Table of Contents
-
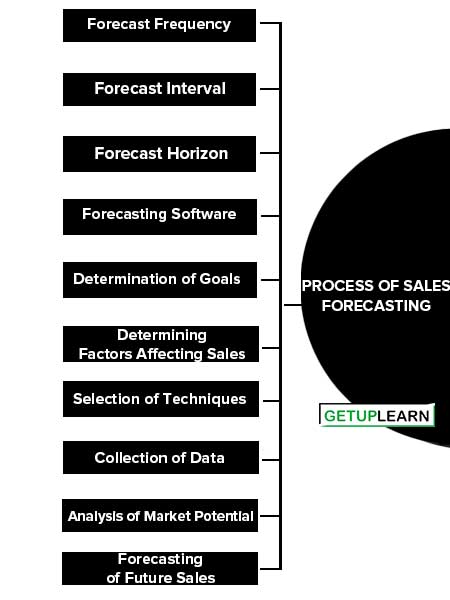
1 Process of Sales Forecasting
- 1.1 Forecast Frequency
- 1.2 Forecast Interval
- 1.3 Forecast Horizon
- 1.4 Forecasting Software
- 1.5 Determination of Goals
- 1.6 Determining Factors Affecting Sales
- 1.7 Selection of Techniques
- 1.8 Collection of Data
- 1.9 Analysis of Market Potential
- 1.10 Forecasting of Future Sales
- 1.11 Converting Industry Forecast to Company Sales Forecast
- 1.12 Making Operational Programmes and Budget
- 1.13 Deriving Sales Volume Objective
- 1.14 Evaluation and Revision of Forecasts
- 2 FAQs About the Process of Sales Forecasting
Process of Sales Forecasting
Sales forecasting is a process but not a physical one, such as building a product or packaging and shipping it. It is an informational and decision-making process. Processes have inputs, a conversion phase, and outputs. When talking about forecasting the three elements in the forecasting process can be studied as follows:
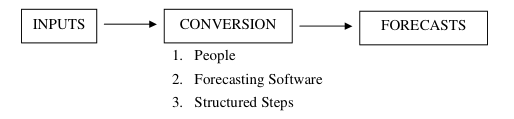
Let us look at these three elements in the process of sales forecasting, 1. People, 2. Forecasting Software, 3. Structured Steps. Let’s discuss each step of the process of sales forecasting:
- Forecast Frequency
- Forecast Interval
- Forecast Horizon
- Forecasting Software
- Determination of Goals
- Determining Factors Affecting Sales
- Selection of Techniques
- Collection of Data
- Analysis of Market Potential
- Forecasting of Future Sales
- Converting Industry Forecast to Company Sales Forecast
- Making Operational Programmes and Budget
- Deriving Sales Volume Objective
- Evaluation and Revision of Forecasts
People
The people involved in the forecasting process have to take some important decisions by which the magnitude and direction of the forecasting are clearly defined. These decisions are:
Forecast Frequency
Depending on the purpose of the forecast, the frequency of the forecast varies. For formal review and update, the most commonly used frequency is once per month.
When demand changes more frequently, then even mind forecasts have to be done. Some companies, on the other hand, who excel at Continuous Replenishment (CR) update their ‘forecasts’ a number of times per week.
Forecast Interval
The gap between two consecutive forecasts is its interval. Companies can use weekly forecasts to monthly ones to project future sales.
Forecast Horizon
Although companies are involved in 12 monthly projections, they should prefer 15 months time horizon for making the budgeting process a lot easier and more routine.
Although for some companies like aerospace or chemicals go out for three years because they require longer lead times for facilities, equipment, materials, and highly trained people. Some might need even longer projections than this.
Forecasting Software
The second component of the forecasting process is software. The ABC approach applies to the forecasting process:
-
The C item is the computer software and hardware: Essential, but not critically important item. Used for statistical projections & handling data.
-
The B item is the data: The validity and utility of the input data are of more significance than the computer.
- The A item is the people: The success of a forecasting improvement initiative will depend almost totally on the people: their dedication, their willingness, and their knowledge.
Structured Steps
The third element, structured steps in the forecasting process is important, because, these steps are the vehicle for the people An item to do their jobs. The sales forecasting process contains the following steps:
- Determination of Goals
- Determining Factors Affecting Sales
- Selection of Techniques
- Collection of Data
- Analysis of Market Potential
- Forecasting of Future Sales
- Converting Industry Forecast to Company Sales Forecast
- Making Operational Programmes and Budget
- Deriving Sales Volume Objective
- Evaluation and Revision of Forecasts
Determination of Goals
The sales manager should decide the goals for sales forecasts. These objects may include:
- Determination of sales publicity program,
- Marketing methods,
- Sales quota determination,
- Estimation of working capital requirements,
- Estimation of income and expenditure, etc.
