Table of Contents
- 1 Functions of Commercial Banks
- 2 Primary Functions of Commercial Banks
-
3 Secondary Functions of Commercial Banks
- 3.1 Collection and Payment of Credit
- 3.2 Purchase and Sale of Securities
- 3.3 Trustee and Executor
- 3.4 Remittance of Money
- 3.5 Representation and Correspondence
- 3.6 Bullion Trading
- 3.7 Locker Facilities
- 3.8 Acting as a Referee
- 3.9 Issuing Letter of Credit
- 3.10 Acting as Underwriters
- 3.11 Acting as Information Banks
- 3.12 Issuing of Traveller’s Cheques
- 3.13 Issuing of Gift Cheques
- 3.14 Dealing in Foreign Exchange
- 3.15 Merchant Banking Services
- 4 Developmental Functions of Commercial Banks
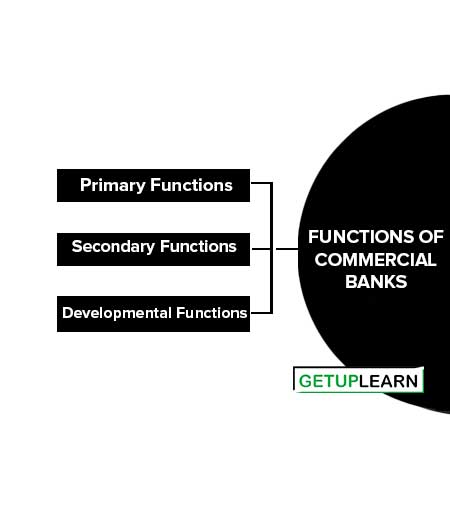
Functions of Commercial Banks
As shown in the figure, the functions of commercial banks can be broadly classified into three parts:
- Primary Functions of Commercial Banks
- Secondary Functions of Commercial Banks
- Developmental Functions of Commercial Banks
Primary Functions of Commercial Banks
The primary functions of commercial banks are also known as the ‘acid test’ functions of commercial banks. The following are the primary functions of a commercial bank:
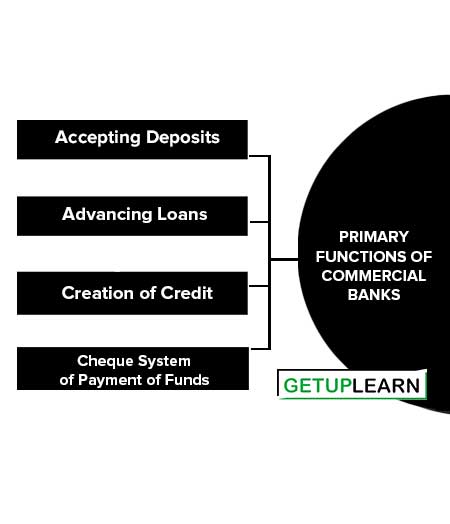
Accepting Deposits
The first main function of a commercial bank is the acceptance of deposits from the public. This function is important because banks mainly depend on the funds deposited with them by the public. The banks collect money from those who have a surplus to lend to those who require loans.
The deposits must be of money and not of other assets. The deposits are accepted by the public at large and not merely by its shareholders or members. Banks accept deposits by mobilizing the savings of the public. Commercial banks pay interest on the deposits to mobilize the savings and to hold deposits. People can deposit their cash balances in either of the following accounts as per their requirements:
- Fixed Deposit Account
- Current Deposit Account
- Savings Deposit Account
- Recurring Deposit Account
Fixed Deposit Account
Cash is deposited in this account for a fixed period. The depositors can withdraw money only on the expiry of the period for which the deposit has been made. On such deposits, the banks pay a higher rate of interest depending on the length of the time period and the amount of deposit.
Current Deposit Account
In this account, a depositor can deposit and withdraw his funds any number of times he likes. Businessmen deposit their funds in this account. Generally, no interest is paid by the bank on the Current Deposit Account.
Savings Deposit Account
This account is meant for small savings. There is a limit on total weekly withdrawals. Banks pay interest on this account. But the rate of interest is less than the rate of interest paid on a fixed deposit account.
Recurring Deposit Account
Under this account, a specified amount is deposited every month for a specified period e.g. for 12,24,36 or 60 months. The amount cannot be withdrawn before the expiry of the given period except under exceptional circumstances.
Advancing Loans
Another primary function of commercial banks is to advance loans. A certain part of the cash received by the banks as deposits are kept in the reserve and the remaining is given as a loan. Banks advance loans mostly for productive purposes against approved security.
The amount of the loan is generally less than the value of the security. Advancing loan is essential because banks undertake to pay interest on deposits they receive from the public. They charge more on the loans than they pay on deposits and the difference constitutes their profits. Banks advance the following types of loans:
- Money at Call
- Overdraft
- Cash Credit
- Discounting of Bills
Money at Call
It is the money lent for a very short period generally from 1 to 14 days. Such advances are usually made to other banks and financial institutions only. Money at call ensures liquidity.
