Table of Contents
- 1 What is Sales Forecasting?
- 2 Definition of Sales Forecasting
- 3 Need for Sales Forecasting
- 4 Importance of Sales Forecasting
- 5 Factors Affecting Sales Forecasting
- 6 Internal Factors Affecting Sales Forecasting
- 7 External Factors Affecting Sales Forecasting
- 8 Approaches to Sales Forecasting
- 9 Principles of Sales Forecasting
-
10 Limitations of Sales Forecasting
- 10.1 Lack of Sales History
- 10.2 Change in Business Environment
- 10.3 Change in Consumer Behaviour
- 10.4 Lack of Facts and Data
- 10.5 Based on Assumption
- 10.6 Availability of Substitute Products
- 10.7 Uncertain Growth Rate
- 10.8 Higher Cost
- 10.9 Changing Demand and Changes in Consumer
- 10.10 Influence of Psychological Factors
- 10.11 Complex Techniques
- 10.12 Lack of Trained Forecasters
- 11 FAQs About the Sales Forecasting
What is Sales Forecasting?
The sales forecast is one of the major planning premises in business organizations. It is the result of numerous assumptions made about the external and internal environments of the firm.
Sales forecasting of an established business is easier than that for a new business. For an established business, past sales combined with present economic and market scenarios work well for predicting a business sale in the future. Whereas, a new business has no past sales baseline.
Hence, it requires researching the target markets, trading area, and the state of competition to guesstimate future sales.
Definition of Sales Forecasting
Sales forecasting can be defined as,To foresee means both to assess the future and make provision for it.
Henry Fayol
Sales forecast is the expected level of company sales based on chosen marketing plan and assumed marketing environment.
Philip Kotler
Need for Sales Forecasting
There is often a debate about the accuracy of forecasts. And on that premise some might feel that there is no need for forecasting as it is time-consuming, doesn’t add value to the product directly and of course, the most important reason is that they are wrong. It is absolutely OK for companies to not take to forecasting if:
- They have enough time to buy material, make the product, and ship it after the procurement of customer orders.
- They can add or reduce capacity very economically.
- The owners of the business do not require forward financial planning.
The above three conditions are not found in the practical world and hence, companies cannot do away with forecasting. Hence, every kind of company needs to forecast. And the above reasons are strong enough to prove the need for forecasting in all kinds of companies.
Need for Sales Forecasting
| 1. Meeting customer demand such that there is neither excessive inventory, nor stock-out situations. |
Producing for Stock: Forecasts about the purchase of raw material made formally or informally based on past history. Producing for Order: Predict future sales and undertake production, planning, and scheduling |
| 2. Change capacity which requires that equipment and workforce are efficient and effective enough for smooth and cost-effective functioning of the organization. |
When Labor is a Key Factor: Forecasting is essential to hire and train people in the lead time. When Equipment is a Key Factor: Forecasts are essential for equipment upgrading replacement etc. |
| 3. Financial Planning is essential to attract investors, acquire loans. | Projections regarding income, expenses, benefits investments, cash flow, asset levels, and so on, are important. |
Importance of Sales Forecasting
These are the importance of sales forecasting explained below:
- It helps in the evaluation of past and current sales levels and annual growth.
- Comparison of one’s own company to industry benchmarks is possible.
- It helps in establishing policies to monitor prices and operating costs.
- It also enables a company to detect minor problems before they become major problems.
- Companies that implement accurate sales forecasting processes realize important benefits such as:
- Optimized cash flow
- Knowing when and how much to buy.
- In–depth knowledge of customers and the products they order.
- The ability to plan for production and capacity.
- The ability to identify the pattern or trend of sales.
- Determine the value of a business above the value of its current assets.
- Ability to determine the expected return on investment.
