Table of Contents
- 1 Concept of Organizational Behavior
- 2 Definition of Organizational Behavior
- 3 Importance of Studying Organizational Behavior
- 4 Understanding Human Behavior
- 5 Controlling and Directing Human Behavior
- 6 Goals of Organizational Behavior
- 7 Elements of Organizational Behavior
- 8 Nature of Organizational Behavior
- 9 Modern Approach to Organizational Behavior
- 10 FAQs Related to the Concept of Organizational Behavior
Concept of Organizational Behavior
Organizational behavior (OB) is a field of study that investigates the impact that individuals, groups, and structures have on behavior within an organization, then applies that knowledge to make organizations work more effectively (Robbins, 2003).
In recent times, we notice the following changes in the organizational setup:
- The demise of traditional hierarchical structure,
- The emergence of a workforce with different expectations from organizations,
- Advancement of information technology,
- Increasing importance on empowerment and teamwork,
- Concern for work-life balance
Definition of Organizational Behavior
The following are the definitions of organizational behavior given by economists throughout the past to now:
Social arrangements, constructed by people who can also change them. Organizations can be repressive and stifling, but they can also be designed to provide opportunities for self-fulfillment and individual expression. The point is that human consequences depend on how organizations are designed and run.
Buchanan and Huczynski (1997)
As system of co-operative activities and their co-ordination requires something intangible and personal that is largely a matter of personal relationships”. There are a number of definitions that we can draw on to illuminate and deepen our understanding of the concept of organizational behavior.
Barnard (1938)
OB is concerned with “The study of the structure, functioning and performance of organizations, and the behavior of groups and individuals within them”.
According to Pugh, (1971)
Ivancevich and Matteson, (1998) in their book Organizational Behavior and Management.
They opine that OB is about “the study of human behavior, attitudes and performance within an organizational setting; drawing on theory, methods, and principles from such disciplines as psychology, sociology, and cultural anthropology to learn about individual perception, values, learning capabilities, and actions while working with groups and within the total organization; analyzing the external environment’s effect on the organization and its human resources, missions, objectives and strategies”.
Ivancevich and Matteson, (1998)
Importance of Studying Organizational Behavior
A study of OB is beneficial in many ways. Some of the benefits of studying OB are the following:
- Understanding human behavior
-
Controlling and directing human behavior
- Organizational adaption.
Understanding Human Behavior
To shape human behavior in a definite direction to achieve certain predetermined objectives, managers must know how the people in the organization behave:
Individual Level
The behavior of human beings as social man is the first issue in behavioral science. It provides for analyzing why and how an individual behaves in a particular way.
Interpersonal Level
Human behavior can be understood at the level of interpersonal interaction. Such interpersonal interaction is normally in paired relationships which represent man’s most natural attempt at socialization. OB provides a means for understanding this interpersonal relationship in the organization.
Group Level
Though people interpret anything at their individual level, they are often modified by group pressure which, thus, becomes a force in shaping human behavior. Thus, individuals should be studied in groups also.
Controlling and Directing Human Behavior
After understanding the mechanisms of human behavior, managers are required to control and direct the behavior so that it conforms to the standards required for achieving organizational objectives:
Organizational behavior can be controlled and directed by the use of power and sanction which are formally prescribed by the organization. Power is referred to as the capacity of an individual to take certain actions and may be utilized in many ways. The use of power is related to sanctions in the organization.
Leadership
Another method of bringing human behavior in tune with organizational requirements is leadership. Today, the difference between a successful and failing organization lies in the quality of leadership of its managerial personnel. OB identifies various leadership styles available to a manager and analyzes which style is more appropriate in a given situation.
Communication
People in the organization particularly at higher levels, spend considerable time communicating. To achieve organizational effectiveness, communication must be effective.
Organizational Climate
Organizational climate refers to total organizational situations affecting human behavior. OB suggests the approach to creating an organizational climate in totality rather than merely improving the psychological conditions or increasing employee satisfaction by changing isolated work processes.