Overdraft
Overdraft means allowing the borrower to overdraw his current balance. The drawee has to pay interest on the extra amount withdrawn. The amount has to be repaid within a short period. The facility of overdraft is available for short-term to reliable customers only. It is a short-term and temporary accommodation.
Cash Credit
It is also a very popular form of advancing loans. Under this system, the bank advances loans to the customer on the basis of his current assets, receivables, or fixed assets by hypothecating them in favor of the banker. These loans are given in the form of a fixed amount.
Bank enters the number of loans in the account books of the debtor. The customer can withdraw it at any time. The interest is chargeable on the whole amount from the day the loan is sanctioned irrespective of the fact that the debtor withdraws the whole amount or part of it.
Discounting of Bills
It is another very popular method of advancing credit. The banks facilitate trade and commerce by discounting bills of exchange. Discounting a bill of exchange means advancing a loan against a promise of repayment in the future. It is the most favored method of lending by commercial banks because such loans are self-liquidation in character.
Credit to Government
Commercial banks provide indirect credit to the Central Government or state government by investing in their securities.
Creation of Credit
One of the most important functions, which the banking system plays in a modern capitalist economy is to create demand for deposit and helps in circulating it as the medium of exchange. This is also called credit creation. It has become the most important function of the commercial banks.
When a bank advances a loan or credit, it does not lend cash but opens an account in favor of the customer and credits the amount to the account. It creates a claim against itself that is acceptable by the public for the settlement of debts.
As these claims, against the banks are accepted by the public for settling their debts, it is an important part of the money supply. In this process the bank creates money. Banks need not keep the entire deposits in cash. Only a part of the deposits is required to be kept in cash because the bank in practice is never required to repay all the deposits in cash. This enables the bank to create money many times more than the deposits with it.
Cheque System of Payment of Funds
A cheque as a negotiable instrument is the most popular credit instrument used by the customer to make payments. The cheque system evolved in the very early stages of banking and now it has become the main credit instrument in the banking world. Through a cheque, the customer directs the bank to make payment to the payee.
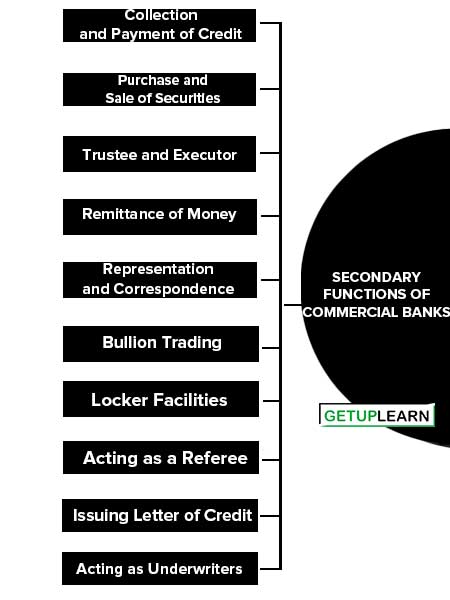
Secondary Functions of Commercial Banks
We can categorize the secondary functions of commercial banks:
- Collection and Payment of Credit
- Purchase and Sale of Securities
- Trustee and Executor
- Remittance of Money
- Representation and Correspondence
- Bullion Trading
- Locker Facilities
- Acting as a Referee
- Issuing Letter of Credit
- Acting as Underwriters
- Acting as Information Banks
- Issuing of Traveller’s Cheques
- Issuing of Gift Cheques
- Dealing in Foreign Exchange
- Merchant Banking Services
Agency Functions
Banks render a number of useful services to customers apart from performing the primary functions. Commercial banks act as agents of their customers in the following ways:
- Collection and Payment of Credit
- Purchase and Sale of Securities
- Trustee and Executor
- Remittance of Money
- Representation and Correspondence
- Bullion Trading
Collection and Payment of Credit
Commercial banks collect and pay various negotiable instruments like cheques, bills of exchange, promissory notes, hundreds, etc. Banks also make payments on behalf of the customers like payment of rent, income-tax, fees, insurance premiums, etc.
The customers have to leave standing instructions with the bank for various periodic payments ensuring the regular payments and avoiding the trouble of performing it themselves.
Purchase and Sale of Securities
Modern commercial banks also undertake the purchase and sale of various securities like shares, stocks, bonds, units, debentures, etc. on behalf of the customers. Banks perform the functions of a broker and do not give any advice regarding the suitability of a security.
Trustee and Executor
Banks also act as trustees and executors of the property of their advice. Banks undertake the administration of will or settlement and trusteeship functions through their expert staff and specialized departments. Sometimes, banks also undertake income-tax services on behalf of the customer.
