews
When the applicant directly writes to the organisation or walks in to express their interest in becoming an employee of the organisation, it is known as a walk-in-interview. It is a method that helps the organisation to strengthen the applicant pool and is a suitable method for immediate selection and placement. It is used by Business Process Outsourcing (B.P.O.) companies and Information Technology (I.T.) companies to meet their huge workforce demand.
E- Recruiting
Developing various sources of recruitment. is very important for an organisation as it is essential to choose the best employee from the pool without compromising the quality. But each source of recruitment has its merits and demerits which are as under.
Advantages of Internal Recruitment
The following are advantages of internal recruitment:
- Internal recruitment is less time consuming and economical.
- It is reliable as the organization is aware of the employee’s knowledge and skill set.
- There is no need for induction and training as the employee is already aware of the processes, procedures and culture of the organization.
- It increases the motivation level of the employees as they look forward to getting a higher job in the organization instead of looking for greener pastures outside.
- It boosts the morale of the employees, improves their relations with the organization and reduces employee turnover.
- It develops the spirit of loyalty in the employees and ensures continuity of employment and organizational stability.
Disadvantages of Internal Recruitment
These are the main points disadvantages of internal recruitment:
- Internal sourcing prevents new blood, originality and innovative ideas from entering the organization.
- The scope is limited as not all the vacancies can be filled by the limited pool of talent available in the organization.
- The position of the person who is transferred or promoted falls vacant.
- It can create dissatisfaction amongst the rest of the employees as there can be bias or partiality in promoting an employee in the organization.
Advantages of External Recruitment
The following are advantages of external recruitment:
- New and young blood enters the organization, which has innovative ideas, and new approaches that can help to stir up the existing employees.
- It offers a wider pool for selection. Companies can pick up candidates with requisite qualifications.
- It creates a competitive environment as it helps the existing employees to work harder in order to match the standard that the new employees bring in.
- It leads to long term benefits to the organization. Talented pools of people bring along with them new methods of working and new approaches to situations that help the organization to stay abreast with the competitive world outside.
Disadvantages of External Recruitment
These are the disadvantages of external recruitment:
- It is a time-consuming process as it involves attracting the right candidates, screening them, going through a series of tests and interviews etc. When suitable candidates are not available this process has to be repeated again and again.
- This process proves to be very expensive for the organization as the companies have to resort to advertisements, hiring consultants etc for attracting the right pool of talent.
- It can lower morale and demotivate the existing employees as they can feel that their services have not been recognized.
- It is less reliable than internal sourcing. Since the organizations hire candidates on the basis of their resumes, tests, interviews etc they may not turn out to be as expected. It may end up hiring someone who ends up being a misfit and may not be able to adjust to the new set-up.
Alternatives to Recruitment
Since recruitment and selection costs are high (search process, interviewing, agency fee, etc.) firms these days are trying to look at alternatives to recruitment, especially when market demand for a firm’s products and services is sluggish.
Moreover, once employees are placed on the payroll, it may be extremely difficult to remove them if their performance is marginal. Some of the options in this regard may be listed thus:
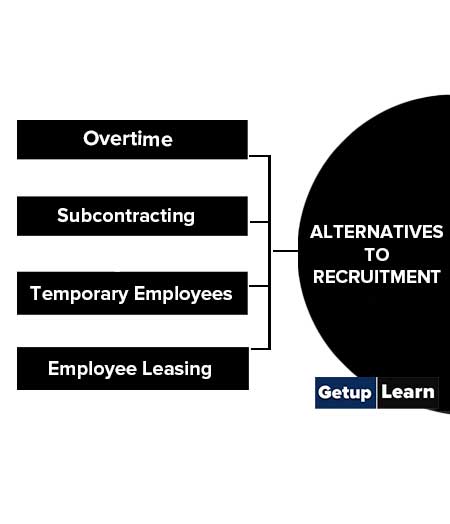
Overtime
Short-term fluctuations in work volume could best be solved through overtime. The employer benefits because the costs of recruitment, selection and training could be avoided. The employee benefits in the form of higher pay. However, an overworked employee may prove to be less productive and turn out less than optimal performance.
Employees may slow down their pace of work during normal working hours in order to earn overtime daily. In course of time, overtime payments become quite routine and for any reason, these payments do not accrue regularly, employees become resentful and disgruntled.
Subcontracting
To meet a sudden increase in demand for its products and services, sometimes, the firm may go for subcontracting – instead of expanding capacities immediately. Expansion becomes a reality only when the firm experiences increased demand for its products for a specified period of time. Meanwhile, the firm can meet increased demand by allowing an outside specialist agency to undertake part of the work to mutual advantage.
Temporary Employees
Employees hired for a limited time to perform a specific job are called temporary employees. They are particularly useful in meeting short term human resource needs. A short-term increase in demand could be met by hiring temporary hands from agencies specializing in providing such services.
In this case, the firm can avoid the expenses of recruitment and the painful effects of absenteeism, labour turnover, etc. It can also avoid fringe benefits associated with regular employment. However, temporary workers do not remain loyal to the company; they may take more time to adjust and their inexperience may come in the way of maintaining high quality.
Employee Leasing
Hiring permanent employees of another company who possess certain specialized skills on a lease basis to meet short-term requirements – although not popular in India is another recruiting practice followed by firms in developed countries. In this case, individuals work for the leasing firm as per the leasing agreement/arrangement. Such an arrangement is beneficial to small firms because it avoids expenses and problems of personnel administration.
What is meant by HR recruitment?
Recruitment is the process of finding and attracting capable applicants for employment. The process begins when new recruits are sought and ends when their applications are submitted. The result is a pool of applicants from which new employees are selected.
What is the definition of recruitment?
Recruitment is the process of searching for prospective employees and stimulating them to apply for jobs in the organization.
What are the factors affecting recruitment?
These are the factors affecting recruitment:
1. The size of the organization
2. The employment conditions in the country where the organization is located.
3. The effects of past recruiting efforts show the organization’s ability to locate and keep good performing people.
4. Working conditions and salary and benefits packages offered by the organization.
5. The level of the seasonality of operations and future expansion and production programmes.
Which is the step by step process of recruitment?
These are the steps in a general recruitment process:
1. Recruitment and planning
2. Determination of Strategy
3. Evaluation of Sources of Recruitment
4. Implementation of Recruitment Methods and Strategies
5. Feedback and Control etc.
What are the sources of recruitment internal and external?
Internal Sources of Recruitment: Existing Employees, Former Employees, Employee Referrals etc. External Sources of Recruitment: Employment Exchanges, Outsources to Recruitment Agencies, advertisement, Campus Recruiting, Walk-in Interviews, E- Recruiting etc.
What is an advantage of internal recruitment?
1. Internal recruitment is less time consuming and economical.
2. It is reliable as the organization is aware of the employee’s knowledge and skill set.
3. There is no need for induction and training as the employee is already aware of the processes, procedures and culture of the organization.
What are the disadvantages of internal recruitment?
1. Internal sourcing prevents new blood, originality and innovative ideas from entering the organization.
2. The scope is limited as not all the vacancies can be filled by the limited pool of talent available in the organization.
3. The position of the person who is transferred or promoted falls vacant.