Goals of Organizational Behavior
There are some goals of organizational behavior which are as follows:
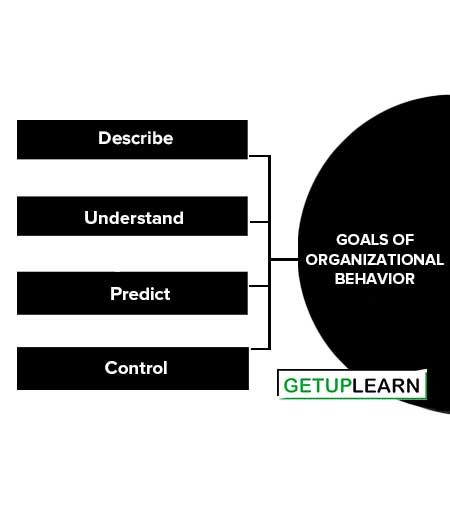
Describe
The first goal is to describe, systematically how people behave under a variety of conditions. Achieving this goal allows managers to communicate about human behavior at work using a common language.
Understand
A second goal is to understand any people behave as they do. The managers would be frustrated if they could talk about the behavior of their employees, but not understand the reasons behind those actions.
Predict
The managers would have the capacity to predict which employees might be dedicated and productive or which ones might have been absent, causing problems. And thus the managers could take preventive actions.
Control
The final goal of OB is to control and develop some human activity at work. Since managers are held responsible for performance outcomes, they are vitally interested in being able to make an impact on employee behavior, skill development, team effort, and productivity.
Managers need to be able to improve results through the actions they and their employees take, and organizational behavior can aid them in their pursuit of this goal.
Elements of Organizational Behavior
Organizations operate their functional activities by some elements, which affect organizations. The following are the elements of organizational behavior:
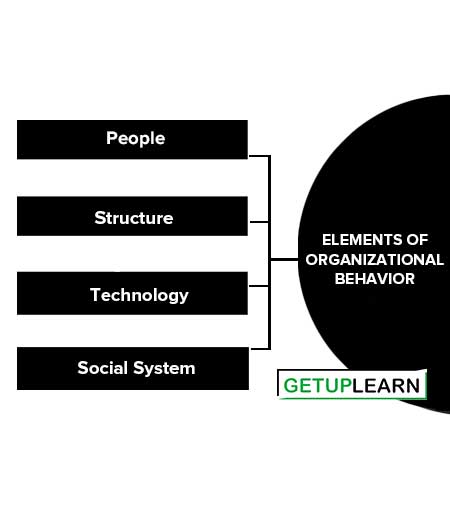
People
People make up the internal social system in the organization. They consist of individuals and groups. Groups may be large or small, formal and informal, official or unofficial. Human organization changes every day. People are living, thinking, and feeling beings that create the organization and try to achieve the objectives and goals.
Structure
Structure defines the formal relationship and use of people in the organization. Different people in an organization are given different roles and they have certain relationships with others. Those people have to be related in some structural way so that their work can be effectively coordinated.
Technology
Technology imparts the physical and economic conditions within which people work. With their bare hands, people can do nothing. So they are given assistance in building, machines, tools, processes, and resources. The nature of technology depends very much on the nature of the organization and influences the work or working conditions.
Social systems provide an external environment within which an organization operates. A single organization cannot exist alone. It is a part of the whole. A single organization cannot give everything and therefore there are many other organizations. All these organizations influence each other.
Nature of Organizational Behavior
Organizational behavior is emerging as a separate field of study. Therefore its nature is likely, to change over the period of time. However, the nature of organizational behavior is as follows:
- A Field of Study and not a Discipline
- Interdisciplinary Approach
- An Applied Science
- Normative and Value Centred
- Humanistic and Optimistic
- Oriented Toward Organizational Objectives
- A Total System Approach
A Field of Study and not a Discipline
Organizational behavior can be treated as a distinct field of study and not a discipline or even an emerging discipline A discipline is an accepted science with a theoretical foundation that serves as the basis for research and analysis.
Organizational behavior because of its broad base recent emergence and inter-disciplinary orientation is not accepted as science. We have just begun to synthesize principles, concepts, and processes in this field of inquiry. Therefore, it is reasonable to call it a field of study rather than a discipline.
Interdisciplinary Approach
OB is basically an interdisciplinary approach. An interdisciplinary approach integrates the relevant knowledge drawn from different disciplines for some specific purpose. As discussed later, OB draws heavily from psychology, sociology, and anthropology.
