Table of Contents
What is Process Design?
Product-focused design is also known as a line flow production system. This type of processing system is used mostly in production departments that are organized according to the type of product or service being produced. Products or services usually flow along linear paths.
A vital decision for an organization is to determine the type of process design that should be used to produce each product or service. The various types of process designs that are generally used can be classified as product-focused design and process-focused design.
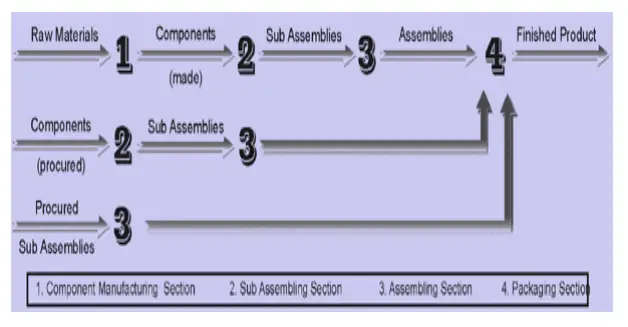
There is no scope for backtracking or side-tracking in product design. Items follow a sequence of similar production. It may be anything from a pipeline (for oil) to an assembly line (for televisions or radios). Figure 1 illustrates the direct, linear, and continuous paths in which raw materials, components, sub-assemblies, assemblies, and finished products flow in the production of a hypothetical product.
A product-focused production system is generally designed for three forms of production which are as follows:
Discrete Unit Manufacturing
In discrete unit manufacturing, the production of distinct products like television sets takes place. These products can be made in batches. The system can be reallocated to produce other products in similar batches.
Process Manufacturing
The movement of materials between operations such as screening, crushing, storing, mixing, milling, blending, cooking, fermenting, evaporating and distilling takes place in process manufacturing. Cement, plastic, paper, chemical, and steel industries are using process manufacturing.
Delivery of Services
In this system, services are administered to customers while they move in a queue. Services delivered by waiters in hotels use such type of system.
Low unit costs, high volumes of production, and ease of planning are some benefits of Product-focused systems. However, they require higher initial investments because of the use of specialized and expensive fixed-position processing equipment in the production process.
Firms prefer this system for the advantages it provides like low labor skill requirements, reduced worker training, reduced supervision, and ease of control. The Process-focused production system is popularly known as the intermittent production system.
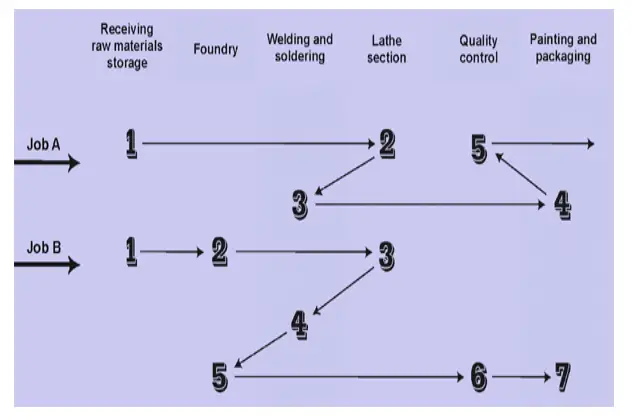
Production is carried out intermittently i.e. on a start and stop basis. In a process-focused production system, all the operations are grouped according to the type of process. The other name of this system is job shop. It is because the products move from department to department in batches (jobs) that are usually produced on the basis of customers’ orders.
Process-focused production systems are usually used to produce small quantities (or batches) of different items. The equipment and personnel for processing are located according to the functions. The products flow through the facilities on irregular paths.
Figure 2 shows the irregular path in which products flow in this type of production system. Unlike the product-focused system, this system permits both sidetracking and backtracking in the product flow. Job A and Job B, in Figure 2, represent two different product designs. As they require different designs, they are routed accordingly through different production departments, different operations, and different sequences.