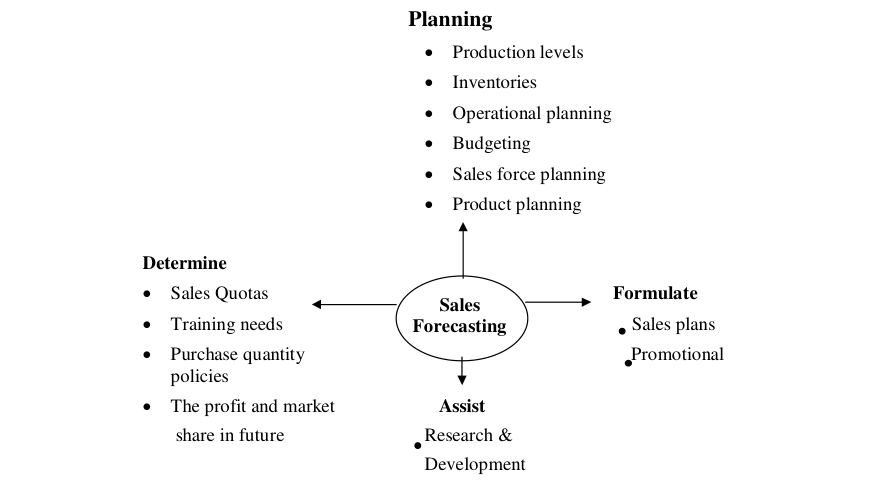
Factors Affecting Sales Forecasting
Sales forecasting is the basis for a number of decisions ranging from tactical ones to strategic decisions. A host of factors & affect sales forecasting both internally, as well as Externally. For forecasting to be more precise and accurate, a company needs to consider all of the following factors affecting sales forecasting:
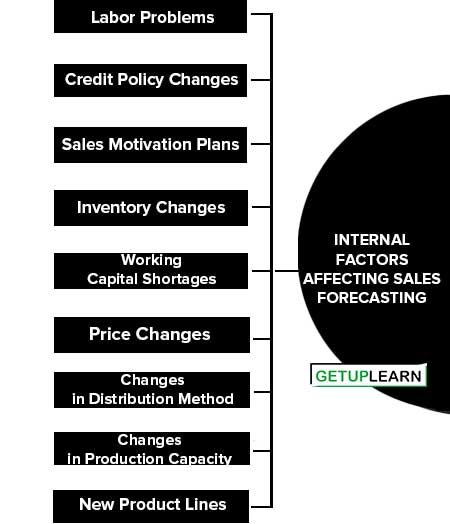
Internal Factors Affecting Sales Forecasting
The factors internal to the organization which can have a bearing on the volume of expected sales in the future can be discussed as follows:
- Labor Problems
- Credit Policy Changes
- Sales Motivation Plans
- Inventory Changes
- Working Capital Shortages
- Price Changes
- Changes in Distribution Method
- Changes in Production Capacity
- New Product Lines
Labor Problems
It can have an adverse impact on production levels and thereby affect future sales.
Credit Policy Changes
If the credit policy is made liberal sales can be affected positively and vice-versa.
Sales Motivation Plans
The sales force of any company has a direct relationship with its sales. Hence, a motivated sales force can add up to sales and market share.
Inventory Changes
The position of inventory also has an impact on the sales of a company. Overstocking and under-stocking, both affect sales adversely.
Working Capital Shortages
This can again lead to irregular and fluctuating production, which in turn affects sales.
Price Changes
in raw material and other inputs lead to cost escalations which can again have an impact on sales.
Changes in Distribution Method
Every channel of distribution has its own advantages and disadvantages changes in the distribution system can affect sales and the state of competition.
Changes in Production Capacity
When production capacity increases/ decreases, sales will be affected because of production volumes and costs. Hence forecasting becomes difficult.
New Product Lines
When new product lines are added, sales might not be easily predicted.
Internal factors are controllable factors and hence organizations can have a bearing on them and can use them to not only predict sales but also impact sales.
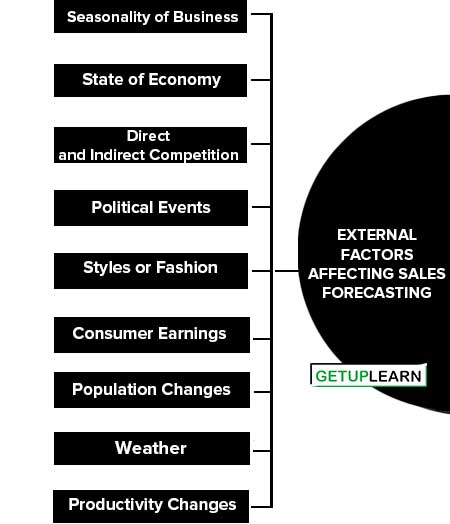
External Factors Affecting Sales Forecasting
Just as internal factors affect sales forecasting, external factors also have an impact on sales forecasting. The external factors affecting sales forecasting are:
- Seasonality of Business
- State of Economy
- Direct and Indirect Competition
- Political Events
- Styles or Fashion
- Consumer Earnings
- Population Changes
- Weather
- Productivity Changes
Seasonality of Business
When business is on a seasonal basis, sales are also irregular and hence forecasting is more difficult.
