Table of Contents
Who gave the concept of time element in price determination?
Professor Marshall has explained the importance role of time elements in price determination. The supply of a commodity cannot be adjusted to the quantity demanded because time is the most important constraint. The scale of production, size of firm, supply of raw material and other factors of production can be changed only when there is sufficient time.
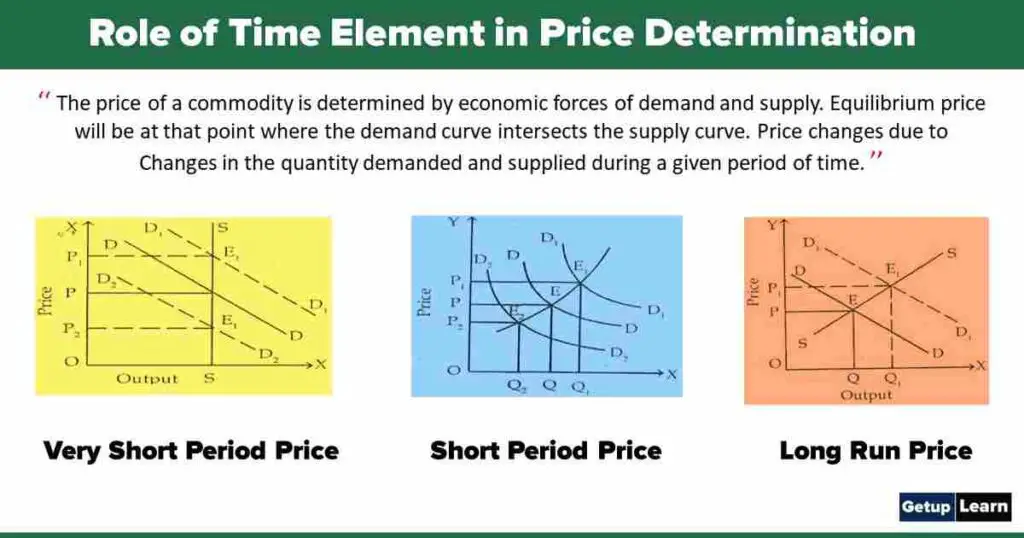
Generally, the price of a commodity is determined by economic forces of demand and supply. Equilibrium price will be at that point where the demand curve intersects the supply curve. Price changes due to changes in the quantity demanded and supplied during a given period of time.
Role of Time Element in Price Determination
Time can be classified into four categories as given below:
Very Short Period Market
A very short period market is a period in which the supply of a product or commodity is limited, to the available stock. In other words, the supply of the commodity cannot be increased. The time is so short that the supply of the commodity is equal to its stock available.
If the commodity is perishable its supply will be perfectly inelastic because it cannot be stored and the total quantity cannot be changed but in the case of durable a part of it can be stored for some time by the producer or seller. Demand plays a dominant role in price determination during this period because supply is a passive factor.
The price is determined by the interaction of the demand curve and supply curve and equilibrium price is called market price. There is a direct relationship between demand and the price of a commodity during a very short period.
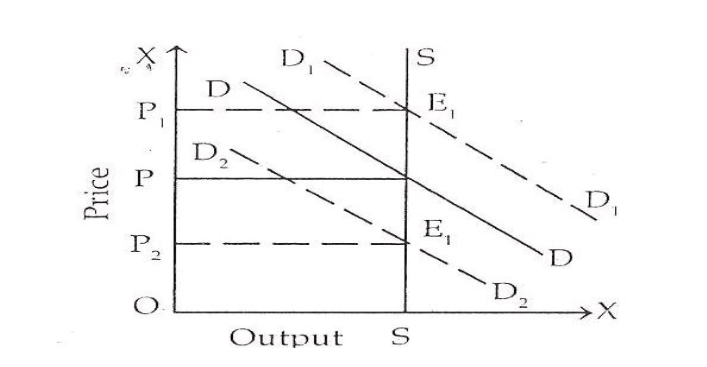
Price and output are shown on the oy-axis and ox-axis respectively. SS is the supply curve and DD is the demand curve. SS is a perfectly inelastic supply curve. The initial price was OP and the output was OS. When the demand increases the demand curve shift upward and the new demand curve is D1D1.
The price is determined at E1 point where the price is op1 and the output remains constant. When demand decreases the demand curve shift downwards and it becomes D2D2 and the new price equilibrium is at point E2 where the price is OP2 and output remains the same. Thus, in the case of perishable goods, there is a direct relationship between the change in quantity demanded and the change in price as has been explained in the diagram.
