Table of Contents
What is Job Demotion?
Job Demotion is just the opposite of promotion. In demotion, the employee is shifted to a job lower in status, grade, and responsibilities. “Demotion refers to the lowering of the status, salary, and responsibilities of an employee.” In the words of Dale Yoder, “Demotion is a shift to a position in which responsibilities are decreased.

Promotion is, in a sense, an increase in rank and demotion is the decrease in rank.” When an employee is demoted, his pride suffers a more severe jolt than it does when he is superseded by his junior.
Some managers hesitate to demote a man. They prefer to discharge him rather than demote him to the lower job because he will not accept the lower job and will turn out to be a disgruntled employee and his position will not be good for better industrial relations.
Causes of Job Demotion
There are several Causes of job demoting a man from his present position. Some of these reasons are as follows:
- Inadequacy on the part of the employees in terms of job performance, attitude, and capability. It happens when an employee finds it difficult to meet job requirement standards, following his promotion.
- Demotion may result from organizational staff reductions. Due to adverse business conditions, organizations may decide to lay off some and downgrade some jobs.
- Demotions may be used as disciplinary tools against errant employees.
- If there is a mistake in staffing i.e. a person is promoted wrongly.
- When, because of a change in technology, methods, and practices, old hands are unable to adjust, or when employees because of ill health or personal reasons, cannot do their job properly.
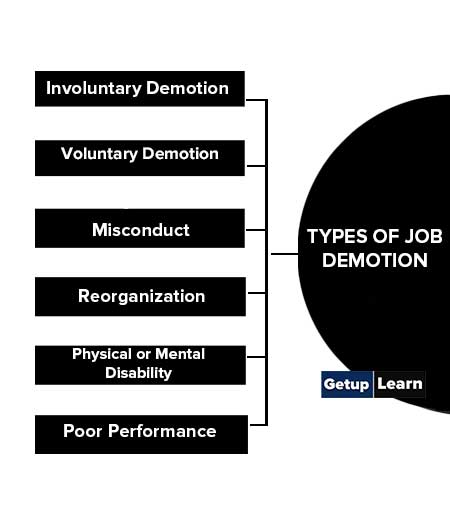
Types of Job Demotion
These are the types of job demotion of employees:
- Involuntary Demotion
- Voluntary Demotion
- Misconduct
- Reorganization
- Physical or Mental Disability
- Poor Performance
Involuntary Demotion
An employee may be demoted for cause, or as otherwise provided by these Rules, after the Appointing Authority furnishes both the employee and the Director with a written statement of intent to demote. The written statement shall contain specific reasons for such demotions and shall provide the employee with a minimum of twenty-four (24) hours to respond orally or in writing.
The written statement shall also state that a pre-demotion review will be held a minimum of twenty-four (24) hours after furnishing such written statement to the employee. The employee shall be entitled to respond to the reasons given for the demotion at the pre- demotion review.
The pre-demotion review is not an evidentiary hearing and the employee is not entitled to be represented by counsel to cross-examine or confront witnesses, or to present testimony of witnesses on their own behalf. An extension shall be granted only for good cause.
Voluntary Demotion
If an employee makes a written request for voluntary demotion within his/her Department, the Appointing Authority may make the demotion either competitively or noncompetitively, upon certification by the Director that the employee meets the minimum qualifications. A copy of the employee’s written request shall be provided to the Director. An employee demoted under this section shall have no right of Appeal.
Misconduct
In the event of the employee being demoted on the grounds of misconduct, his/her salary/wage shall be adjusted from the first day of the working month/working week, as the case may be, in which the Council decides to demote him/her or, in the event of the Council so decides, on the first working day of the succeeding working month/working week to such notch of the salary scale of the post to which he/she is demoted as the Council may decide.
Reorganization
In the event of an employee’s post being declared redundant and the position being abolished as a result of the reorganization of the Council’s service, and such employee being demoted by the Council, he/she shall retain his grouping as applicable before such demotion as “personal-to-incumbent” or “contractual-to- incumbent”, as the case may be.
Physical or Mental Disability
In the event of an employee being demoted by the Council as a result of physical or mental disability as determined by medical professionals, the Council may not adjust such employee’s salary either to the comparative notch, or in the event of there being no comparative notch, to the nearest lower notch of the post to which he/she is demoted, or allow such employee to retain the salary scale applicable to him/her before the date of demotion as “personal-to-holder” or “contractual-to-holder” as the case may be.
A demotion in terms of the above paragraph shall take effect from the first day of the working month/working week of the relevant employee that follows on the working month/working week in which it is decided to demote an employee. Where a demotion has the effect on the salary of an employee being adjusted to a notch lower than the maximum of the salary scale of the relevant post, such employee shall retain the incremental date applicable to him/her before such demotion.
Poor Performance
In the event of an employee being demoted as a result of poor, sub-standard, or non-performance, an inquiry should be conducted in terms of the provisions of the Labour Relations Act, 66 of 1995.
Job Demotion Policy
Demotion is very harmful to the employees’ morale. It is an extremely painful action, impairing relationships between people permanently. While effecting demotions, a manager should be extremely careful not to place himself on the wrong side of the fence. It is, therefore, necessary to formulate a demotion policy so that there may be no grievance on the part of the trade unions.
- A clear list of rules along with punishable offenses is made available to all the employees.
- Any violation is investigated thoroughly by a competent authority.
- In case of violations, it is better to state the reasons for taking such a punitive step clearly and elaborately.
- Once violations are proved, there should be a consistent and equitable application of the penalty.
- There should be enough room for review.
Demotions have a serious impact on the need fulfillment. Needs for esteem and belongingness are frustrated leading to defensive behavior on the part of the person demoted. There may be complaints, emotional turmoil, inefficiency, or resignation. Hence, demotions, are very rarely resorted to by managers. Managers prefer to discharge employees rather than face the problems arising from demotion.
What are the types of demotion?
Following are the types of demotion of employees:
1. Involuntary Demotion
2. Voluntary Demotion
3. Misconduct
4. Reorganization
5. Physical or Mental Disability
6. Poor Performance.