State of Economy
Sales have a direct correlation with the state of the economy. When the economy is in depression, sales do not pick up so easily.
Direct and Indirect Competition
When the competition is direct, sales can be forecasted easily in comparison to when it is indirect.
Political Events
In the case of political uncertainty sales forecast is a difficult task.
Styles or Fashion
If the product is a stylish or fashionable product, its life cycle is much shorter, and hence sales forecasting is more complex and difficult.
Consumer Earnings
When the income of consumers increases, sales also increase.
Population Changes
The changes in the demographic pattern of the population have a direct relationship with sales. When the population has a geographical shift (from rural to urban) or the younger population is higher in percentage, sales rise proportionately.
Weather
Sales forecasting is also affected by trends due to changes in weather conditions.
Productivity Changes
An increase and Decrease in the productivity of the organization also impact sales forecasting.
Approaches to Sales Forecasting
William J. Stanton, Etzel, and Walker have described two types of approaches to sales forecasting. These are as follows:
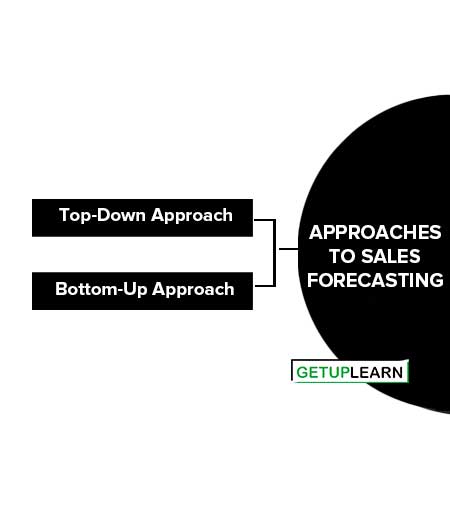
Top-Down Approach
A company can forecast sales by using a top-down approach. Using this approach, management needs to:
- Develop a forecast of general economic conditions.
- Determine the market potential for a product.
- Measure the share of this market the firm is currently getting or plans to capture.
- Forecast the firm’s sales of its brand of the product.
Bottom-Up Approach
In bottom-up forecasting, management follows a two-step procedure:
- Generate estimates of future demand by acquiring information from segments of the market or from organizational units (salespeople or branches) in the company.
- Add the individual estimates to get one total forecast.
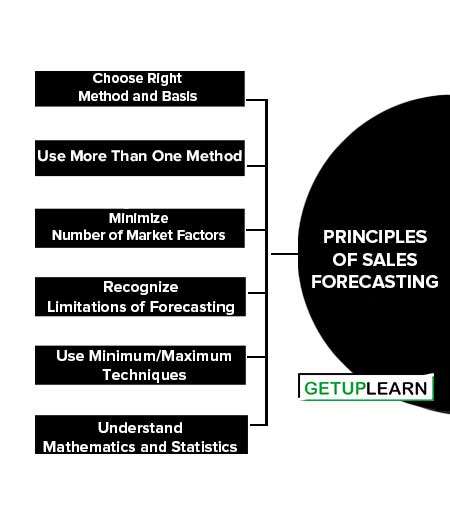
Principles of Sales Forecasting
Sales forecasting is undoubtedly a difficult and challenging task. The principles of sales forecasting are explained below:
- Choose Right Method and Basis
- Use More Than One Method
- Minimize Number of Market Factors
- Recognize Limitations of Forecasting
- Use Minimum/Maximum Techniques
- Understand Mathematics and Statistics
Choose Right Method and Basis
Forecasts can be either based on products or geographical location. Depending on the nature of the product and competition, the right forecast method and basis should be chosen.
Use More Than One Method
Using more than one method can improve the accuracy of a sales forecast.
Minimize Number of Market Factors
Including the greater number of market factors results in a confused sales forecast because it becomes difficult to determine exactly what affects the demand for a product.
Recognize Limitations of Forecasting
For some products say innovative and highly competitive products, forecasts are difficult; similarly, for products that have variable demand, forecasting becomes more complex.
Use Minimum/Maximum Techniques
Sound research strategy dictates the use of both minimum and maximum estimates in all computations in order to obtain a range of variations.
Understand Mathematics and Statistics
Sales forecasting makes wide use of mathematics and statistics hence understanding statistical and mathematical techniques is important to avoid any errors.