Besides, it also takes relevant things from economics, political science, law, and history. These disciplines exist separately, but OB integrates the relevant contents with these disciplines to make them applicable for Organizational analysis. Thus, OB imparts knowledge from the integration of knowledge from different disciplines.
An Applied Science
The basic objective of OB is to make application of various research to solve organizational problems particularly related to human beings aspect. Though much of the research may be carried on in a laboratory situation or controlled conditions, they are meant for general. Thus organizational behavior is both a science as well an art.
Normative and Value Centred
OB is a normative science. A normative or positive science suggests only cause-effect relationships and prescribes how the findings of the research can be applied to get Organizational results that are acceptable to society. Thus, what is acceptable by society is a matter of value to the people concerned.
Humanistic and Optimistic
OB focuses the attention on people from a humanistic point of view. It is based on the belief that the needs and motivations of people are of high concern There is an acceptance of the value of the individual as a thinking and feeling organism and without these considerations, the Organisation may not be fully operational as a social entity.
There is optimism about the innate potential of man to be independent, creative, proud, and capable of contributing positively to the objectives of the Organisation. The man will actualize this potential if proper conditions and environments are given to him.
Oriented Toward Organizational Objectives
OB being an applied science and emphasizing the aspect of the Organisation, is oriented towards organizational objectives.
Though an organization may have several objectives and sometimes conflicting objectives with individuals should not be understood that OB only emphasizes the objectives at the cost of Organizational objectives.
In fact, OB tries to integrate two types of objectives so that these are achieved simultaneously. For this purpose, it suggests various behavioral approaches.
A Total System Approach
OB is a total systems approach wherein the living system of an organization is viewed as an enlargement of a man. The systems approach is an integrative approach that takes into account all the variables affecting Organizational functioning.
In fact, system thinking in Organizational analysis has been developed by behavioral scientists. Behavioral science while analyzing organizational behavior does not take human beings in isolation but as the product of socio-psychological factors.
Thus his behavior can be analyzed keeping in view his psychological framework interpersonal orientation group influence and social and cultural factors. Thus man’s nature is quite complex and OB by applying a systems approach tries to find the solution to this complexity.
Modern Approach to Organizational Behavior
These are the four modern approaches to organizational behavior:
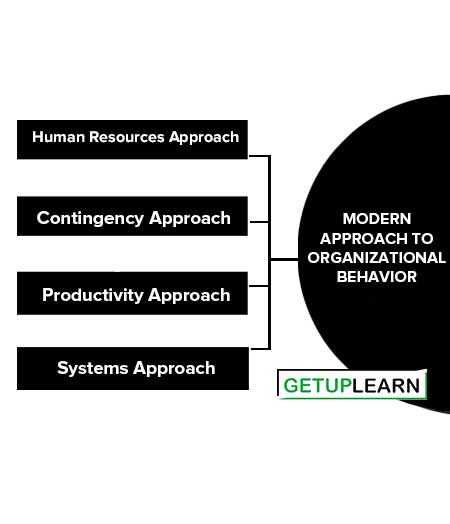
Human Resources Approach
The human resources approach is concerned with the growth and development of people towards higher levels of competency, creativity, and fulfillment because people are the central resource in any organization.
Contingency Approach
A contingency approach to organizational behavior implies that different situations require different behavioral practices for effectiveness instead of following a traditional approach for all situations.
Productivity Approach
Productivity is considered to be improved, if more outputs can be produced from the same amount of inputs.
Systems Approach
Within the organization ‘people’ employ ‘technology’ in performing the ‘task’ that they are responsible for, while the ‘structure’ of the organization serves as a basis for co-ordinating all their different activities.
The systems view emphasizes the interdependence of each of these elements within the organization if the organization as a whole is to function effectively.
What is the concept of organizational behavior?
Organizational behavior is the study and application of knowledge about how people act within an organization. It is a human tool for human benefit. It applies broadly to the behavior of people in all types of organizations.
What is the nature of organizational behavior?
The following is the nature of organizational behavior:
1. A Field of Study and not a Discipline
2. Interdisciplinary Approach
3. An Applied Science
4. Normative and Value Centred
5. Humanistic and Optimistic
6. Oriented Toward Organizational Objectives
7. A Total System Approach.