Table of Contents
-
1 Scope of Control in Management
- 1.1 Controls over Policies
- 1.2 Control over Organization
- 1.3 Control over Personnel
- 1.4 Control on Wages and Salaries
- 1.5 Control Over Costs
- 1.6 Control Over Methods and Manpower
- 1.7 Control Over Capital Expenditure
- 1.8 Control Over Service Departments
- 1.9 Control Over Line of Products
- 1.10 Control over Research and Development
- 1.11 Control over Foreign Operations
- 1.12 Control over External Relations
- 1.13 Overall Control
- 2 FAQs Section
Scope of Control in Management
For effective control, it is important to know what are the critical areas where control would be exercised. The identification of these areas of control enhances the management to (i) delegate authority and fixing up of responsibility (ii) reduce the burden of supervising each activity in detail and (iii) have means of securing satisfactory results.
Though controls are needed in every area where performance and results directly and vitally affect the survival and prosperity of the organization, these areas need to be specifically spelled out. The following discussion points out the problems and methods of control in each major area:
- Controls over Policies
- Control over Organization
- Control over Personnel
- Control on Wages and Salaries
- Control Over Costs
- Control Over Methods and Manpower
- Control Over Capital Expenditure
- Control Over Service Departments
- Control Over Line of Products
- Control over Research and Development
- Control over Foreign Operations
- Control over External Relations
- Overall Control
Controls over Policies
Policies are formulated to govern the behavior and action of personnel in the organization. These may be written or otherwise, and policies are generally controlled through policy manuals, which are generally prepared by top management. Each individual in the organization is expected to function according to policy manuals.
Control over Organization
Organization charts and manuals are used to keep control over the organization’s structure. Organization manuals attempt to solve organizational problems and conflicts, making long-range organizational planning possible, enabling rationalization of the organization structure, helping in proper designing and clarification of each part of the organization, and conducting a periodic check of facts about organization practice.
Control over Personnel
Generally, the personnel manager or head of the personnel department, whatever his designation may be, keeps control over personnel in the organization. Sometimes, a personnel committee is constituted to act as an instrument of control over key personnel.
Control on Wages and Salaries
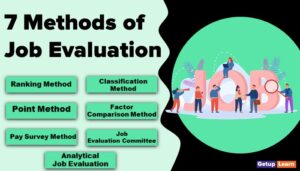
Control over wages and salaries is done by having a program of job evaluation, and wage and salary analysis. The functions are carried on by personnel and industrial engineering departments. Often wage and salary committee is constituted to provide help to these departments.
Control Over Costs
Control over costs is exercised by making a comparison between standard costs and actual costs. Standard costs are set in respect of different elements of costs.
Cost control is also supplemented by the budgetary control system, which includes different types of budgets. Controller’s department provides information for setting standard costs, calculating actual costs, and pointing out differences between these two.
Control Over Methods and Manpower
Control over methods and manpower is kept to ensure that each individual is working properly and timely. For this purpose, periodic analysis of the activities of each department is conducted.
The functions performed, methods adopted, and time consumed by every individual is studied to eliminate non-essential functions, methods, and time. Many organizations create separate departments or sections known as organization and methods to keep control over methods and manpower.
Control Over Capital Expenditure
Control over capital expenditure is exercised through the system of evaluation of projects, and ranking of projects on the basis of their importance, generally on the basis of their earning capacity. A capital budget is prepared for the business as a whole.
The budget committee or appropriation committee reviews the budget. For effective control over capital expenditure, there should be a plan to identify the realization of benefits from capital expenditure and to make a comparison with anticipated results. Such comparison is important in the sense that it serves as an important guide for future capital budgeting activities.
Control Over Service Departments
Control over service departments is effected either (i) through budgetary control within operating departments, (ii) through putting limits upon the amount of service an individual department can ask, or (iii) through authorizing the head of the service department to evaluate the request for service made by other departments and to use his discretion about the quantum of service to be rendered to a particular department: Sometimes, a combination of these methods may be used.
Control Over Line of Products
A committee whose members are drawn from production, sales, and research departments exercises control over the line of products. The committee controls through studies about market needs. Efforts are made to simplify and rationalize the line of products.
Control over Research and Development
Control over research and development is exercised in two ways: by providing a budget for research and development and by evaluating each project keeping in view savings, sales, or profit potentialities.
Research and development being a highly technical activity is also controlled indirectly. Improving the ability and judgment of the research staff through training programs and other devices does this.
Control over Foreign Operations
Foreign operations are controlled in the same way as domestic ones. The tools and techniques applied are the same. The only difference is that the chief executive of foreign operations has a relatively greater amount of authority.
Control over External Relations
The public relations department regulates external relations. This department may prescribe certain measures to be followed by other departments while dealing with external parties.
Overall Control
Control over each segment of the organization contributes to the overall organizational control. However, some special measures are devised to exercise overall control. This is done through budgetary control project profit and loss account and balance sheet.
Integrating and coordinating budgets prepared by each segment prepare a master budget. The budget committee reviews such budget This budget acts as an instrument for overall control. Profit and loss accounts and balance sheets are also used to measure the overall results.
FAQs Section
What is the scope of control in management?
Scope of Control in Management:
1. Controls over Policies
2. Control over Organization
3. Control over Personnel
4. Control on Wages and Salaries
5. Control Over Costs
6. Control Over Methods and Manpower
7. Control Over Capital Expenditure
8. Control Over Service Departments
9. Control Over the Line of Products
10. Control over Research and Development
11. Control over Foreign Operations
12. Control over External Relations
13. Overall Control.