Table of Contents
What are the 7 Functions of HR?
The functions of an HR manager are very comprehensive and varied. They are determined and influenced by factors such as size, nature, and location of the business or industry. The Human Resource manager has been playing a variety of roles. In the modern era, he typically performs the roles of a counselor, a mediator, a problem solver, and a change agent. Below that we will discuss the functions of HRM in detail.
Functions of HRM
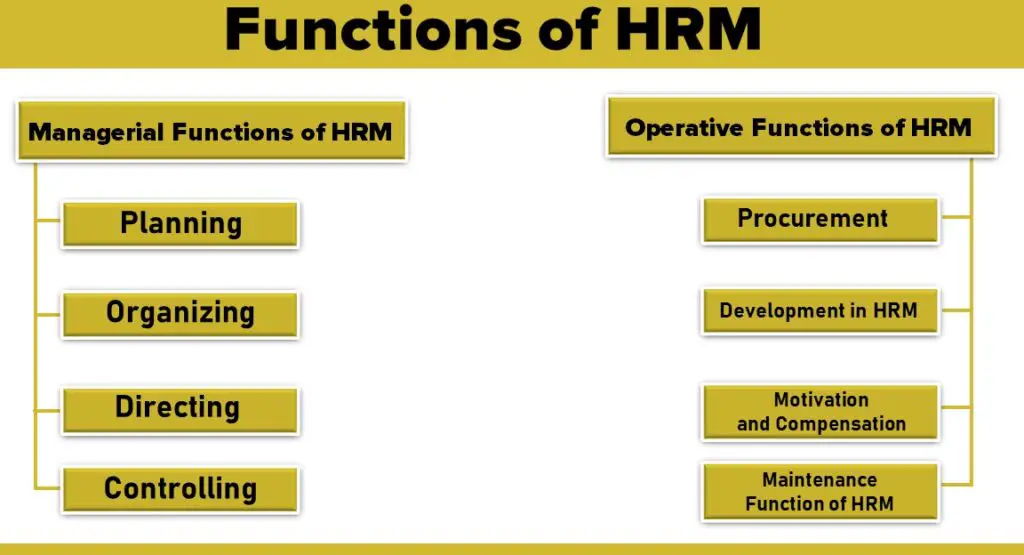
The functions of HRM may broadly be classified into two categories:
Managerial Functions of HRM
The human resource manager is part of the management of the enterprise. So he must perform the basic managerial functions of planning, organizing, directing, and controlling in relation to his own department. These managerial functions of HRM are briefly discussed below:
Planning
This function deals with the determination of the future course of action to achieve desired results. Planning of personnel today prevents crises of tomorrow. The personnel manager is expected to determine the personnel program regarding recruitment, selection, and training of employees.
Organizing
This function is primarily concerned with the proper grouping of personnel activities, assigning of different groups of activities to different individuals, and delegation of authority. The creation of a proper structural framework is his primary task.
Organizing, in fact, is considered to be the wool of the entire management fabric and hence cannot afford to be ignored.
Directing
This involves supervising and guiding the personnel. To execute plans, the direction is essential, for without direction there is no destination. Many a time, the success of the organization depends on the direction of things rather than their design.
Direction then consists of motivation and leadership. The personnel manager must be an effective leader who can create winning teams. While achieving results, the personnel manager manner must, invariably, take care of the concerns and expectations of employees at all levels.
Controlling
The controlling function of personnel management comprises measuring the employee’s performance, correcting negative deviations, and industrial assuring an efficient accomplishment of plans.
It makes individuals aware of their performance through review reports, records, and personnel audit programs. It ensures that the activities are being carried out in accordance with stated plans.
Operative Functions of HRM
The operative functions of HRM are related to specific activities of personnel management, viz. employment, development, compensation, and industrial relations. These functions are to be performed in conjunction with managerial functions:
- Procurement Function
- Development in HRM
- Motivation and Compensation
- Maintenance Function of Hrm
- Integration Function of HRM
- Emerging Issues in HRM
Procurement Function
The first operative function of personnel management is procurement. It is concerned with procuring and employing people who possess the necessary skills, knowledge, and aptitude. Under its purview, you have job analysis, manpower planning, recruitment, selection, placement, induction, and internal mobility.