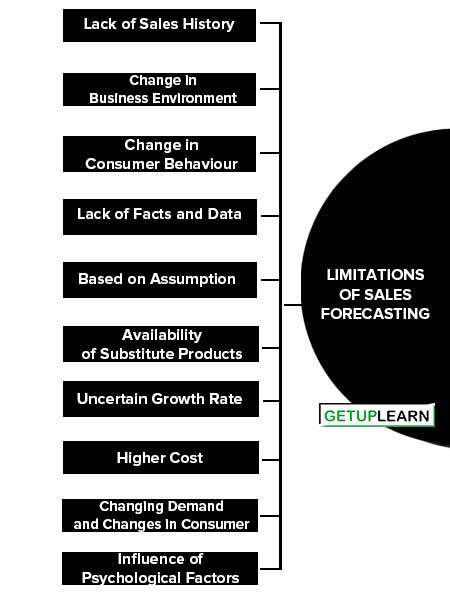
Limitations of Sales Forecasting
Despite the use of statistical and mathematical techniques used in sales forecasting which makes it quite accurate, These are some of the limitations of sales forecasting:
- Lack of Sales History
- Change in Business Environment
- Change in Consumer Behaviour
- Lack of Facts and Data
- Based on Assumption
- Availability of Substitute Products
- Uncertain Growth Rate
- Higher Cost
- Changing Demand and Changes in Consumer
- Influence of Psychological Factors
- Complex Techniques
- Lack of Trained Forecasters
Lack of Sales History
For new products there is a lack of past sales data; hence it limits the accuracy of the forecast.
Change in Business Environment
Changes in business environmental factors like income, price, demand, supply, etc. bring about changes in sales forecasts and if these changes are fluctuating, forecasting becomes difficult.
Change in Consumer Behaviour
Similarly, changes in consumer preferences, habits, consumption patterns, attitudes, and needs, also impact sales forecasting and its degree of accuracy.
Lack of Facts and Data
Inaccurate data and incomplete facts hinder the process of sales forecasting and can have incorrect forecasts.
Based on Assumption
Sales forecasting is based on certain assumptions, and if these assumptions are over or under-optimistic, it can lead to inaccurate sales forecasting.
Availability of Substitute Products
When substitute products are available in plenty, sales forecasting becomes complex and difficult.
Uncertain Growth Rate
Since the business environment has become very dynamic and complex, resulting in fluctuating demand, investments, and income levels. Hence, correct sales forecasting has become difficult.
Higher Cost
For smaller firms, it is not viable to use sales forecasting techniques due to the high cost of statistical and mathematical techniques.
Changing Demand and Changes in Consumer
Changing demand and changes in consumer preferences, and consuming habits lead to a lot of changes in demand, hence making sales forecasting difficult.
Influence of Psychological Factors
Psychological factors such as attitudes, perceptions, personality, lifestyles, self-concept, etc. are difficult to assess and measure. And since these form an important input to sales forecasting, reliable and accurate forecasting becomes difficult.
Complex Techniques
The techniques used in sales forecasting are complex and difficult making the process of sales forecasting a tedious and complex one.
Lack of Trained Forecasters
A lack of efficient, trained, and experienced forecasters can have an adverse impact on sales forecasting. If these limitations are taken care of, the chances of the occurrence of errors in forecasting can be minimized.
FAQs About the Sales Forecasting
What are the factors affecting sales forecasting?
The factors affecting sales forecasting are Internal Factors: 1. Labor Problems 2. Credit Policy Changes 3. Sales Motivation Plans 4. Inventory Changes 5. Working Capital Shortages 6. Price Changes 7. Changes in Distribution Method 8. Changes in Production Capacity 9. New Product Lines.
What are the principles of sales forecasting?
The following are the principles of sales forecasting:
1. Choose the Right Method and Basis
2. Use More Than One Method
3. Minimize the Number of Market Factors
4. Recognize the Limitations of Forecasting
5. Use Minimum/Maximum Techniques
6. Understand Mathematics and Statistics.
What are the limitations of sales forecasting?
The limitations of sales forecasting are:
1. Lack of Sales History
2. Change in Business Environment
3. Change in Consumer Behaviour
4. Lack of Facts and Data
5. Based on Assumption
6. Availability of Substitute Products
7. Uncertain Growth Rate
8. Higher Cost
9. Changing Demand and Changes in Consumer
10. Influence of Psychological Factors
11. Complex Techniques
12. Lack of Trained Forecasters.