Short Period Market
During a short period, the supply of a commodity can be adjusted to its quantity demanded to the extent which the installed capacity of a plant has not been fully utilized. A producer can increase the supply by the maximum utilization of capacity and resources available.
During this period price is determined by the demand and supply of a commodity but demand is more powerful than the supply. The equilibrium price is called the short-run price. The following diagram shows the price determination during a short period:
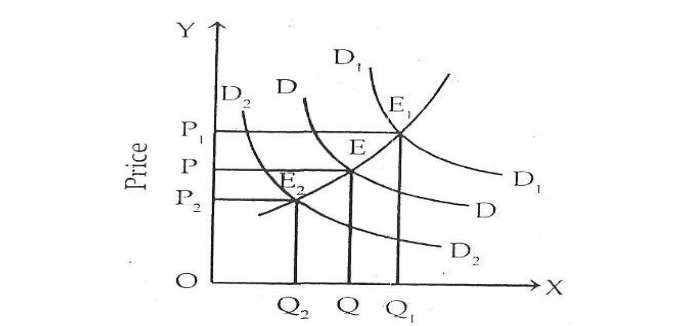
The diagram shows that the initial equilibrium is at E where the price is OP and output is OQ. When demand increases the new demand curve (D1D1) will intersect SS at El point and the price will be OP1 and the quantity demanded will be OQ1. When demand decreases the demand curve will shift downward to D2D2 and E2 price will be determined.
The price will be OP2 and the amount demanded will be OQ2 only. Thus, during a short period supply of a commodity can be increased and it is elastic. However, the demand affects the price and there is a direct relationship between the demand of a commodity and its price during a short period.
Thus on the basis of the short-run price determination, we can come to the following conclusions:
- Short-run price is affected by demand and supply both. But demand has more influence than supply.
- Price increases with the increase in demand during a short period but the increase in price is lesser than that of a very short period during the short period.
Long Period Market
During this period producer of a commodity has sufficient time. All the factors of production are variable and even the scale of production can be changed. The supply of a commodity can be adjusted to its demand during this period. Firms take into consideration the concept of the total cost. During this period equilibrium is attained which is called long-run normal price. It can be shown from the following diagram:
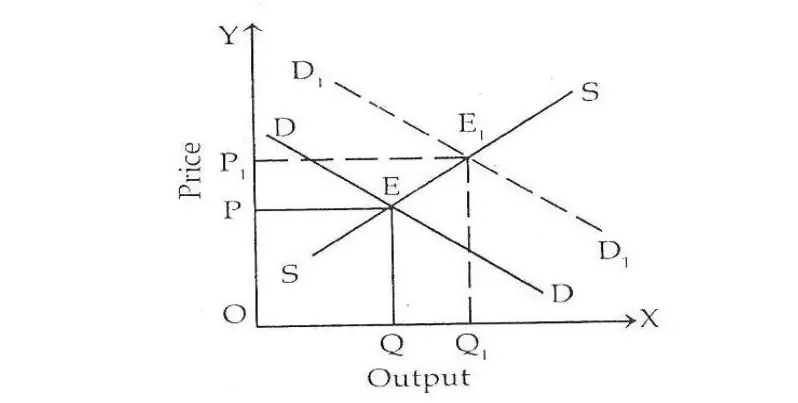
Price and output are shown on oy-axis and ox-axis respectively. Price is determined at Point E where the supply curve (SS) intersects the demand curve (DD). Price is OP and output is OQ. At this price demand and supply of a commodity are equal.
During this period the supply plays an important role in price determination because the producer is in a position to adjust its supply according to its demand. During the long period with the increase in demand for a commodity, its price will increase but this increase in price will be less than very short period and short period prices as shown in the diagrams.
Very Long Period Market
It is the aggregate of various long periods. The period is very lengthy. Determinants of demand and supply of a commodity go under change over a very long period. Size of population, sources and supply of raw materials, techniques of production, supply of capital, habit, fashion and tastes of consumers etc. undergo a rapid change over a very long period.
It is very difficult to know which type of changes will take place during this period. Hence price determination is not studied and analyzed during this period. This period has theoretical importance only.
What is very long period market?
A very short period market is a period in which the supply of a product or commodity is limited, to the available stock.
What are the 4 types of markets?
Role of Time Element in Price Determination: Time can be classified into four categories as given below: Very Short Period Market, Short Period Market, Long-Period Market, and Very Long Period Market.
Who gave the concept of the time element in price determination?
The supply of a commodity cannot be adjusted to the quantity demanded because time is the most important constraint. The scale of production, size of the firm, supply of raw material and other factors of production can be changed only when there is sufficient time.