- Job Analysis
- Human Resources Planning
- Recruitment
- Selection
- Placement
- Induction and Orientation
- Internal Mobility
Job Analysis
Job analysis is the process of collecting information relating to the operations and responsibilities pertaining to a specific job.
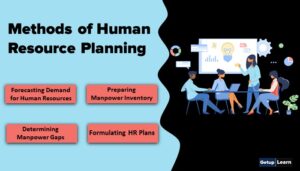
Human Resources Planning
Human resources planning is a process of determining and assuring that the organization will have an adequate number of qualified persons, available at proper times, performing jobs that would meet their needs and provide satisfaction for the individuals involved.
Recruitment
Recruitment is the process of searching for prospective employees and stimulating them to apply for jobs in the organization.
Selection
Selection is the process of ascertaining the qualifications, experience, skills, and knowledge of an applicant with a view to appraising his/her suitability for the job in question.
Placement
Placement is a process that ensures a 3600 fit, matching the employee’s qualifications, experience, skills, and interest with the job on offer. It is the personnel manager’s responsibility to position the right candidate at the right level.
Induction and Orientation
Induction and orientation are techniques by which a new employee is rehabilitated in his new surroundings and introduced to the practices, policies, and people. He must be acquainted with the principles which define and drive the organization, its mission statement, and the values which form its backbone.
Internal Mobility
The movement of employees from one job to another through transfer and promotions is called internal mobility. Some employees leave an organization due to various reasons leading to resignation, retirement, and even termination. These movements are known as external mobility. In the best interest of an organization and its employees, such job changes should be guided by well-conceived principles and policies.
Development in HRM
It is the process of improving, molding, changing, and developing the skills, knowledge, creative ability, aptitude, attitude, values, and commitment based on present and future requirements both at the individual’s and organization’s level. This function includes:
Training
Training is a continuous process by which employees learn skills, knowledge, abilities and attitude, and attitudes to further organizational and personnel goals.
Executive Development
Executive development is a systematic process of developing managerial skills and capabilities through appropriate programs.
Career Planning and Development
Career planning and development is the planning of one’s career and implementation of career plans by means of education, training, job search, and acquisition of work experiences. It includes succession planning which implies identifying developing and tracking key individuals for executive positions.
Human Resource Development
HRD aims at developing the total organization. It creates a climate that enables every employee to develop and use his capabilities in order to further both individual and organizational goals.
Motivation and Compensation
Motivation and compensation is a process that inspires people to give their best to the organization through the use of intrinsic (achievement, recognition, responsibility) and extrinsic (job design, work schedules, appraisal-based incentives) rewards.
- Job Design
- Work Scheduling
- Motivation
- Job Evaluation
- Performance Appraisal
- Compensation Administration
- Incentives and Benefits
Job Design
Organizing tasks, and responsibilities toward having a productive unit of work are called job design. The main purpose of job design is to integrate the needs of employees to suit the requirements of an organization.
Work Scheduling
Organizations must realize the importance of scheduling work to motivate employees through job enrichment, shorter work weeks flexi-time, work sharing, and homework assignments. Employees need to be challenged at work and the job itself must be one that they value.
A work schedule is an attempt to structure work, incorporating the physical, physiological and behavioral aspects of work.
Motivation
Combining forces that allow people to behave in certain ways is an integral aspect of motivation. People must have both the ability and the motivation if they are to perform at a high level. Managers generally try to motivate people through properly administered rewards (financial as well as non-financial).
Job Evaluation
Organizations formally determine the value of jobs through the process of job evaluation. Job evaluation is the systematic process of determining the relative worth of jobs in order to establish which jobs should be paid more than others within the organization. Job evaluation helps to establish internal equality between various jobs.