The clarity in goals set the right direction for the sales forecasting process.
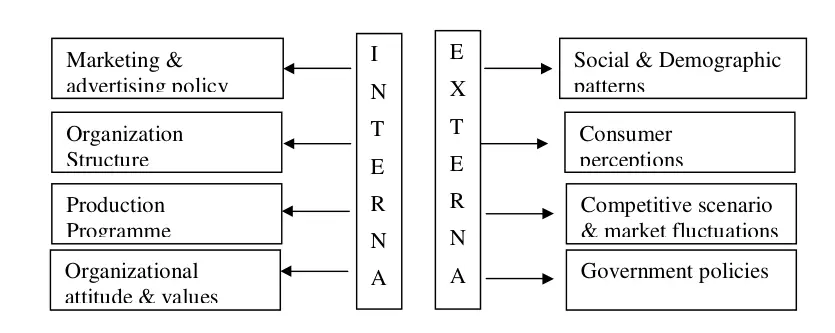
Determining Factors Affecting Sales
Identifying and analyzing the controllable and uncontrollable factors scientifically will help in assessing their impact on future sales. The controllable factors are basically internal to the organization, whereas, the uncontrollable ones are mostly external.
Selection of Techniques
Suitable methods for forecasting sales must be selected keeping in view the sales objectives, time intervals, resources of the firm, and the nature of the product. The manager should ensure that the information gathered is sufficient and collected from reliable sources.
Collection of Data
Field research and motivation research is conducted to obtain relevant information for estimating future demand.
A study of consumer behavior to know about the consumer profile that is who the present consumers are, who can be in the future, what they buy, why they buy, and when and from where they buy, is of utmost importance. On this basis, market potential can be determined. This is the next step in the process.
Analysis of Market Potential
Analysis of market potential requires a two-step process. (i) Select the market factors associated with the product’s demand. (ii) Eliminate those target segments that do not contain prospective buyers of the product. The sales manager should ensure that the information gathered is sufficient, before doing analysis.
Forecasting of Future Sales
Sales projections should be made on the basis of the analysis done. A company may make a forecast for an entire product line or for individual items within the line.
Sales may be forecasted for a company’s total market or for individual market segments. After determining the market or sales potential for a product or service, management can make a sales forecast.
Converting Industry Forecast to Company Sales Forecast
Many companies forecast both their own sales and sales of the industry. The general practice is to forecast industry sales early in the procedure and from it derive a company sales forecast for use as a check against forecasts arrived at through other methods.
Deriving a company sales forecast from an industry sales forecast requires an appraisal of company strengths and weaknesses against those of competitors. The result is an estimate of the expected market share that results in a forecast of company sales.
Making Operational Programmes and Budget
After the sales forecasts have been made, budgets are made. The requirements of various operational activities such as production, purchasing, marketing, capital assets, workforces, etc. are met if the budget estimations are correct. If the sales forecasts have large deviations from actual sales, then the budgets might need revisions.
Deriving Sales Volume Objective
A sales forecast (1) contains an estimate of sales tied to a proposed marketing plan or program and (2) assumes a particular set of economic and other forces outside the unit for which the forecast is made. The sales forecast estimate does not necessarily become the company’s sales volume objective, but it provides an orientation point for management’s thinking.
Further adjustments in the sales forecast estimate are necessary whenever management decides to alter its marketing plan or program or changes occur in competitors’ marketing strategies.
Evaluation and Revision of Forecasts
Every forecast contains elements of uncertainty. All are based on assumptions. So the first step is evaluating a sales forecast is to examine the assumptions on which it is based. The company should review the forecasting process periodically.
The first step in the review is to determine the accuracy of past forecasts to learn if changes are needed in the way forecasts are made. If the company finds that sales forecasts are significantly different from actual sales in the period, it should undertake a review of the sales forecasting process before making any more forecasts.
The evaluation process then should review the data used in sales forecasting Poor data collection methods can decrease the quality of the data used for forecasting, or the data may be inappropriate for forecasting sales of the product.
Forecasts should be checked against actual results, differences explained and indicated adjustments made for the remainder of the period. When the period’s sales results are all recorded, all variations should be explained and stored for future use in improving forecasting accuracy.
FAQs About the Process of Sales Forecasting
What is the process of sales forecasting?
These are the following steps process of sales forecasting:
1. Forecast Frequency
2. Forecast Interval
3. Forecast Horizon
4. Forecasting Software
5. Determination of Goals
6. Determining Factors Affecting Sales
7. Selection of Techniques
8. Collection of Data
9. Analysis of Market Potential
10. Forecasting of Future Sales.