Remittance of Money
Banks also remit money from one place to the other. Commercial banks remit funds on behalf of customers from one place to another through cheques, drafts, mail transfers, telegraphic transfers, etc.
Representation and Correspondence
Sometimes, commercial banks act as representatives and/or correspondents of the clients, especially in obtaining passports, travel tickets, booking vehicles, plots, etc.
Bullion Trading
Commercial banks trade in bullion like gold and silver in many countries. Commercial banks like SBI, IOB, Canara Bank, and Allahabad Bank have been allowed import gold which has been put under the open general license category in October 1997.
General Utility Services
Banks provide many more utility services in addition to agency services:
- Locker Facilities
- Acting as a Referee
- Issuing Letter of Credit
- Acting as Underwriters
- Acting as Information Banks
- Issuing of Traveller’s Cheques
- Issuing of Gift Cheques
- Dealing in Foreign Exchange
- Merchant Banking Services
Locker Facilities
Banks provide locker facilities to their customers. People can keep their gold or silver jewelry or other important documents in these lockers at a very nominal annual rent. In this way, the bank accepts valuable articles and documents for safe custody.
Acting as a Referee
Banks also act as a referee. Banks give information about the economic position of their customers to domestic and foreign traders.
Banks can be referred by third parties for getting information regarding the financial position of the customer. The bank will act as a referee only if it is desired by the customer, otherwise, the secrecy of a customer’s account is maintained very carefully.
Issuing Letter of Credit
A letter of credit is a very popular document in foreign trade. Banks certify the creditworthiness of their customers in a way by issuing letters of credit. Issuing letters of credit to their customers enables them to go abroad.
Acting as Underwriters
Banks also underwrite the new issues of Government and Corporate bodies for a commission. The name of a bank as an underwriter encourages investors to have faith in the shares of the company.
Acting as Information Banks
Commercial banks also act as information bureaus as they collect financial, economic, and statistical data relating to industry, trade, and commerce. The information is made available to various interested parties.
Issuing of Traveller’s Cheques
Banks have been rendering great service by issuing traveler’s cheques, which enable a person to travel without fear of theft or loss of money.
Now, some banks have started a credit card system under which a credit card holder is allowed to avail of credit from the listed outlets without any additional cost or effort. So, a credit card holder need not carry cash all the time.
Issuing of Gift Cheques
Certain banks issue gift cheques of various denominations e.g. some Indian banks issue gift cheques of denominations of Rs. 11, 21, 31, 51, 101, 501, etc. These are generally issued free of charge.
Dealing in Foreign Exchange
Major commercial banks also transact the business of foreign exchange through their main branches. Commercial banks are the main authorized dealers of foreign exchange in India.
Merchant Banking Services
Commercial banks also render merchant banking services to customers. They help in availing loans from non-banking financial institutions. However, in the recent past, most of the banks have transferred merchant banking services to their separate subsidiaries.
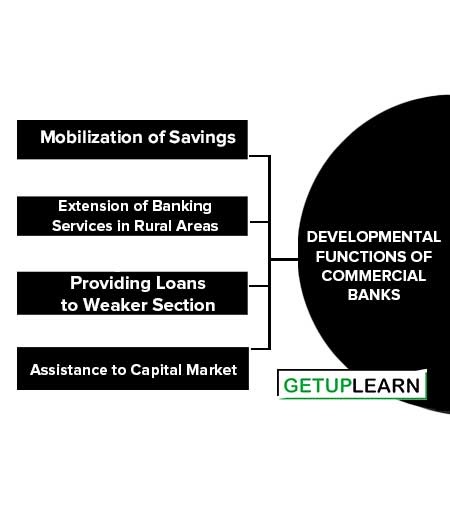
Developmental Functions of Commercial Banks
These are the developmental functions of commercial banks:
- Mobilization of Savings
- Extension of Banking Services in Rural Areas
- Providing Loans to Weaker Section
- Assistance to Capital Market
Mobilization of Savings
Banks collect idle savings of the people and invest the same in productive activities. Banks help in accelerating the rate of capital formation in the country by mobilizing savings. The most important role in mobilizing the savings of society is played by the commercial bank.
Extension of Banking Services in Rural Areas
Commercial banks have opened their branches in rural areas and small towns to provide banking facilities to the people living therein. Banks also give loans at a low rate of interest to finance programs meant for rural development and the removal of unemployment.
Providing Loans to Weaker Section
Banks give loans to weaker sections of society at a low rate of interest. Small artisans, landless agricultural laborers, and poor classes get cheap loans from the banks.
Assistance to Capital Market
Banks also take part in the capital by giving long-term loans to industry, agriculture, small-scale industry, trader, transporters, etc.