Performance Appraisal
After an employee has been selected for a job, has been trained to do it, and has worked on it for a period of time, his performance should be evaluated. Performance evaluation or appraisal is the process of deciding how employees do their jobs. It is a method of evaluating the behavior of employees at the workplace and normally includes both the quantitative and qualitative aspects of job performance.
It is a systematic and objective way of evaluating work-related behavior and the potential of employees. It is a process that involves determining and communicating to an employee how he or she is performing and ideally, establishing a plan of improvement.
The performance appraisal process consists of six steps:
- Establish performance standards with employees.
- Set measurable goals (manager and employee).
- Measure actual performance; (4) compare actual performance with standards; (5) discuss the appraisal with the employees and (6) if necessary initiate corrective action.
Compensation Administration
It is the process of dividing how much an employee should be paid. The important goals of compensation administration are to design a low-cost pay plan that will attract, motivate and retain competent employees which are also perceived to be fair by these employees.
Incentives and Benefits
In addition to a basic wage structure, most organizations nowadays offer incentive compensation based on actual performance. Unlike incentives, benefits and services are offered to all employees as required by law including social security, insurance, workers’ compensation, welfare amenities, etc.
Organizations have been offering a plethora of other benefits and services as well as a means of ‘sweetening the pot’ (employee stock options, birthday gifts, anniversary gifts, paid holidays, club membership).
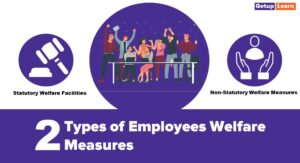
Maintenance Function of HRM
Maintenance aims at protecting and preserving the physical and psychological health of employees through various welfare measures:
Health and Safety
Managers at all levels are expected to know and enforce safety and health standards throughout the organization. They must ensure a work environment that protects employees from physical hazards, unhealthy conditions, and unsafe acts of other personnel.
Through proper safety and health programs, the physical and psychological well-being of employees must be preserved and even improved.
Employee Welfare
Employee welfare includes the services, amenities, and facilities offered to employees within or outside the establishment for their physical, psychological, and social well-being. Housing, transportation, education, and recreation facilities are all included in the employee welfare package.
Social Security Measures
Managers provide social security to their employees in addition to fringe benefits. These measures include:
- Workmen’s compensation to those workers (or their dependents) who are involved in accidents.
- Maternity benefits to women employees.
- Sickness benefits and medical benefits.
- Disablement benefits/allowance.
- Dependent benefits.
- Retirement benefits like Provident Fund, Pension, Gratuity, etc.
Integration Function of HRM
This tries to integrate the goals of an organization with employee aspirations through various employee-oriented programs, like redressing grievances promptly, instituting proper disciplinary measures, empowering people to decide things independently, encouraging a participative culture, and offering constructive help to the trade unions. etc:
- Grievance Redressal
- Discipline
- Teams and Teamwork
- Collective Bargaining
- Employee Participation and Empowerment
- Trade Unions and Employees Association
- Industrial Relations
Grievance Redressal
A grievance is any factor involving wage, hours, or conditions of employment that is used as a complaint against the employer. Constructive grievance handling depends first on the manager’s ability to recognize, diagnose and correct the causes of potential employee dissatisfaction before it converts into a formal grievance.
Discipline
Discipline is the force that prompts an individual or a group to observe the rules, regulations, and procedures, which are deemed necessary for the attainment of an objective.
Teams and Teamwork
Self-managed teams have emerged as the most important formal groups in today’s organizations. They enhance employee involvement and have the potential to create positive synergy. By increasing worker interaction, they create camaraderie among team members.
They encourage individuals to sublimate their individual goals for those of the group. Teams have inherent strengths which ultimately lead to organizational success at various levels.
Collective Bargaining
Collective bargaining is the process of agreeing on a satisfactory labor contract between management and union. The contract contains agreements about conditions of employment such as wages, hours, promotion, and discipline; layoff, benefits, vacations, rest pauses, and the grievance procedure.
The process of bargaining generally takes time, as both parties tend to make proposals and counter-proposals. The resulting agreement must be ratified by unions, workers, and management.
