Table of Contents
7 Factors Affecting HRP
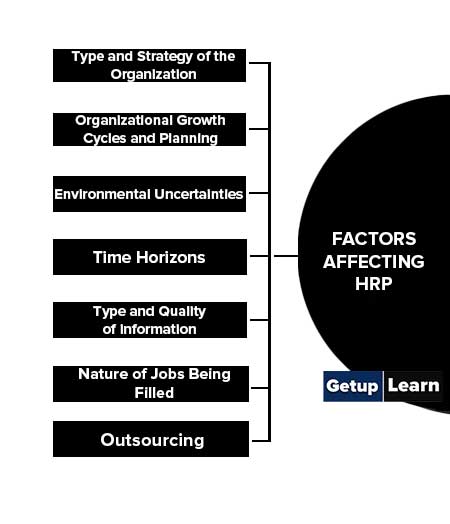
These are some factors affecting HRP:
- Type and Strategy of the Organization
- Organizational Growth Cycles and Planning
- Environmental Uncertainties
- Time Horizons
- Type and Quality of Information
- Nature of Jobs Being Filled
- Outsourcing
Type and Strategy of the Organization
The type of organization determines the production processes involved, the number and type of staff needed and the supervisory and managerial personnel required. HR need is also defined by the strategic plan of the organization. If the organization has a plan for organic growth then the organization needs to hire additional employees.
On the other hand, If the organization is going for mergers and acquisition, then the organization need to plan for layoffs, as mergers can create, duplicate or overlap positions that can be handled more efficiently with fewer employees. The organization first decides whether to be reactive or proactive in Human Resource Planning.
Organizations either carefully anticipate the needs and systematically plan to fill the need in advance (proactive) or can simply react to the needs as they arise (reactive). Likewise, the organization must determine the width of the HR plan. Organizations can choose a narrow focus by planning in only one or two HR areas like recruitment and selection or can have a broad perspective by planning in all areas including training and remuneration.
The nature of the HR plan is also decided by the formality of the plan. They can decide to have an informal plan that lies mostly in the minds of the managers and personnel staff or can have a formal plan which is properly documented in writing The nature of an HR plan is also dependent upon the flexibility that is practiced in the organization.
HR plan should have the ability to anticipate and deal with contingencies. Organizations frame HRP in such a way that it can contain many contingencies, which reflect different scenarios thereby assuring that the plan is flexible and adaptable.
Organizational Growth Cycles and Planning
All organizations pass through different stages of growth from the day of their inception. The stage of growth in which an organization determines the nature and extent of HRP. Small organizations in the earlier stages of growth may not have well-defined personnel planning. But as the organization enters the growth stage they feel the need to plan its human resource.
At this stage, the organization gives emphasis on employee development. But as the organization reaches the mature stage it experiences less flexibility and variability resulting in a low growth rate. HR planning becomes more formalized and less flexible and less innovative and problems like retirement and possible retrenchment dominate planning.
During the declining stage of the organization, Human Resource Planning takes a different focus like planning to do layoff, retrenchment, and retire. In a declining situation, planning always becomes reactive in nature towards the financial and sales distress faced by the company.
Environmental Uncertainties
Political, social, and economic changes affect all organizations and the fluctuations that are happening in these environments affect organizations drastically. Personnel planners deal with such environmental uncertainties by carefully formulating recruitment, selection, training, and development policies and programs.
The balance in the organization is achieved through careful succession planning, promotion channels, layoffs, flexi-time, job sharing, retirement, VRS, and other personnel-related arrangements.
Time Horizons
HR plans can be short-term or long-term. Short-term plans span from six months to one year, while long-term plans spread over three to twenty years. The extent of the time period depends upon the degree of uncertainty that is prevailing in an organization’s environment. Greater the uncertainty, the shorter the plan time horizon, and vice versa.
Type and Quality of Information
The information used to forecast personnel needs originates from a multitude of sources. The forecast depends to a large extent upon the type of information and the quality of data that is available to personnel planners. The quality and accuracy of information depend upon the clarity with which the organizational decision-makers have defined their strategy, structure, budgets, production schedule, and so on.
Nature of Jobs Being Filled
Personnel planners need to be really careful with respect to the nature of the jobs being filled in the organization. Employees belonging to lower levels who need very limited skills can be recruited hastily but, while hiring employees for higher posts, selection and recruitment need to be carried out with high discretion.
Organizations need to anticipate vacancies far in advance as possible, to provide sufficient time to recruit suitable candidates.
Outsourcing
Several organizations outsource part of their work to outside parties in the form of subcontracts. Outsourcing is a regular feature both in the public sector as well as in private sector companies. Many organizations have surplus labour and hence instead of hiring more people, they go for outsourcing.
Outsourcing is usually done for non-critical activities. Outsourcing of non-critical activities through subcontracting determines HRP.
Objectives of Human Resource Planning
The basic purpose of having a human resource plan is to have an accurate estimate of the number of employees required, with matching skill requirements to meet organizational objectives. It provides information about the manner in which existing personnel is employed, the kind of skills required for different categories of jobs, and human resource requirements over a period of time in relation to organizational objectives.
It would also give an indication of the lead time that is available to select and train the required number of additional manpower. Following are the objectives of human resource planning given below:
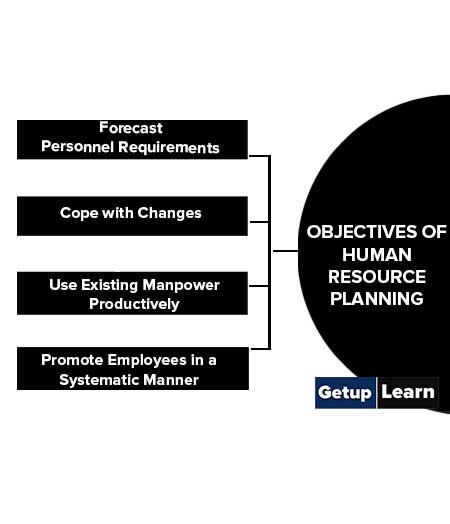
- Forecast Personnel Requirements
- Cope with Changes
- Use Existing Manpower Productively
- Promote Employees in a Systematic Manner
Forecast Personnel Requirements
HR planning is essential to determine the future manpower needs in an organization. In the absence of such a plan, it would be difficult to have the services of the right kind of people at the right time.
Cope with Changes
HR planning is required to cope with changes in market conditions, technology, products, and government regulations in an effective way. These changes may often require the services of people with the requisite technical knowledge and training. In the absence of an HR plan, we may not be in a position to enlist their services in time.
Use Existing Manpower Productively
By keeping an inventory of existing personnel in an enterprise by skill, level, training, educational qualifications, and work experience, it will be possible to utilize the existing resources more usefully in relation to the job requirements. This also helps in decreasing wage and salary costs in the long run.
Promote Employees in a Systematic Manner
HR planning provides useful information on the basis of which management decides on the promotion of eligible personnel in the organization. In the absence of an HR plan, it may be difficult to ensure regular promotions to competent people on a justifiable basis.
What are the factors affecting HRP?
Factors Affecting HRP are:
1. Type and Strategy of the Organization
2. Organizational Growth Cycles and Planning
3. Environmental Uncertainties
4. Time Horizons
5. Type and Quality of information
6. Nature of Jobs Being Filled
7. Outsourcing.
What are the objectives of human resource planning?
These are the objectives of human resource planning:
1. Forecast Personnel Requirements
2. Cope with Changes
3. Use Existing Manpower Productively
4. Promote Employees in a Systematic Manner.