Employee Participation and Empowerment
Participation means sharing the decision-making power with the lower ranks of an organization in an appropriate manner. When workers participate in organizational decisions they are able to see the big picture clearly and how their actions would impact the overall growth of the company.
They can offer feedback immediately based on their experiences and improve the quality of decisions greatly. Since they are now treated with respect, they begin to view the job and the organization as their own and commit themselves to organization objectives wholeheartedly.
Trade Unions and Employees Association
A trade union is an association either of employees or employees or independent workers. It is a relatively permanent body formed by workers, with the objective of countering exploitation and harassment. It strives toward providing economic and social benefits to the labor community.
Trade unions have already played a powerful role in improving a lot of workers in India, using aggressive bargaining tactics. However, since the ’90s, the situation changed dramatically.
Unable to fight the forces of competition, many employers have been forced to shut down units and scale down operations. This has made both parties realize the importance of bargaining for their rights in an atmosphere of ‘give and take’.
Industrial Relations
Harmonious industrial relations between labor and management are essential to achieving industrial growth and higher productivity. When the relationship between the parties is not cordial, discontentment develops and conflicts erupt abruptly.
It is not always easy to put out the fires with the existing dispute settlement machinery, created by the government. Hence both labor and management must appreciate the importance of openness, trust, and collaboration in their day-to-day dealings.
Emerging Issues in HRM
Effective management of human resources depends on refining HRM practices to changing conditions. Hence the need to look at other important issues that can motivate people to give their best in a dynamic and ever-changing environment:
- Personnel Records
- Human Resource Audit
- Human Resources Research
- Human resources accounting (HRA)
- Human Resource Information System
- Stress and Counseling
- International Human Resource Management
Personnel Records
Personnel records such as papers, files, cards, cassettes, and films are maintained to have a tangible record of what is actually happening in an organization and to formulate appropriate HR policies and programs (based on historical records, actual experience, and future trends) from time to time.
Human Resource Audit
A human resource audit refers to an examination and evaluation of policies, procedures, and practices to determine the effectiveness of HRM. Personnel audit (a) measures the effectiveness of personnel programs and practices and (b) determines what should or should not be done in the future.
Human Resources Research
Human resources research is the process of evaluating the effectiveness of human resource policies and practices and developing more appropriate ones.
Human Resources Accounting (HRA)
Human resources accounting is a measurement of the cost and value of human resources to the organization. Human resource management is said to be effective if its value and contribution to any organization are more than its cost.
Human Resource Information System
HRIS is an integrated system designed to improve the efficiency with which HR data is compiled. It makes HR records more beneficial to the management by serving as a source of information.
Stress and Counseling
Stress is the psychological and physical reaction to certain life events or situations. At an organizational level, stress results in burnout, substance abuse in the form of alcohol or drug use/dependence reduced job satisfaction, increased absenteeism, and increased turnover.
Companies, therefore, are closely looking at what should be done to promote the physical and mental well-being of employees through proper counseling and employee development programs.
International Human Resource Management
International business is important to almost every business today and so firms must increasingly be managed with a clear global focus. This, of course, poses many challenges before managers including coordinating production, sales, and financial operations on a worldwide basis.
International HRM places greater emphasis on a number of responsibilities and functions such as relocation, orientation, and training services to help employees adapt to a new and different environment outside their own country.
What are the functions of HRM?
These are important functions of HRM:
1. Planning
2. Organizing
3. Directing
4. Controlling
5. Job Analysis
6. Recruitment
7. Training
8. Job Design
9. Work Scheduling
10. Motivation
11. Job Evaluation
12. Performance Appraisal etc.
Explained the managerial functions of HRM?
Following are the managerial functions of HRM: planning, organizing, directing and controlling, etc.
What are the operative functions of HRM?
These are the operative functions of HRM:
1. Procurement Function
2. Development in HRM
3. Motivation and Compensation
4. Maintenance Function of Hrm
5. Integration Function of HRM
6. Emerging Issues in HRM.